Transforming education: the power of ICT policies - Commonwealth ...
Transforming education: the power of ICT policies - Commonwealth ...
Transforming education: the power of ICT policies - Commonwealth ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
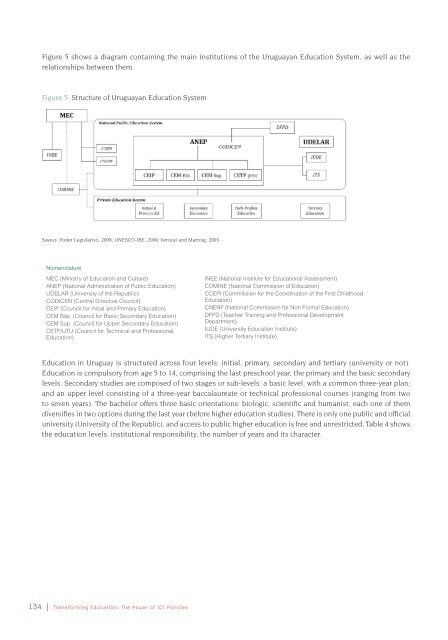
Figure 5 shows a diagram containing <strong>the</strong> main institutions <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> Uruguayan Education System, as well as <strong>the</strong><br />
relationships between <strong>the</strong>m.<br />
Figure 5: Structure <strong>of</strong> Uruguayan Education System<br />
Sources: Poder Legislativo, 2008; UNESCO-IBE, 2006; Verocai and Marroig, 2003<br />
Nomenclature<br />
MEC (Ministry <strong>of</strong> Education and Culture)<br />
ANEP (National Administration <strong>of</strong> Public Education)<br />
UDELAR (University <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> Republic)<br />
CODICEN (Central Directive Council):<br />
CEIP (Council for Initial and Primary Education)<br />
CEM Bás. (Council for Basic Secondary Education)<br />
CEM Sup. (Council for Upper Secondary Education)<br />
CETP/UTU (Council for Technical and Pr<strong>of</strong>essional<br />
Education)<br />
134 | <strong>Transforming</strong> Education: The Power <strong>of</strong> <strong>ICT</strong> Policies<br />
INEE (National Institute for Educational Assessment)<br />
COMINE (National Commission <strong>of</strong> Education)<br />
CCEPI (Commission for <strong>the</strong> Coordination <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> First Childhood<br />
Education)<br />
CNENF (National Commission for Non Formal Education)<br />
DFPD (Teacher Training and Pr<strong>of</strong>essional Development<br />
Department)<br />
IUDE (University Education Institute)<br />
ITS (Higher Tertiary Institute)<br />
Education in Uruguay is structured across four levels: initial, primary, secondary and tertiary (university or not).<br />
Education is compulsory from age 5 to 14, comprising <strong>the</strong> last preschool year, <strong>the</strong> primary and <strong>the</strong> basic secondary<br />
levels. Secondary studies are composed <strong>of</strong> two stages or sub-levels: a basic level, with a common three-year plan;<br />
and an upper level consisting <strong>of</strong> a three-year baccalaureate or technical pr<strong>of</strong>essional courses (ranging from two<br />
to seven years). The bachelor <strong>of</strong>fers three basic orientations: biologic, scientifi c and humanist, each one <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>m<br />
diversifi es in two options during <strong>the</strong> last year (before higher <strong>education</strong> studies). There is only one public and <strong>of</strong>fi cial<br />
university (University <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> Republic), and access to public higher <strong>education</strong> is free and unrestricted. Table 4 shows<br />
<strong>the</strong> <strong>education</strong> levels, institutional responsibility, <strong>the</strong> number <strong>of</strong> years and its character.