Chapter 15: Support, Movement, and Responses - Science
Chapter 15: Support, Movement, and Responses - Science
Chapter 15: Support, Movement, and Responses - Science
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
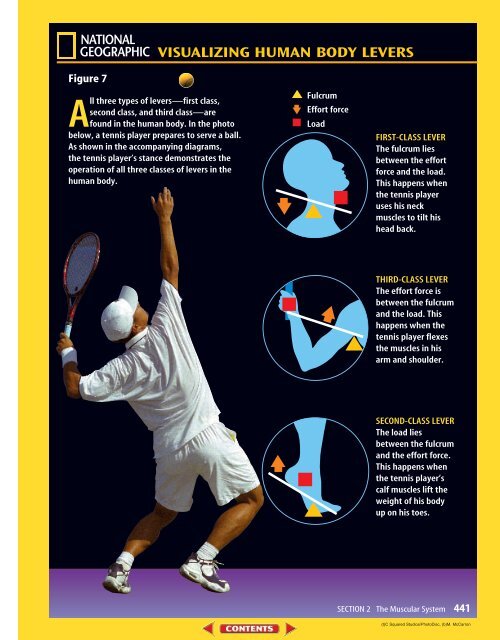
Figure 7<br />
NGS VISUALIZING TITLE HUMAN BODY LEVERS<br />
All three types of levers—first class,<br />
second class, <strong>and</strong> third class—are<br />
found in the human body. In the photo<br />
below, a tennis player prepares to serve a ball.<br />
As shown in the accompanying diagrams,<br />
the tennis player’s stance demonstrates the<br />
operation of all three classes of levers in the<br />
human body.<br />
Fulcrum<br />
Effort force<br />
Load<br />
FIRST-CLASS LEVER<br />
The fulcrum lies<br />
between the effort<br />
force <strong>and</strong> the load.<br />
This happens when<br />
the tennis player<br />
uses his neck<br />
muscles to tilt his<br />
head back.<br />
THIRD-CLASS LEVER<br />
The effort force is<br />
between the fulcrum<br />
<strong>and</strong> the load. This<br />
happens when the<br />
tennis player flexes<br />
the muscles in his<br />
arm <strong>and</strong> shoulder.<br />
SECOND-CLASS LEVER<br />
The load lies<br />
between the fulcrum<br />
<strong>and</strong> the effort force.<br />
This happens when<br />
the tennis player’s<br />
calf muscles lift the<br />
weight of his body<br />
up on his toes.<br />
SECTION 2 The Muscular System 441<br />
(t)C Squared Studios/PhotoDisc, (b)M. McCarron