Cadence - Michigan Optometric Association
Cadence - Michigan Optometric Association
Cadence - Michigan Optometric Association
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
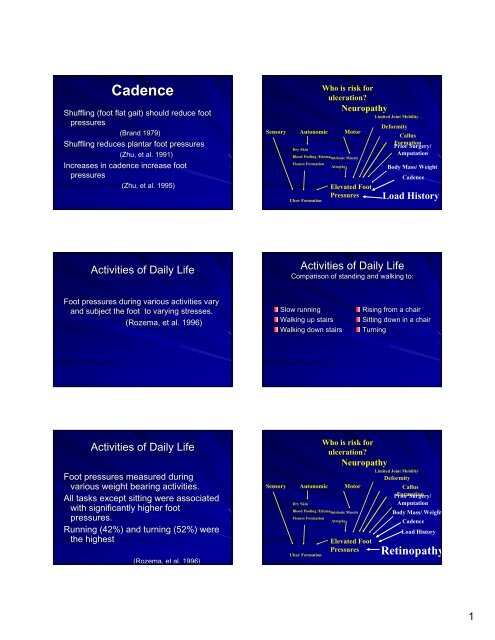
<strong>Cadence</strong><br />
Shuffling (foot flat gait) should reduce foot<br />
pressures<br />
(Brand 1979)<br />
Shuffling reduces plantar foot pressures<br />
(Zhu, et al. 1991)<br />
Increases in cadence increase foot<br />
pressures<br />
(Zhu, et al. 1995)<br />
Activities of Daily Life<br />
Foot pressures during various activities vary<br />
and subject the foot to varying stresses.<br />
(Rozema Rozema, , et al. 1996)<br />
Activities of Daily Life<br />
Foot pressures measured during<br />
various weight bearing activities.<br />
All tasks except sitting were associated<br />
with significantly higher foot<br />
pressures.<br />
Running (42%) and turning (52%) were<br />
the highest<br />
(Rozema Rozema, , et al. 1996)<br />
Who is risk for<br />
ulceration?<br />
Neuropathy<br />
Sensory Autonomic Motor<br />
Dry Skin<br />
Blood Pooling /EdemaIntrinsic<br />
Muscle<br />
Fissure Formation<br />
Atrophy<br />
Ulcer Formation<br />
Elevated Foot<br />
Pressures<br />
Limited Joint Mobility<br />
Deformity<br />
Callus<br />
Formation<br />
Prior Surgery/<br />
Amputation<br />
Activities of Daily Life<br />
Body Mass/ Weight<br />
<strong>Cadence</strong><br />
Load History<br />
Comparison of standing and walking to:<br />
Slow running<br />
Walking up stairs<br />
Walking down stairs<br />
Who is risk for<br />
ulceration?<br />
Neuropathy<br />
Sensory Autonomic Motor<br />
Dry Skin<br />
Blood Pooling /EdemaIntrinsic<br />
Muscle<br />
Fissure Formation<br />
Atrophy<br />
Ulcer Formation<br />
Elevated Foot<br />
Pressures<br />
Rising from a chair<br />
Sitting down in a chair<br />
Turning<br />
Limited Joint Mobility<br />
Deformity<br />
Callus<br />
Prior Formation Surgery/<br />
Amputation<br />
Body Mass/ Weight<br />
<strong>Cadence</strong><br />
Load History<br />
Retinopathy<br />
1
ETIOLOGY OF DIABETIC<br />
FOOT ULCERATION<br />
Vascular<br />
Insufficiency<br />
Distal vessels<br />
Poor collateral<br />
Medial calcinosis<br />
Neuropathy<br />
Sensory<br />
Motor<br />
Autonomic<br />
Minor<br />
Trauma<br />
Infection<br />
Increased risk<br />
Defective host<br />
defense<br />
Systemic signs and<br />
symptoms absent<br />
Multidisciplinary Approach<br />
Vascular Surgery<br />
Infectious Disease<br />
Diabetologist<br />
Physical Therapy<br />
Prosthetist/ Prosthetist<br />
Orthotists<br />
Podiatric Surgery<br />
Orthopedics<br />
Radiology<br />
Nursing<br />
Pharmacy<br />
Physical Examination<br />
Vascular Assessment<br />
Pulses<br />
Skin Temperature<br />
Presence of Hair<br />
Skin Texture and Turgor<br />
Skin Color<br />
Multidisciplinary Approach<br />
Vascular Surgery<br />
Infectious Disease<br />
Diabetologist<br />
Physical Therapy<br />
Prosthetist/<br />
Orthotists<br />
Podiatric<br />
Surgery<br />
Orthopedics<br />
Radiology<br />
Nursing<br />
Pharmacy<br />
Assessment of Patients with<br />
Diabetic Foot Ulcers<br />
Patient history<br />
Ulcer status &<br />
duration<br />
Treatment<br />
modality review<br />
Understanding of<br />
ulcer condition<br />
Glucose control<br />
Physical exam<br />
Nutritional status<br />
Neurological status<br />
Vascular status<br />
Footwear<br />
Patient’s Patient s support<br />
network<br />
Physical Examination<br />
Vascular Assessment<br />
2
Noninvasive Testing Complements<br />
A thorough history and physical exam<br />
Sound clinical judgment<br />
Experience<br />
Technical expertise<br />
Diabetic Lower Extremity Ischemia:<br />
Optimal Management<br />
Physical<br />
Examination<br />
Neurological<br />
Examination<br />
Multidisciplinary Approach<br />
Nursing<br />
Physical Therapy<br />
Infectious<br />
Disease<br />
Diabetologist<br />
Orthotist/ Orthotist<br />
Prosthetist<br />
Radiology<br />
Orthopedics<br />
Vascular<br />
Surgery<br />
Podiatric<br />
Surgery<br />
“The The direct restoration of pulsatile<br />
pedal flow allowed for more limited<br />
procedures, such as osteotomies,<br />
local ulcer and bony excision, and<br />
skin grafting to maximize limb<br />
salvage.” salvage.<br />
Gibbons, et al, Archives of Surgery,<br />
May 1993..<br />
Physical Examination<br />
Musculoskeletal<br />
Deformities<br />
Range of Motion<br />
Foot posture<br />
Evaluate dynamics of the<br />
foot<br />
3
Physical Examination<br />
Ulceration<br />
Size<br />
Location<br />
Depth<br />
Base<br />
Presence of<br />
Cellulitis/<br />
Lymphangitis<br />
Probing<br />
Characteristics<br />
The Art of Probing<br />
Superficial Ulcer<br />
No probing deep<br />
Less chance of deeper<br />
contamination<br />
Greater margin of comfort<br />
Multidisciplinary Approach<br />
Nursing<br />
Physical<br />
Therapy<br />
Infectious<br />
Disease<br />
Diabetologist<br />
Radiology<br />
Orthopedics<br />
Vascular Surgery<br />
Podiatric Surgery<br />
Orthotist/Prosthetist<br />
The Art of Probing<br />
Physical Examination<br />
Radiology<br />
Plain radiographs<br />
Bone scans<br />
MRI<br />
CT scan<br />
Physical Examination<br />
Laboratory<br />
Bloodwork to assess<br />
metabolic status<br />
4
Multidisciplinary Approach<br />
Nursing<br />
Physical Therapy<br />
Infectious Disease<br />
Diabetologist<br />
Prosthetist/ Prosthetist<br />
Orthotist<br />
Radiology<br />
Orthopedics<br />
Vascular<br />
Surgery<br />
Podiatric<br />
Surgery<br />
Multidisciplinary Approach<br />
Nursing<br />
Physical<br />
Therapy<br />
Infectious<br />
Disease<br />
Diabetologist<br />
Orthotist/ Orthotist<br />
Prosthetist<br />
Radiology<br />
Orthopedics<br />
Vascular<br />
Surgery<br />
Podiatric<br />
Surgery<br />
Gold Standards of Foot<br />
Ulcer Treatment<br />
Debride wound extensively<br />
Treat infection<br />
Restore adequate blood flow<br />
Abolish (or reduce) trauma<br />
Optimal Offloading<br />
Physical Examination<br />
Laboratory<br />
Wound cultures, aerobic,<br />
anaerobic<br />
Blood cultures<br />
Treatment of<br />
Diabetic<br />
Neuropathic<br />
Ulcerations<br />
Superficial<br />
Ulcerations<br />
Debridement Effects<br />
Removes foreign bodies, necrotic<br />
tissue<br />
Decreases bacterial load<br />
Cleans ulcer bed<br />
Increases platelets and<br />
endogenous growth factors at<br />
ulcer site<br />
Allows better visualization of ulcer<br />
area<br />
5
Sharp Debridement<br />
Pressure Relief in the<br />
Ulcerated Foot<br />
Non weight-bearing weight bearing (w/ crutches)<br />
Total contact cast<br />
Felted foam dressing<br />
Healing sandal<br />
IPOS shoe/half shoe<br />
Prefabricated walking brace<br />
Total Contact Cast Total Contact Cast<br />
Forefoot pressure reduction of 75 to 85%<br />
Shift of 30% load from cast to leg<br />
Greater load of heel<br />
Shaw, et al 1997<br />
6