Populations, Parameters, Statistics, and Sampling
Populations, Parameters, Statistics, and Sampling
Populations, Parameters, Statistics, and Sampling
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
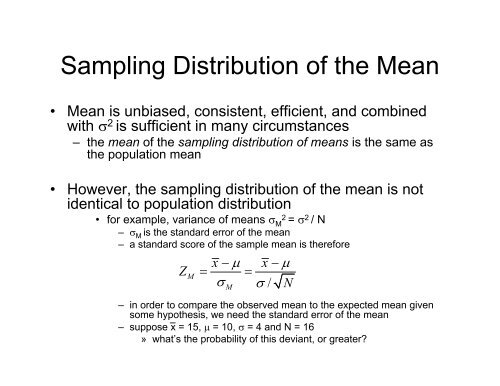
<strong>Sampling</strong> Distribution of the Mean<br />
• Mean is unbiased, consistent, efficient, <strong>and</strong> combined<br />
with σ 2 is sufficient in many circumstances<br />
– the mean of the sampling distribution of means is the same as<br />
the population mean<br />
• However, the sampling distribution of the mean is not<br />
identical to population distribution<br />
• for example, variance of means σ M 2 = σ 2 / N<br />
– σ M is the st<strong>and</strong>ard error of the mean<br />
– a st<strong>and</strong>ard score of the sample mean is therefore<br />
Z<br />
M<br />
x − μ x − μ<br />
= =<br />
σ σ / N<br />
M<br />
– in order to compare the observed mean to the expected mean given<br />
some hypothesis, we need the st<strong>and</strong>ard error of the mean<br />
– suppose x = 15, μ = 10, σ = 4 <strong>and</strong> N = 16<br />
» what’s the probability of this deviant, or greater?