Nuclear chemistry notes packet
Nuclear chemistry notes packet
Nuclear chemistry notes packet
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Nuclear</strong> Chemistry<br />
Definition – the study of the structure and changes within the nucleus of an atom. These<br />
changes may affect the stability of the nucleus.<br />
Difference from chemical changes – new elements form as a result of nuclear changes.<br />
Review:<br />
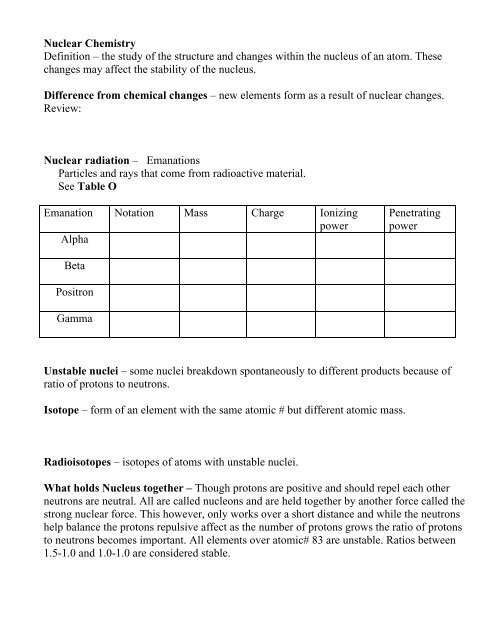
<strong>Nuclear</strong> radiation – Emanations<br />
Particles and rays that come from radioactive material.<br />
See Table O<br />
Emanation<br />
Alpha<br />
Notation Mass Charge Ionizing<br />
power<br />
Beta<br />
Positron<br />
Gamma<br />
Penetrating<br />
power<br />
Unstable nuclei – some nuclei breakdown spontaneously to different products because of<br />
ratio of protons to neutrons.<br />
Isotope – form of an element with the same atomic # but different atomic mass.<br />
Radioisotopes – isotopes of atoms with unstable nuclei.<br />
What holds Nucleus together – Though protons are positive and should repel each other<br />
neutrons are neutral. All are called nucleons and are held together by another force called the<br />
strong nuclear force. This however, only works over a short distance and while the neutrons<br />
help balance the protons repulsive affect as the number of protons grows the ratio of protons<br />
to neutrons becomes important. All elements over atomic# 83 are unstable. Ratios between<br />
1.5-1.0 and 1.0-1.0 are considered stable.