Lecture 3 Magnetic Circuits
Lecture 3 Magnetic Circuits
Lecture 3 Magnetic Circuits
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
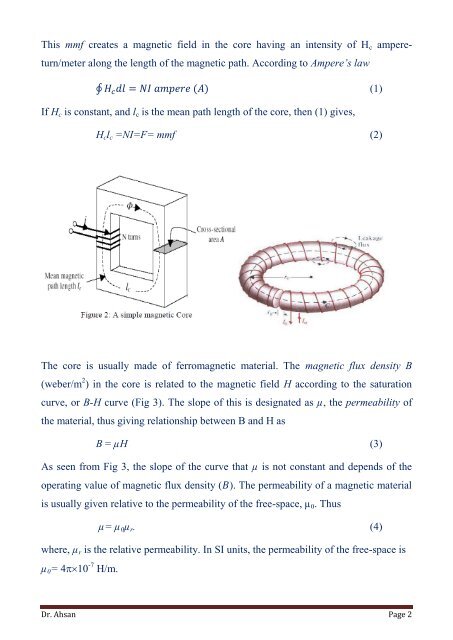
This mmf creates a magnetic field in the core having an intensity of H c ampereturn/meter<br />
along the length of the magnetic path. According to Ampere’s law<br />
∮ (1)<br />
If H c is constant, and l c is the mean path length of the core, then (1) gives,<br />
H c l c =NI=F= mmf (2)<br />
The core is usually made of ferromagnetic material. The magnetic flux density B<br />
(weber/m 2 ) in the core is related to the magnetic field H according to the saturation<br />
curve, or B-H curve (Fig 3). The slope of this is designated as µ, the permeability of<br />
the material, thus giving relationship between B and H as<br />
B = µH (3)<br />
As seen from Fig 3, the slope of the curve that µ is not constant and depends of the<br />
operating value of magnetic flux density ( ). The permeability of a magnetic material<br />
is usually given relative to the permeability of the free-space, µ 0 . Thus<br />
µ= µ 0 µ r . (4)<br />
where, µ r is the relative permeability. In SI units, the permeability of the free-space is<br />
µ 0 = 410 -7 H/m.<br />
Dr. Ahsan Page 2