(pet) and poly(ethylene terephthalate)-glycol
(pet) and poly(ethylene terephthalate)-glycol
(pet) and poly(ethylene terephthalate)-glycol
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
MOLECULAR DYNAMICS IN POLY(ETHYLENE TEREPHTHALATE)<br />
(PET) AND POLY(ETHYLENE TEREPHTHALATE)-GLYCOL (PETG)<br />
M. Baranowski a) , A. Woźniak-Braszak a) , K. Jurga a) , J Jurga b) , K. Hołderna-Natkaniec a)<br />
a) High Pressure Physics Division, Institute of Physics, Adam Mickiewicz University,<br />
Umultowska 85, 61-614 Poznań, Pol<strong>and</strong><br />
e-mail:mikbar@ amu.edu.pl<br />
b) Polymer Processing Division, Institute of Materials Technology, Poznan University of<br />
Technology, Piotrowo 3, 61-138 Poznań, Pol<strong>and</strong><br />
e-mail:jan.jurga@put.poznan.pl<br />
The work presents the studies of molecular motions in two <strong>poly</strong>mers <strong>poly</strong>(<strong>ethylene</strong><br />
<strong>terephthalate</strong>) (PET) <strong>and</strong> amorphous co<strong>poly</strong>mer of PET <strong>poly</strong>(<strong>ethylene</strong> <strong>terephthalate</strong>)-<strong>glycol</strong><br />
(PETG) by solid-state NMR techniques. These <strong>poly</strong>mers have a great commercial <strong>and</strong><br />
industrial application in fibers, food containers, bottles, pharmaceutical packagings, toys etc<br />
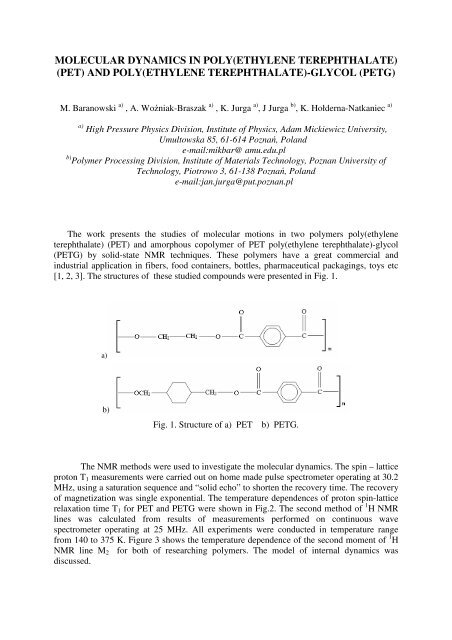
[1, 2, 3]. The structures of these studied compounds were presented in Fig. 1.<br />
a)<br />
b)<br />
Fig. 1. Structure of a) PET<br />
b) PETG.<br />
The NMR methods were used to investigate the molecular dynamics. The spin – lattice<br />
proton T 1 measurements were carried out on home made pulse spectrometer operating at 30.2<br />
MHz, using a saturation sequence <strong>and</strong> “solid echo” to shorten the recovery time. The recovery<br />
of magnetization was single exponential. The temperature dependences of proton spin-lattice<br />
relaxation time T 1 for PET <strong>and</strong> PETG were shown in Fig.2. The second method of 1 H NMR<br />
lines was calculated from results of measurements performed on continuous wave<br />
spectrometer operating at 25 MHz. All experiments were conducted in temperature range<br />
from 140 to 375 K. Figure 3 shows the temperature dependence of the second moment of 1 H<br />
NMR line M 2 for both of researching <strong>poly</strong>mers. The model of internal dynamics was<br />
discussed.
Ea=11.3[kJ/mol]<br />
PETG<br />
PET<br />
T 1<br />
[s]<br />
1<br />
Ea=14.7[kJ/mol]<br />
0,1<br />
2,5 3,0 3,5 4,0 4,5 5,0 5,5 6,0<br />
1000/T [1/K]<br />
Fig.2. The temperature dependences of 1 H NMR spin-lattice relaxation time T 1 for<br />
PET <strong>and</strong> PETG, respectively.<br />
20<br />
18<br />
16<br />
14<br />
PETG<br />
PET<br />
M 2<br />
[G 2 ]<br />
12<br />
10<br />
8<br />
6<br />
4<br />
100 150 200 250 300 350 400<br />
T [K]<br />
Fig.3. The temperature dependence of the second moment M 2 of 1 H NMR line of PET<br />
<strong>and</strong> PETG, respectively.<br />
References:<br />
[1] C. P. Papadopoulou <strong>and</strong> N. K. Kalfoglou, Compatibility behaviour of blends of<br />
<strong>poly</strong>(<strong>ethylene</strong> <strong>terephthalate</strong>) with an amorphous co<strong>poly</strong>ester, POLYMER 38, Number<br />
3, (1997).<br />
[2] R.B. Dupaix, M. C. Boyce, Finite strain behavior of <strong>poly</strong>(<strong>ethylene</strong> <strong>terephthalate</strong>)<br />
(PET) <strong>and</strong> <strong>poly</strong>(<strong>ethylene</strong> <strong>terephthalate</strong>)-<strong>glycol</strong> (PETG), POLYMER 46 4827-4838<br />
(2005).<br />
[3] A. R. Donovan, G. Moad, A novel method for determination of <strong>poly</strong>ester end-groups<br />
by NMR spectroskopy, POLYMER 46 5005-5011 (2005).