Exergy saving and exergy production in municipal wastewater ...
Exergy saving and exergy production in municipal wastewater ...
Exergy saving and exergy production in municipal wastewater ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Exergy</strong> <strong>sav<strong>in</strong>g</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>exergy</strong> <strong>production</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>municipal</strong> <strong>wastewater</strong> treatment<br />
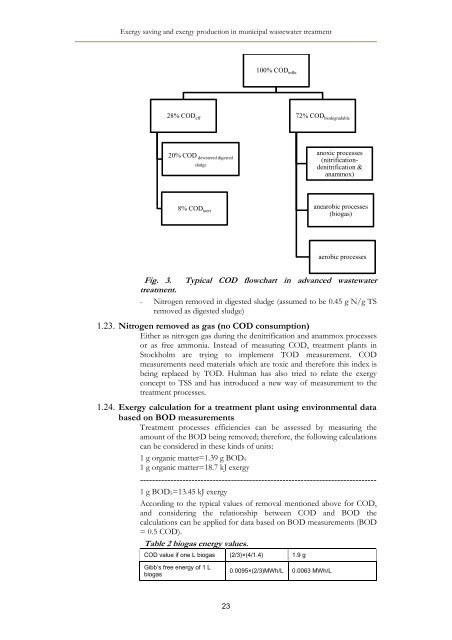
100% COD <strong>in</strong>flu<br />
28% COD eff<br />
72% COD biodegradable<br />
20% COD anoxic processes<br />
dewatered digested<br />
(nitrificationdenitrification<br />
&<br />
sludge<br />
anammox)<br />
8% COD <strong>in</strong>ert<br />
anearobic processes<br />
(biogas)<br />
aerobic processes<br />
Fig. 3. Typical COD flowchart <strong>in</strong> advanced <strong>wastewater</strong><br />
treatment.<br />
- Nitrogen removed <strong>in</strong> digested sludge (assumed to be 0.45 g N/g TS<br />
removed as digested sludge)<br />
1.23. Nitrogen removed as gas (no COD consumption)<br />
Either as nitrogen gas dur<strong>in</strong>g the denitrification <strong>and</strong> anammox processes<br />
or as free ammonia. Instead of measur<strong>in</strong>g COD, treatment plants <strong>in</strong><br />
Stockholm are try<strong>in</strong>g to implement TOD measurement. COD<br />
measurements need materials which are toxic <strong>and</strong> therefore this <strong>in</strong>dex is<br />
be<strong>in</strong>g replaced by TOD. Hultman has also tried to relate the <strong>exergy</strong><br />
concept to TSS <strong>and</strong> has <strong>in</strong>troduced a new way of measurement to the<br />
treatment processes.<br />
1.24. <strong>Exergy</strong> calculation for a treatment plant us<strong>in</strong>g environmental data<br />
based on BOD measurements<br />
Treatment processes efficiencies can be assessed by measur<strong>in</strong>g the<br />
amount of the BOD be<strong>in</strong>g removed; therefore, the follow<strong>in</strong>g calculations<br />
can be considered <strong>in</strong> these k<strong>in</strong>ds of units:<br />
1 g organic matter=1.39 g BOD 5<br />
1 g organic matter=18.7 kJ <strong>exergy</strong><br />
------------------------------------------------------------------------------<br />
1 g BOD 5=13.45 kJ <strong>exergy</strong><br />
Accord<strong>in</strong>g to the typical values of removal mentioned above for COD,<br />
<strong>and</strong> consider<strong>in</strong>g the relationship between COD <strong>and</strong> BOD the<br />
calculations can be applied for data based on BOD measurements (BOD<br />
= 0.5 COD).<br />
Table 2 biogas energy values.<br />
COD value if one L biogas (2/3)×(4/1.4) 1.9 g<br />
Gibb’s free energy of 1 L<br />
biogas<br />
0.0095×(2/3)MWh/L<br />
0.0063 MWh/L<br />
23