Exergy saving and exergy production in municipal wastewater ...
Exergy saving and exergy production in municipal wastewater ...
Exergy saving and exergy production in municipal wastewater ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Exergy</strong> <strong>sav<strong>in</strong>g</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>exergy</strong> <strong>production</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>municipal</strong> <strong>wastewater</strong> treatment<br />
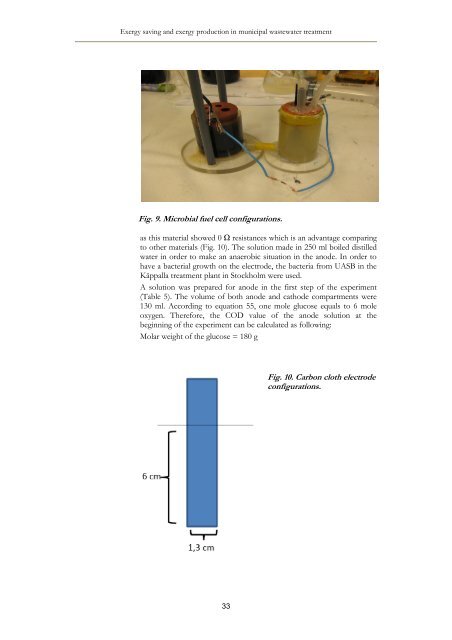
Fig. 9. Microbial fuel cell configurations.<br />
as this material showed 0 resistances which is an advantage compar<strong>in</strong>g<br />
to other materials (Fig. 10). The solution made <strong>in</strong> 250 ml boiled distilled<br />
water <strong>in</strong> order to make an anaerobic situation <strong>in</strong> the anode. In order to<br />
have a bacterial growth on the electrode, the bacteria from UASB <strong>in</strong> the<br />
Käppalla treatment plant <strong>in</strong> Stockholm were used.<br />
A solution was prepared for anode <strong>in</strong> the first step of the experiment<br />
(Table 5). The volume of both anode <strong>and</strong> cathode compartments were<br />
130 ml. Accord<strong>in</strong>g to equation 55, one mole glucose equals to 6 mole<br />
oxygen. Therefore, the COD value of the anode solution at the<br />
beg<strong>in</strong>n<strong>in</strong>g of the experiment can be calculated as follow<strong>in</strong>g:<br />
Molar weight of the glucose = 180 g<br />
Fig. 10. Carbon cloth electrode<br />
configurations.<br />
33