Seasonal Variation of Landfill Methane Emissions from ... - JGSEE
Seasonal Variation of Landfill Methane Emissions from ... - JGSEE
Seasonal Variation of Landfill Methane Emissions from ... - JGSEE
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
The 2 nd Joint International Conference on “Sustainable Energy and Environment (SEE 2006)”<br />
D-026 (O) 21-23 November 2006, Bangkok, Thailand<br />
Table 1 Characteristics <strong>of</strong> study sites<br />
Site Disposal practice Began<br />
operation<br />
Waste stream<br />
(tons/day)<br />
Waste in place<br />
(tons)<br />
<strong>Landfill</strong>ing area<br />
(hectares)<br />
Pattaya sanitary landfill 2002 245 ~350,000 22.4<br />
Cha Am sanitary landfill 2000 56 ~50,000 19<br />
Hua Hin sanitary landfill 1998 68 ~160,000 12<br />
Nonthaburi open dump 1986 850 ~5,500,000 29.8<br />
Nakhonpathom open dump 1997 180 ~590,000 5<br />
Samutprakan open dump 1999 80 ~180,000 2.5<br />
Rayong open dump 1998 70 ~114,000 3.5<br />
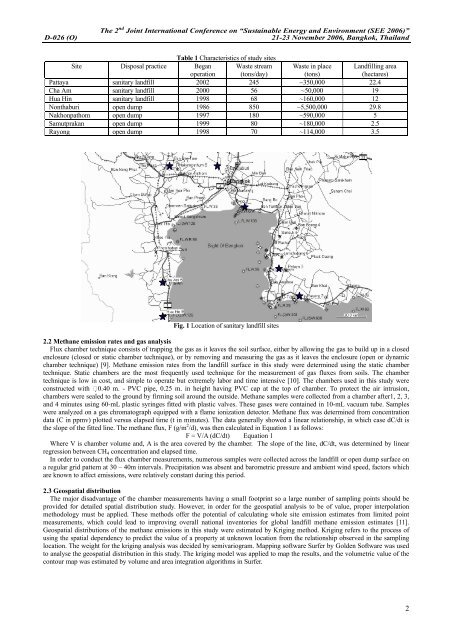
Fig. 1 Location <strong>of</strong> sanitary landfill sites<br />
2.2 <strong>Methane</strong> emission rates and gas analysis<br />
Flux chamber technique consists <strong>of</strong> trapping the gas as it leaves the soil surface, either by allowing the gas to build up in a closed<br />
enclosure (closed or static chamber technique), or by removing and measuring the gas as it leaves the enclosure (open or dynamic<br />
chamber technique) [9]. <strong>Methane</strong> emission rates <strong>from</strong> the landfill surface in this study were determined using the static chamber<br />
technique. Static chambers are the most frequently used technique for the measurement <strong>of</strong> gas fluxes <strong>from</strong> soils. The chamber<br />
technique is low in cost, and simple to operate but extremely labor and time intensive [10]. The chambers used in this study were<br />
constructed with 0.40 m. - PVC pipe, 0.25 m. in height having PVC cap at the top <strong>of</strong> chamber. To protect the air intrusion,<br />
chambers were sealed to the ground by firming soil around the outside. <strong>Methane</strong> samples were collected <strong>from</strong> a chamber after1, 2, 3,<br />
and 4 minutes using 60-mL plastic syringes fitted with plastic valves. These gases were contained in 10-mL vacuum tube. Samples<br />
were analyzed on a gas chromatograph equipped with a flame ionization detector. <strong>Methane</strong> flux was determined <strong>from</strong> concentration<br />
data (C in ppmv) plotted versus elapsed time (t in minutes). The data generally showed a linear relationship, in which case dC/dt is<br />
the slope <strong>of</strong> the fitted line. The methane flux, F (g/m 2 /d), was then calculated in Equation 1 as follows:<br />
F = V/A (dC/dt) Equation 1<br />
Where V is chamber volume and, A is the area covered by the chamber. The slope <strong>of</strong> the line, dC/dt, was determined by linear<br />
regression between CH 4 concentration and elapsed time.<br />
In order to conduct the flux chamber measurements, numerous samples were collected across the landfill or open dump surface on<br />
a regular grid pattern at 30 – 40m intervals. Precipitation was absent and barometric pressure and ambient wind speed, factors which<br />
are known to affect emissions, were relatively constant during this period.<br />
2.3 Geospatial distribution<br />
The major disadvantage <strong>of</strong> the chamber measurements having a small footprint so a large number <strong>of</strong> sampling points should be<br />
provided for detailed spatial distribution study. However, in order for the geospatial analysis to be <strong>of</strong> value, proper interpolation<br />
methodology must be applied. These methods <strong>of</strong>fer the potential <strong>of</strong> calculating whole site emission estimates <strong>from</strong> limited point<br />
measurements, which could lead to improving overall national inventories for global landfill methane emission estimates [11].<br />
Geospatial distributions <strong>of</strong> the methane emissions in this study were estimated by Kriging method. Kriging refers to the process <strong>of</strong><br />
using the spatial dependency to predict the value <strong>of</strong> a property at unknown location <strong>from</strong> the relationship observed in the sampling<br />
location. The weight for the kriging analysis was decided by semivariogram. Mapping s<strong>of</strong>tware Surfer by Golden S<strong>of</strong>tware was used<br />
to analyse the geospatial distribution in this study. The kriging model was applied to map the results, and the volumetric value <strong>of</strong> the<br />
contour map was estimated by volume and area integration algorithms in Surfer.<br />
2