Sequences from Pentagonal Pyramids of Integers - HIKARI Ltd
Sequences from Pentagonal Pyramids of Integers - HIKARI Ltd
Sequences from Pentagonal Pyramids of Integers - HIKARI Ltd
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
622 T. Aaron Gulliver<br />
2. <strong>Pentagonal</strong> <strong>Pyramids</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Integers</strong><br />
A pentagonal pyramidal array <strong>of</strong> integers has a structure with 1 at the top,<br />
2 to 6 on the second level, 7 to 18 on the third level, etc. An illustration <strong>of</strong><br />
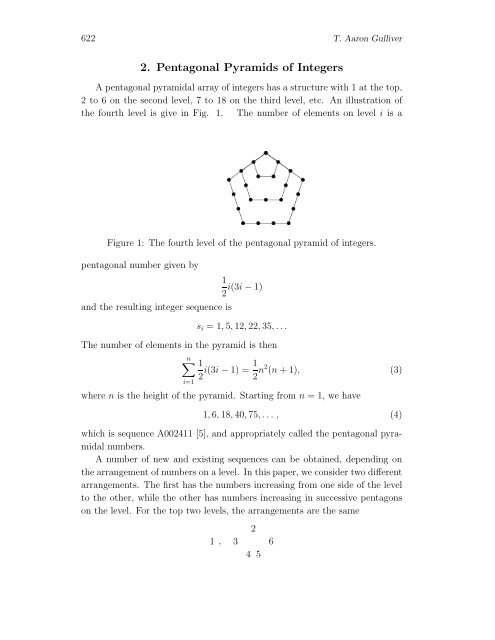
the fourth level is give in Fig. 1. The number <strong>of</strong> elements on level i is a<br />
Figure 1: The fourth level <strong>of</strong> the pentagonal pyramid <strong>of</strong> integers.<br />
pentagonal number given by<br />
1<br />
i(3i − 1)<br />
2<br />
and the resulting integer sequence is<br />
s i =1, 5, 12, 22, 35,...<br />
The number <strong>of</strong> elements in the pyramid is then<br />
n∑ 1<br />
2 i(3i − 1) = 1 2 n2 (n +1), (3)<br />
i=1<br />
where n is the height <strong>of</strong> the pyramid. Starting <strong>from</strong> n = 1, we have<br />
1, 6, 18, 40, 75,..., (4)<br />
which is sequence A002411 [5], and appropriately called the pentagonal pyramidal<br />
numbers.<br />
A number <strong>of</strong> new and existing sequences can be obtained, depending on<br />
the arrangement <strong>of</strong> numbers on a level. In this paper, we consider two different<br />
arrangements. The first has the numbers increasing <strong>from</strong> one side <strong>of</strong> the level<br />
to the other, while the other has numbers increasing in successive pentagons<br />
on the level. For the top two levels, the arrangements are the same<br />
1 ,<br />
2<br />
3 6<br />
4 5