Kinetic Molecular Theory Gas Laws - Oakland Schools
Kinetic Molecular Theory Gas Laws - Oakland Schools
Kinetic Molecular Theory Gas Laws - Oakland Schools
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
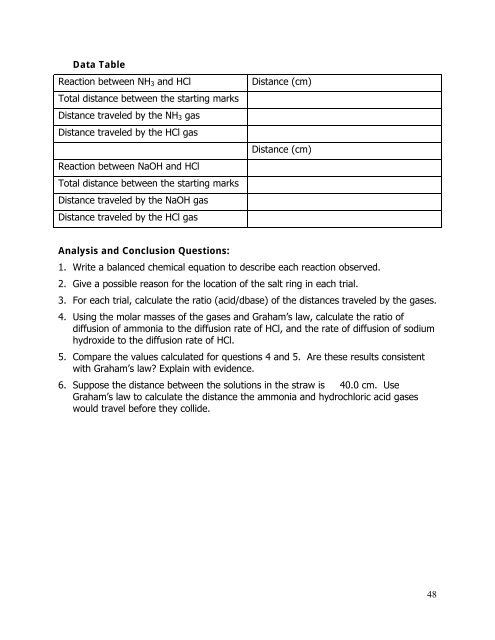
Data Table<br />
Reaction between NH 3 and HCl<br />
Total distance between the starting marks<br />
Distance traveled by the NH 3 gas<br />
Distance traveled by the HCl gas<br />
Reaction between NaOH and HCl<br />
Total distance between the starting marks<br />
Distance traveled by the NaOH gas<br />
Distance traveled by the HCl gas<br />
Distance (cm)<br />
Distance (cm)<br />
Analysis and Conclusion Questions:<br />
1. Write a balanced chemical equation to describe each reaction observed.<br />
2. Give a possible reason for the location of the salt ring in each trial.<br />
3. For each trial, calculate the ratio (acid/dbase) of the distances traveled by the gases.<br />
4. Using the molar masses of the gases and Graham’s law, calculate the ratio of<br />
diffusion of ammonia to the diffusion rate of HCl, and the rate of diffusion of sodium<br />
hydroxide to the diffusion rate of HCl.<br />
5. Compare the values calculated for questions 4 and 5. Are these results consistent<br />
with Graham’s law? Explain with evidence.<br />
6. Suppose the distance between the solutions in the straw is 40.0 cm. Use<br />
Graham’s law to calculate the distance the ammonia and hydrochloric acid gases<br />
would travel before they collide.<br />
48