Kinetic Molecular Theory Gas Laws - Oakland Schools
Kinetic Molecular Theory Gas Laws - Oakland Schools
Kinetic Molecular Theory Gas Laws - Oakland Schools
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Assessment Ideas<br />
Consider a balloon filled with helium and a balloon filled with air. Explain why the<br />
balloon deflates more quickly if it is filled with helium than if filled with air.<br />
Compare the rates of loss of helium from a Mylar balloon and a latex balloon.<br />
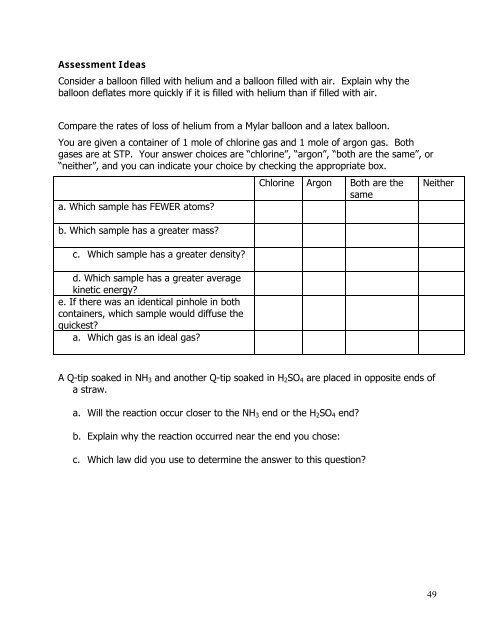
You are given a container of 1 mole of chlorine gas and 1 mole of argon gas. Both<br />
gases are at STP. Your answer choices are “chlorine”, “argon”, “both are the same”, or<br />
“neither”, and you can indicate your choice by checking the appropriate box.<br />
a. Which sample has FEWER atoms?<br />
b. Which sample has a greater mass?<br />
c. Which sample has a greater density?<br />
d. Which sample has a greater average<br />
kinetic energy?<br />
e. If there was an identical pinhole in both<br />
containers, which sample would diffuse the<br />
quickest?<br />
a. Which gas is an ideal gas?<br />
Chlorine Argon Both are the<br />
same<br />
Neither<br />
A Q-tip soaked in NH 3 and another Q-tip soaked in H 2 SO 4 are placed in opposite ends of<br />
a straw.<br />
a. Will the reaction occur closer to the NH 3 end or the H 2 SO 4 end?<br />
b. Explain why the reaction occurred near the end you chose:<br />
c. Which law did you use to determine the answer to this question?<br />
49