Dialogue and Diagnosis - American Osteopathic Association
Dialogue and Diagnosis - American Osteopathic Association
Dialogue and Diagnosis - American Osteopathic Association
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
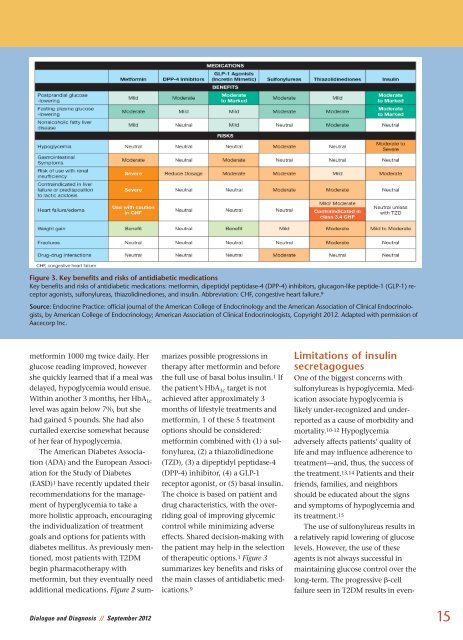
Figure 3. Key benefits <strong>and</strong> risks of antidiabetic medications<br />
Key benefits <strong>and</strong> risks of antidiabetic medications: metformin, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor<br />
agonists, sulfonylureas, thiazolidinediones, <strong>and</strong> insulin. Abbreviation: CHF, congestive heart failure. 9<br />
Source: Endocrine Practice: official journal of the <strong>American</strong> College of Endocrinology <strong>and</strong> the <strong>American</strong> <strong>Association</strong> of Clinical Endocrinologists,<br />
by <strong>American</strong> College of Endocrinology; <strong>American</strong> <strong>Association</strong> of Clinical Endocrinologists, Copyright 2012. Adapted with permission of<br />
Aacecorp Inc.<br />
metformin 1000 mg twice daily. Her<br />
glucose reading improved, however<br />
she quickly learned that if a meal was<br />
delayed, hypoglycemia would ensue.<br />
Within another 3 months, her HbA 1c<br />
level was again below 7%, but she<br />
had gained 5 pounds. She had also<br />
curtailed exercise somewhat because<br />
of her fear of hypoglycemia.<br />
The <strong>American</strong> Diabetes Associa -<br />
tion (ADA) <strong>and</strong> the European <strong>Association</strong><br />
for the Study of Diabetes<br />
(EASD) 1 have recently updated their<br />
recommend ations for the manage -<br />
ment of hyperglycemia to take a<br />
more holistic approach, encouraging<br />
the individualization of treatment<br />
goals <strong>and</strong> options for patients with<br />
diabetes mellitus. As previously mentioned,<br />
most patients with T2DM<br />
begin pharmacotherapy with<br />
metformin, but they eventually need<br />
additional medications. Figure 2 summarizes<br />
possible progressions in<br />
therapy after metformin <strong>and</strong> before<br />
the full use of basal bolus insulin. 1 If<br />
the patient’s HbA 1c target is not<br />
achieved after approximately 3<br />
months of lifestyle treatments <strong>and</strong><br />
metformin, 1 of these 5 treatment<br />
options should be considered:<br />
metformin combined with (1) a sulfonylurea,<br />
(2) a thiazolidinedione<br />
(TZD), (3) a dipeptidyl peptidase-4<br />
(DPP-4) inhibitor, (4) a GLP-1<br />
receptor agonist, or (5) basal insulin.<br />
The choice is based on patient <strong>and</strong><br />
drug characteristics, with the over -<br />
riding goal of improving glycemic<br />
control while minimizing adverse<br />
effects. Shared decision-making with<br />
the patient may help in the selection<br />
of therapeutic options. 1 Figure 3<br />
summarizes key benefits <strong>and</strong> risks of<br />
the main classes of antidiabetic medications.<br />
9<br />
Limitations of insulin<br />
secretagogues<br />
One of the biggest concerns with<br />
sulfonylureas is hypoglycemia. Medication<br />
associate hypoglycemia is<br />
likely under-recognized <strong>and</strong> under -<br />
reported as a cause of morbidity <strong>and</strong><br />
mortality. 10-12 Hypoglycemia<br />
adversely affects patients’ quality of<br />
life <strong>and</strong> may influence adherence to<br />
treatment—<strong>and</strong>, thus, the success of<br />
the treatment. 13,14 Patients <strong>and</strong> their<br />
friends, families, <strong>and</strong> neighbors<br />
should be educated about the signs<br />
<strong>and</strong> symptoms of hypoglycemia <strong>and</strong><br />
its treatment. 15<br />
The use of sulfonylureas results in<br />
a relatively rapid lowering of glucose<br />
levels. However, the use of these<br />
agents is not always successful in<br />
maintaining glucose control over the<br />
long-term. The progressive -cell<br />
failure seen in T2DM results in even-<br />
<strong>Dialogue</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Diagnosis</strong> // September 2012<br />
15