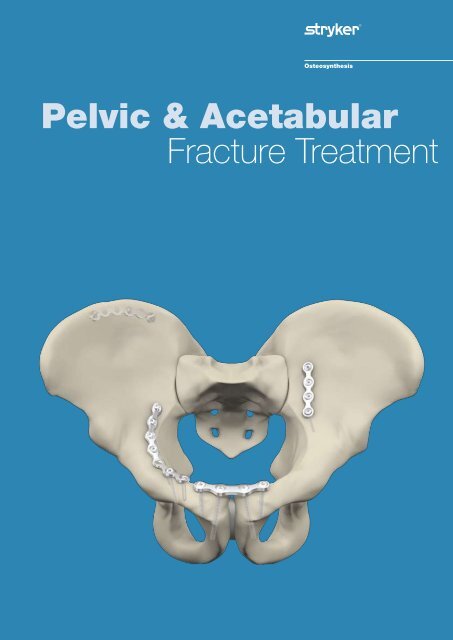
Pelvic & Acetabular Fracture Treatment - Stryker
Pelvic & Acetabular Fracture Treatment - Stryker
Pelvic & Acetabular Fracture Treatment - Stryker
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Pelvic</strong> & <strong>Acetabular</strong><br />
<strong>Fracture</strong> <strong>Treatment</strong><br />
1
Contents<br />
Acknowledgments<br />
<strong>Stryker</strong> acknowledges Joel Matta, M.D.<br />
and Henry Claude Sargi, M.D. for<br />
their support in the preparation of this<br />
brochure.<br />
This publication sets forth detailed<br />
recommended procedures for using<br />
<strong>Stryker</strong> Osteosynthesis devices and<br />
instruments.<br />
It offers guidance that you should<br />
heed, but, as with any such technical<br />
guide, each surgeon must consider the<br />
particular needs of each patient and<br />
make appropriate adjustments when<br />
and as required.<br />
A workshop training is required prior<br />
to first surgery. See package insert<br />
(V15011, V15013 and V15034) for<br />
a complete list of potential adverse<br />
effects, contraindications, warnings and<br />
precautions. the surgeon must discuss<br />
all relevant risks, including the finite<br />
lifetime of the device, with the patient,<br />
when necessary.<br />
Page<br />
1. Introduction 4<br />
2. Rationale 5<br />
Matta <strong>Pelvic</strong> System<br />
External Fixation<br />
Apex Pin Fixation<br />
Asnis Screw Fixation<br />
HydroSet<br />
3. Indications 6<br />
Matta <strong>Pelvic</strong> System Indications<br />
Contraindications<br />
4. Features and Benefits 7<br />
Plates<br />
Screws<br />
Instrumentation<br />
5. Plate Types 8<br />
Female Pelvis<br />
Male Pelvis<br />
6. The <strong>Pelvic</strong> Ring and Acetabulum 9<br />
<strong>Pelvic</strong> Ring<br />
Acetabulum<br />
7. Assessment of <strong>Fracture</strong>s 10<br />
Inlet Projection<br />
Outlet Projection<br />
6. <strong>Pelvic</strong> Ring <strong>Fracture</strong> Types 11<br />
Pubis Symphysis Disruption<br />
Iliac <strong>Fracture</strong><br />
Sacroiliac Dislocation<br />
Sacroiliac <strong>Fracture</strong> – Dislocation<br />
Sacrum <strong>Fracture</strong><br />
9. <strong>Acetabular</strong> <strong>Fracture</strong> Types 14<br />
Posterior Wall<br />
Posterior Column<br />
Anterior Wall<br />
Anterior Column<br />
Transverse<br />
T-Shaped<br />
Posterior Column & Posterior Wall<br />
Transverse & Posterior Wall<br />
Anterior Column Posterior-Hemitransverse<br />
Both Column<br />
Warning:<br />
All bone screws referenced in<br />
this document here are not<br />
approved for screw attachment or<br />
fixation to the posterior elements<br />
(pedicles) of the cervical, thoracic<br />
or lumbar spine.<br />
2
Contents - Cont’d<br />
Page<br />
14. Plate Bending 19<br />
15. Screw Fixation 20<br />
17. Reduction Instruments 22<br />
19. External Fixation <strong>Pelvic</strong> Frame 24<br />
Features and Benefits<br />
20. Hoffmann II MRI-Pin Placement Techniques 25<br />
21. Hoffmann Xpress Immediate Care 26<br />
Hoffmann II MRI<br />
Apex Pins<br />
22. Apex Pin Fixation 27<br />
Technical Details - Self-Drilling/Self-Tapping Apex Pin<br />
23. Asnis III Screw Fixation 28<br />
Features and Benefits<br />
24. Asnis III <strong>Pelvic</strong> Screws 29<br />
25. <strong>Acetabular</strong> Articular Fragments Augmentation with HydroSet 30<br />
Features and Benefits<br />
Ordering Information – MPS Plates 31<br />
Ordering Information – MPS Screws 32<br />
Ordering Information – MPS Screws 33<br />
Ordering Information – MPS Instruments 34<br />
Ordering Information – MPS Cases and Trays 35<br />
Ordering Information – Hoffmann II MRI Components 36<br />
Ordering Information – Hoffmann II MRI Instruments 37<br />
Ordering Information – Hoffmann Xpress 38<br />
Ordering Information – Apex <strong>Pelvic</strong> Pins 39<br />
Ordering Information - Asnis III 40<br />
Ordering Information – HydroSet Injectable HA Bone Substitute 41<br />
3
Introduction<br />
“The perfect restoration of the articular surface and associated osseous architecture”<br />
was the goal set forth by R.Judet and E. Letournel in their surgical treatment of<br />
fractures of the pelvis and the acetabulum.<br />
However, before surgical intervention in a fractured acetabulum can be accepted as<br />
a means of treatment, accurate diagnosis based on radiology is essential. As in other<br />
conditions, classification also aids in the accurate understanding of these sometimes<br />
complex fractures.<br />
No one surgical approach is applicable for all acetabulum fractures. After<br />
examination of the plain films as well as the CT scan the surgeon should be<br />
knowledgeable of the precise anatomy of the fracture he is dealing with. A surgical<br />
approach is selected with the expectation that the entire reduction and fixation can<br />
be performed through the surgical approach.<br />
The Letournel classification was first published in 1961. Apart from some minor<br />
early modifications, it has since remained unchanged and is now the most widely<br />
used classification system for acetabular fractures. This classification proposes the<br />
division of the various fracture types into two large groups:<br />
Elementary <strong>Fracture</strong>s comprise those in which a part or all of one or both columns<br />
supporting the acetabulum has been detached by a single fracture line. The five<br />
elementary fracture types are:<br />
- <strong>Fracture</strong> of the posterior wall<br />
- <strong>Fracture</strong> of the posterior column<br />
- <strong>Fracture</strong> of the anterior wall<br />
- <strong>Fracture</strong> of the anterior column<br />
- Transverse fracture<br />
Associated <strong>Fracture</strong>s comprise those in which two or more elementary patterns are<br />
combined. The five associated fracture types are:<br />
- T-shaped fracture<br />
- Posterior column and posterior wall fracture<br />
- Transverse and posterior wall fractures<br />
- Anterior column or anterior wall with posterior<br />
hemi-transverse fracture<br />
- Both–column fracture<br />
Judet and Letournel concluded early on the most important factor in a successful<br />
operation was a thorough pre-operative three dimensional understanding of the<br />
X-rays and fracture pattern. The same is true today. The surgeon’s knowledge, skill<br />
and dedication remain the primary determinants of the patient’s outcome, and the<br />
<strong>Stryker</strong> <strong>Pelvic</strong> & <strong>Acetabular</strong> <strong>Fracture</strong> <strong>Treatment</strong> Solutions seek to facilitate this.<br />
4
Rationale<br />
Matta <strong>Pelvic</strong> System<br />
The Matta <strong>Pelvic</strong> System is designed to address all fractures of the acetabulum<br />
and pelvis. The shape, material properties, plate malleability and hole spacing of<br />
the plates take into account today’s physician’s need for sufficient fatigue strength,<br />
optimized transfer of loading forces and a standardized operative technique with<br />
broad applicability. The current set also includes a variety of clamps and reduction<br />
External Fixation<br />
Hoffmann II External Fixation plays a definitive role in the treatment of unstable<br />
pelvic fractures using the device as provisional fixation. In contrast to internal<br />
fixation, this method has two major advantages: safety and simplicity.<br />
Apex Pin Fixation<br />
Solid pin fixation is essential for effective external fixation frames. The Apex Pin<br />
uses advanced thread geometry designed to yield outstanding cutting performance<br />
and optimal pin fixation.<br />
Asnis Screw Fixation<br />
Asnis III 6.5mm or 8.0mm cannulated screws can be utilized in surgical stabilization<br />
of sacroiliac joint disruption and/or sacral fractures using a minimally invasive<br />
HydroSet<br />
HydroSet injectable HA bone void substitute can be utilized in comminuted<br />
posterior wall fractures as an effective osteoconductive and osteointegrative material, as<br />
well as to help support pelvic bone fragments.<br />
5<br />
Matta – Page 7 Ex–Fix – Page 25 Asnis – Page 29 HydroSet – Page 30
Indications<br />
Matta <strong>Pelvic</strong> System Indications:<br />
• Acetabulum fracture<br />
• <strong>Pelvic</strong> Ring fracture<br />
• Sacrum fracture<br />
• Ilium fracture<br />
• Sacroiliac joint dislocations<br />
• Symphysis Pubis disruption<br />
• Revision surgery of pseudoarthroses, non-unions and mal-unions<br />
• Osteotomies<br />
• <strong>Pelvic</strong> arthrodeses<br />
• Total hip revision surgery<br />
Contraindications<br />
The physician’s education, training and professional judgment must be relied on<br />
to choose<br />
the most appropriate device and treatment.<br />
Conditions presenting an increased risk of failure include:<br />
Any active or suspected latent infection, or marked local inflammation in or about<br />
the affected area. Compromised vascularity that would inhibit adequate blood<br />
supply to the fracture or the operative site.<br />
Bone stock compromised by disease, infection or prior implantation that cannot<br />
provide adequate support and/or fixation of the devices.<br />
Material sensitivity, documented or suspected. Obesity. An overweight or obese<br />
patient can produce<br />
loads on the implant that can lead to failure of the fixation of the device or to<br />
failure of the device itself. Patients having inadequate tissue coverage over the<br />
operative site. Implant utilization that would interfere with anatomical structures or<br />
physiological performance.<br />
Any mental or neuromuscular disorder that would create an unacceptable risk of<br />
fixation failure or complications in postoperative care. Other medical or surgical<br />
conditions that would preclude the potential benefit of surgery.<br />
6
Features & Benefits<br />
Modular case design<br />
Dedicated basic<br />
instrument case<br />
Flexibility for sterilization method<br />
in either outerbase or in sterilization<br />
container.<br />
All instruments for three screw sizes in<br />
one set.<br />
Matta<br />
Plates<br />
Stainless steel cold–worked<br />
processed and annealed<br />
plates available<br />
Straight and curved plate options<br />
Dedicated symphysis pubis<br />
plate<br />
Rounded plate ends<br />
3.5/4.5mm screw plate hole<br />
option<br />
Low screw head profile<br />
in plate hole<br />
Plate screw hole angulation<br />
with 3.5mm screws<br />
Equal hole–spacing on plate<br />
Advanced plate bender<br />
Bending templates<br />
Excellent plate malleability for optimum<br />
adaptation to the pelvic surfaces.<br />
Indication–specific coverage.<br />
Precurved to fit anatomically,<br />
with the strength to meet the<br />
demands of load forces.<br />
Reduced potential for soft–tissue irritation.<br />
Flexibility of 3.5mm or 4.5mm<br />
cortical screws.<br />
Reduced potential for<br />
soft–tissue irritation.<br />
Optimized for posterior wall fixation.<br />
Great operative flexibility for screw and<br />
plate placement.<br />
Easy and smooth three–dimensional<br />
bending of plates.<br />
Flexibility to bend plates away from the<br />
surgical field.<br />
Screws<br />
Self-tapping cortical screws<br />
Four options of reduction pins<br />
Reduction Instruments<br />
Instrumentation<br />
Specific Nerve Retractors<br />
Spiked Disk<br />
Elastosil or Canevasit Handles<br />
Screwdriver Holding Sleeve<br />
Quick, simple and more efficient.<br />
Flexibility of choice of ø5mm or ø6mm<br />
and 150mm or 180mm length.<br />
Specialist forceps and optimized clamp<br />
design, uniquely sized for 3.5 and<br />
.5mm screws.<br />
Two sizes available for optimal soft<br />
tissue retraction.<br />
Can be used in combination with<br />
reduction forceps and ball spike for<br />
increased bone contact.<br />
Surgeon choice.<br />
Efficiency in pick up insertion/removal<br />
via “No-touch” technique.<br />
7
Plate Types<br />
Female Pelvis<br />
Radius 88mm<br />
Male Pelvis<br />
Radius 108mm<br />
Curved and straight plates<br />
Hard material, 2.5mm thick, 16mm<br />
spacing between the holes.<br />
Flex plates<br />
Soft (annealed) material, 2.5mm thick,<br />
12mm spacing between the holes,<br />
malleable.<br />
Symphysis plates<br />
Hard material, 3.2mm thick, 16mm<br />
spacing between the holes, 75mm<br />
radius.<br />
8
The <strong>Pelvic</strong> Ring and Acetabulum<br />
<strong>Pelvic</strong> Ring<br />
Matta<br />
<strong>Fracture</strong> Types:<br />
- Pubis Symphysis Disruption<br />
- Ilium <strong>Fracture</strong><br />
- Sacroiliac Dislocation<br />
- Sacroiliac <strong>Fracture</strong> –<br />
Dislocation<br />
- Sacrum <strong>Fracture</strong><br />
Acetabulum<br />
<strong>Fracture</strong> Types:<br />
Elementary <strong>Fracture</strong>s<br />
- Posterior Wall<br />
- Posterior Column<br />
- Anterior Wall<br />
- Anterior Column<br />
- Transverse<br />
Associated <strong>Fracture</strong>s<br />
- T-Shaped<br />
- Posterior Column & Posterior Wall<br />
- Transverse & Posterior Wall<br />
- Anterior Column Posterior–<br />
Hemitransverse<br />
- Both Column<br />
9
Assessment of <strong>Fracture</strong>s<br />
The evaluation of a pelvic injury has to be based on repeated checks of the patient’s<br />
vital parameters, a detailed clinical examination and a structured radiographic<br />
evaluation. Emergency decisions can usually be based on a pelvis AP x-ray, whereas<br />
the detailed classification is assigned after additional oblique projections.<br />
Inlet Projection<br />
Positioning for inlet projection (Fig.1)<br />
and drawing of the X-ray appearance<br />
obtained from the Inlet projection<br />
(Fig 1a).<br />
Fig 1a Fig 1<br />
Outlet Projection<br />
Positioning for outlet projection (Fig 2)<br />
and drawing of the X-ray appearance<br />
obtained from the Outlet projection<br />
(Fig 2a).<br />
Fig 2a Fig 2<br />
10
<strong>Pelvic</strong> Ring <strong>Fracture</strong> Types<br />
Pubis Symphysis Disruption<br />
Matta<br />
• Fixation of a pure disruption<br />
of the Symphysis Pubis using<br />
a dedicated MPS four or<br />
six-hole symphysis plate.<br />
A minimum of two 3.5 or 4.5mm<br />
cortical screws on either side of the<br />
symphysis allows for good support.<br />
Reduction/Fixation through the Symphysis (Anterior) surgical approach<br />
(Pfannenstiel Type approach).<br />
Iliac <strong>Fracture</strong><br />
Reduction/Fixation through the Ilioinguinal or Posterior <strong>Pelvic</strong> Ring surgical<br />
approaches.<br />
• One 6.5mm partially threaded<br />
cancellous screw inserted from the<br />
anterior-inferior iliac spine, passing<br />
1cm to 2cm above the acetabulum.<br />
• One 3.5mm independent lag screw in<br />
the iliac crest starting from the anterior<br />
branch.<br />
• One MPS Straight four-hole plate<br />
screwed over the fracture line in the<br />
area of the pelvic brim.<br />
11
<strong>Pelvic</strong> Ring <strong>Fracture</strong> Types<br />
Sacroiliac Dislocation<br />
• Fixation of a sacroiliac dislocation<br />
by using a 6.5 or 8.0mm cannulated<br />
iliosacral lag screw.<br />
Reduction/Fixation through the Posterior or Anterior <strong>Pelvic</strong> Ring surgical<br />
approach.<br />
Sacroiliac <strong>Fracture</strong> – Dislocation<br />
• One 4.5 or 6.5mm independent lag<br />
screw starting from the posteriorinferior<br />
iliac spine stabilizes the<br />
reduction of the inferior aspect of the<br />
iliac wing.<br />
• One MPS flex six-hole plate (annealed)<br />
stabilizes the reduction of the iliac crest.<br />
• One 6.5 or 8.0 cannulated<br />
ilio-sacral lag screw stablizes<br />
the sacroiliac joint.<br />
Reduction/Fixation through the Posterior <strong>Pelvic</strong> Ring surgical approach.<br />
12
<strong>Pelvic</strong> Ring <strong>Fracture</strong> Types<br />
Sacrum <strong>Fracture</strong><br />
Matta<br />
• Fixation of a sacrum fracture<br />
by placing two 6.5 or 8.0mm<br />
cannulated lag screws (preferably<br />
16mm thread) or 6.5mm cancellous<br />
screw alternatively through the lateral<br />
iliac wing and advancing these screws<br />
into the S1 and S2 vertebral body.<br />
Reduction/Fixation through the Posterior <strong>Pelvic</strong> Ring surgical approach.<br />
13
<strong>Acetabular</strong> <strong>Fracture</strong> Types<br />
Posterior Wall<br />
• Two 3.5mm independent lag screws<br />
initially fix the fragments with the<br />
desired anatomical reduction.<br />
• One MPS Curved R108 six or<br />
seven-hole plate or alternatively a<br />
MPS Flex eight-hole plate (annealed)<br />
spans the fragments along its axis<br />
(Neutralization plate).<br />
Reduction/Fixation through the Kocher-Langenbeck surgical approach.<br />
Posterior Column<br />
• Start definitive fixation with an<br />
independent lag screw from the distal<br />
fragment into the posterior buttress of<br />
the ilium.<br />
• One MPS curved six-hole plate,<br />
alternatively, a Flex eight-hole plate<br />
along the acetabular margin maintains<br />
the reduction.<br />
Reduction/Fixation through the Kocher-Langenbeck surgical approach.<br />
14
<strong>Acetabular</strong> <strong>Fracture</strong> Types<br />
Anterior Wall<br />
Matta<br />
• One or two independent lag screws fix<br />
the reduced fragments.<br />
• One MPS Curved plate<br />
bridges the fragment on the pelvic<br />
brim from the iliac fossa to the intact<br />
part of the pubic ramus.<br />
Reduction/Fixation through the Ilioinguinal surgical approach.<br />
Anterior Column<br />
• An independent lag screw first maintains<br />
the reduction. Then a MPS Curved<br />
10-hole plate is shaped to adapt itself<br />
optimally to the pelvic brim going from<br />
the pubic tubercle to the vicinity of the<br />
sacroiliac joint, with a minimum of two<br />
screws beyond the fracture line.<br />
• All central screws should be parallel to<br />
the quadrilateral surface.<br />
Reduction/Fixation through the Ilioinguinal or modified Stoppa surgical approach.<br />
15
<strong>Acetabular</strong> <strong>Fracture</strong> Types<br />
Transverse<br />
• The posterior column is stabilized<br />
with an independant 3.5 or 4.5mm<br />
lag screw and an MPS annealed<br />
neutralization plate.<br />
• The anterior column is stabilized with<br />
an independant 4.5mm lag screw.<br />
Reduction/Fixation through the Kocher-Langenbeck surgical approach.<br />
T-Shaped<br />
• The posterior column is stabilized<br />
with an independant 3.5 or 4.5mm<br />
lag screw and an MPS curved or<br />
annealed neutralization plate.<br />
• The anterior column is stabilized with<br />
an independant 4.5mm lag screw.<br />
Reduction/Fixation through the Kocher-Langenbeck or Extended Iliofemoral<br />
surgical approaches.<br />
16
<strong>Acetabular</strong> <strong>Fracture</strong> Types<br />
Posterior Column & Posterior Wall<br />
Matta<br />
Reduction/Fixation through the Kocher-Langenbeck surgical approach.<br />
• Initial fixation of the posterior<br />
column with an independent lag<br />
screw and/or five or six-hole plate.<br />
• If the posterior wall fragment is large<br />
enough, it should be fixed into its bed<br />
with one or two lag screws.<br />
• Definitive stabilization of the<br />
posterior wall and column is obtained<br />
by adding a seven or eight-hole MPS<br />
curved plate buttressing the posterior<br />
wall and anchored securely to the<br />
ilium and ischium using 3.5mm<br />
screws.<br />
Transverse & Posterior Wall<br />
Reduction/Fixation through the Kocher-Langenbeck surgical approach.<br />
• Two 3.5 or 4.5mm independent<br />
lag screws stabilize the transverse<br />
fracture component.<br />
• One or two independent 3.5mm lag<br />
screw maintained the reduction of the<br />
posterior wall fragment.<br />
• An MPS flex (annealed) eight-hole<br />
plate or alternatively a six or<br />
seven-hole curved plate is applied<br />
to buttress the posterior wall.<br />
17
<strong>Acetabular</strong> <strong>Fracture</strong> Types<br />
Anterior Column Posterior-Hemitransverse<br />
Reduction/Fixation through the Ilioinguinal surgical approach.<br />
• Initial fixation of the posterior<br />
column is provided by a 3.5 or<br />
4.5mm lag screw through the<br />
pelvic brim.<br />
• Stabilization of the anterior column<br />
with one or two individual 3.5 or<br />
4.5mm lag screws from the ASIS and/<br />
or the AIIS.<br />
• An MPS curved plate can then be<br />
placed along the pelvic brim starting in<br />
the sciatic buttress, just anterior to the<br />
SI joint.<br />
Both Column<br />
• Two 3.5mm independent lag screws in<br />
the iliac crest fix the reduction of the<br />
wing fracture lines.<br />
• One or two 3.5mm independent lag<br />
screws running from the upper aspect<br />
of the true pelvis fix the reduction of<br />
the posterior column.<br />
Reduction/Fixation through the Ilioinguinal or Extended Iliofemoral surgical<br />
approaches.<br />
• One independent lag screw fixes the<br />
reduction of a separated posterior<br />
fragment of the pelvic brim, just in<br />
front of the sacroiliac joint.<br />
• One eight-hole MPS annealed plate<br />
along the iliac crest to stabilize the<br />
iliac wing fracture.<br />
• One long MPS Curved 10 or 12-hole<br />
plate along the pelvic brim to stabilize<br />
the anterior column.<br />
18
Plate Bending<br />
The plate must be shaped correctly to fit with precision to the reduced contour of the pelvis or the acetabulum.<br />
The fitting of the plate on the bony<br />
surface should be as precise as possible<br />
so the insertion of screws will not<br />
cause the fragments to change position<br />
(Figure 1).<br />
During plating and screw insertion,<br />
it is always the bone that is drawn<br />
toward the plate, not the plate<br />
toward the bone (Figure 2).<br />
In certain instances it may be<br />
advantageous to contour the plate<br />
to a slight mismatch with the bone.<br />
Subsequent insertion and tightening<br />
of the screws causes the plate to<br />
manipulate the bone, therefore aiding<br />
in obtaining or maintaining the<br />
reduction.<br />
Matta<br />
Figure 1 – Correct<br />
Precise fitting of the plate.<br />
Less danger of displacement of the<br />
fragments during screw insertion.<br />
Figure 2 – Incorrect<br />
When tightening the screws,<br />
the fragment will be drawn towards<br />
the plate.<br />
For a plate to apply perfectly on a bone, it must be possible to shape it in all directions:<br />
• Bend it along its main axis<br />
(Figure 3a, 3b).<br />
• Bend it along its main axis (twist),<br />
to give it an helicoidal shape<br />
(Figure 4a, 4b).<br />
• Bend it “on the flat” to adapt to the<br />
curves of the iliac crest or the upper<br />
aspect of the pelvic brim, or to make<br />
it possible to span a fragment of the<br />
posterior wall or posterosuperior wall,<br />
along its main axis (Figure 5a, 5b).<br />
This type of on-the-flat bending should<br />
always be performed first, since it is<br />
very difficult to bend the plate in this<br />
fashion after a main axis bend or twist<br />
has been made.<br />
Figure 3a<br />
Figure 4a<br />
Figure 5a<br />
Figure 3b<br />
Figure 4b<br />
Figure 5b<br />
It’s an important fact that the plate<br />
must be bent, as far as possible, in the<br />
spaces between the holes, so as to alter<br />
them as little as possible (Figure 6).<br />
It is a well-known fact that rectangular<br />
plates do not bend in a regular fashion<br />
but rather at their holes (Figure 7).<br />
Sherman type plates with equal hole<br />
spacing and narrowing between the<br />
holes, are best adapted to such shaping<br />
and allow for a more precise adaptation<br />
to the pelvic contours.<br />
Figure 6<br />
Figure 7<br />
19
Screw Fixation<br />
The 3.5mm self-tapping cortical screws<br />
are the recommended screws for plate<br />
fixation and are best adapted to the<br />
pelvic bone. The 4.5mm cortical screw<br />
is often too large and its voluminous<br />
head creates a slight prominence above<br />
the plates, which may lead to soft tissue<br />
irritation in certain applications.<br />
Therefore, these screws should only<br />
be used to fix a plate in exceptional<br />
cases (symphysis pubis fixation), as<br />
when a smaller screw does not<br />
get sufficient purchase.<br />
Furthermore, the plate holes are<br />
designed to accept 3.5mm screws<br />
inserted at extreme angles, up to 35 o<br />
in all directions.<br />
This capability is essential, as it must<br />
be possible to avoid penetrating the<br />
hip joint or to be able to drive a screw<br />
obliquely in the area of the iliac bone,<br />
avoiding a previously inserted, isolated<br />
screw.<br />
35º<br />
Possible lag screws using 4.5mm<br />
cortical or 6.5mm cancellous screws:<br />
a) From the crest of the anterior border<br />
(screw 1) in the thickness of the iliac<br />
wing. It is always possible to insert<br />
a screw from the anteroinferior iliac<br />
spine, passing 1 or 2cm above the<br />
acetabulum (length 100 –120mm)<br />
(screw 2).<br />
b) Along the axis of the anterior<br />
column (screw 3). This screw is very<br />
useful to secure a transverse fracture<br />
or an anterior column, through an<br />
extended ilio–femoral approach.<br />
The screw should start from the<br />
posterior aspect of the iliac wing<br />
pillar approximately 3-4cm above<br />
the acetabulum.<br />
c) In the thickness of the iliac wing,<br />
but from posterior to anterior,<br />
starting from the posterior part<br />
of the iliac wing or the posterior–<br />
superior iliac spine, to reduce a<br />
sacroiliac joint fracture dislocation<br />
(screws 4 and 5).<br />
d) Along the axis of the posterior<br />
column (screw 6).<br />
For each of these lag screw insertions,<br />
it is essential to drill intermittently, step<br />
by step, and change the direction of the<br />
drill if you feel penetration of a cortex.<br />
Remain in the correct axis and advance<br />
the drill as far as possible.<br />
20
Screw Fixation<br />
Independent Interfragmentary<br />
Compression<br />
Often, independent (isolated)<br />
interfragmentary lag screws are used in<br />
conjunction with pelvic and acetabular<br />
fracture fixation.The screw thread<br />
takes no purchase in the near fragment<br />
because the screw has a shaft with no<br />
thread and /or the drill hole in the<br />
near fragment is equal to the outside<br />
diameter of the screw.<br />
Therefore, the cortex in the near<br />
fragment has to be overdrilled to create<br />
a “gliding” hole. Overdrilling the cortex<br />
in this manner allows the screw thread<br />
to take purchase in the bone of the<br />
opposite fragment.<br />
Matta<br />
Drill Guides<br />
Use the Double Drill Guide REF<br />
702417 and the 4.5mm Drill or Double<br />
Drill Guide REF 702418 and Drill<br />
3.5mm for screws 3.5mm to overdrill<br />
the near cortex. Insert the opposite side<br />
of the relevant Drill Guide into the<br />
pre-drilled hole for precise axial<br />
alignment and use the corresponding<br />
drill for the corehole of the screw.<br />
This procedure should prevent the loss<br />
of reduction and fixation during screw<br />
insertion.<br />
21
Reduction Instruments<br />
The Matta <strong>Pelvic</strong> Systems forceps<br />
and other reduction instruments are<br />
designed for use with the irregular,<br />
large and flat bony surfaces of the pelvic<br />
region.<br />
The angles and length of the jaws<br />
are designed to accommodate the<br />
innominate bone from the crest to<br />
the pelvic brim and to provide<br />
flexibility for various surgical<br />
approaches.<br />
Reduction of acetabular fractures<br />
are best performed on the orthopædic<br />
extension table allowing distal and<br />
lateral traction.<br />
Reduction Forceps with Points<br />
Faraboef Forceps<br />
702926 – L130mm<br />
702927 – L200mm<br />
These forceps can be applied directly<br />
to the bone’s surface or be used with<br />
shallow drill holes.<br />
702928 – L190mm<br />
702929 – L250mm<br />
The versatile Faraboef clamps can be<br />
used to grasp and manipulate the iliac<br />
wing, or as reduction forceps with<br />
provisional screws of either 3.5mm or<br />
4.5mm diameter.<br />
22
Matta<br />
Reduction Instruments<br />
Matta Reduction Forceps<br />
Reduction Forceps for Screws,<br />
Jungbluth<br />
Verbrugge Forceps<br />
702921 – Small<br />
702922 – Large<br />
These two oblique forceps are designed<br />
so that the handles angle away from<br />
both the surgeon’s sight line and<br />
critical soft tissue structures. The sharp<br />
points provide a secure hold on the<br />
pelvic surfaces, while the balls prevent<br />
penetration of bone with a thin cortex.<br />
702924 – ø4.5mm<br />
702925 – ø3.5mm Right<br />
702947 – ø3.5mm Left<br />
These two forceps have been designed<br />
to be used with either 3.5mm or 4.5mm<br />
screws (3.5mm version available in left<br />
or right option). Screws inserted on<br />
the opposite side of the fracture allow<br />
considerable reduction forces and<br />
manipulation in all three planes.<br />
700641<br />
For easier reduction, there are times<br />
when only one screw is inserted,<br />
requiring the application of one jaw of<br />
the Verbrugge forceps. The other jaw<br />
takes direct hold on another part of the<br />
bony surface.<br />
Example: The angle of the greater<br />
sciatic notch.<br />
Reduction Forceps, King Tong<br />
Sciatic Nerve Retractor<br />
Straight Ball Spike<br />
702930 – 2x1 Jaws<br />
702948 – 1x1 Jaws<br />
This long forceps with three-pointed-ball<br />
tips allow reduction of perpendicular<br />
fractures. The long handles provide<br />
increased leverage for difficult<br />
reductions. These forceps are also<br />
available in a 1x1 Jaws version.<br />
702915 – Small<br />
702916 – Large<br />
Two sizes available for better<br />
soft-tissue retraction.<br />
702911<br />
This reduction instrument is used<br />
as a pusher with pointed ball tip to<br />
reduce bone fragments.<br />
To distribute the reduction forces over<br />
a increased area, the Spiked Disc can be<br />
clipped onto the ball tip.<br />
23
External Fixation <strong>Pelvic</strong> Frame<br />
Hoffmann II MRI External Fixation System offers rapid application in times of hemodynamic compromise with the ability to<br />
access the abdomen and pelvic viscera for secondary procedures.<br />
External Fixation is most appropriate for open-book pelvic fractures in which the posterior structures are at least partially<br />
intact, or lateral compression injuries with internal rotation of the hemipelvis.<br />
Hoffmann II MRI<br />
Features<br />
‘Snap-Fit’ connections<br />
Single point of tightening<br />
Small, lightweight clamps<br />
Color–coded components<br />
Non-ferromagnetic materials<br />
Benefits<br />
Rapid frame construction.<br />
Fast and easy frame construction.<br />
Visualization and access to the fracture site.<br />
Quick and easy identification.<br />
No frame displacement using MRI.<br />
Apex Pins<br />
Features<br />
Independent, multiplanar pin<br />
placement<br />
Self-drilling tip<br />
316L Stainless Steel<br />
Double helical flute<br />
Cylindrical thread design<br />
Benefits<br />
Stable frame construction.<br />
No pre-drilling necessary.<br />
MRI Conditional.<br />
Improved pin/bone interface.<br />
Improved purchase and pull out<br />
resistance.<br />
Pubis symphysis dislocation. Ex-Fix stabilization. Definitive treatment.<br />
24
Hoffmann II MRI - Pin Placement Techniques<br />
The insertion of two K-wires,<br />
one on the medial side and one on<br />
the lateral side of the iliac wing,<br />
provides an accurate targeting method.<br />
They identify both borders of the crest<br />
and plane of the ilium toward the<br />
acetabular roof, helping to ensure safe<br />
and correct placement of the Apex pins<br />
between the two tables of the ilium.<br />
Avoid penetration of the medial cortex<br />
in order to limit pelvic viscera risk.<br />
Due to the supraacetabular bone mass<br />
being significantly thicker a frame<br />
construct mounted on a single Apex<br />
pin offers improved rigidity. Care has<br />
to be taken not to injure the lateral<br />
femoral cutaneous nerve during pin<br />
incretion. The orientation of the Apex<br />
pin can be perpendicular to the body<br />
axis or directed somewhat cephalad,<br />
depending on the location of the<br />
starting point in relation to the greater<br />
sciatic notch.<br />
Illiac Crest Pin Placement.<br />
Ex–Fix<br />
Illiac Crest and Inferior Illiac spine combined pin placement.<br />
Illiac Spine pin placement.<br />
25
Hoffmann Xpress Immediate Care<br />
Features<br />
Light weight Clamps<br />
Pin clamp with integrated post<br />
Removable/reversible Pin Insert<br />
Coupling with ‘Snap-Fit’<br />
mechanism<br />
360º independent rotation on<br />
either side of the Universal<br />
Coupling<br />
MRI conditional<br />
Sterile packed<br />
Benefits<br />
Visualization and access to the fracture<br />
site.<br />
Complete versatility of the frame.<br />
Fast conversion from pin to tube, into<br />
tube to tube coupling.<br />
Allows for a non-slip connection to the<br />
rod or pin.<br />
Unlimited frame configuration options.<br />
No additional risk for the patient in a<br />
MRI environment up to 3.0 Tesla.<br />
Safe and fast for accute trauma<br />
situations.<br />
26
Apex Pin Fixation<br />
Technical Details –<br />
Self-Drilling/Self-Tapping Apex Pin<br />
Pin Design<br />
The self-drilling tip of the Apex Pin<br />
acts like a new, sharp drill bit every<br />
time, and therefore, pre-drilling is<br />
not necessary. Combined with unique<br />
cutting geometry, this one-step<br />
procedure allows the pin to maintain a<br />
reduced insertion temperature below<br />
50°C due to decreased friction.<br />
A double helical flute creates a<br />
homogeneous thread profile that<br />
transports bone chips out of the drill<br />
hole for improved pin/bone interface.<br />
Ex–Fix<br />
The U-shaped thread maximizes contact<br />
with the bone and controls stress<br />
distribution on the pin/bone interface<br />
by optimizing radial tension.<br />
The highly advanced cutting geometry<br />
allows for more precise pin insertion<br />
with reduced insertion time and<br />
temperature for optimal performance.<br />
The cylindrical thread is designed to<br />
improve bone purchase, and pull-out<br />
resistance, and offers the possibility<br />
to backing out the pin without<br />
compromising fixation.<br />
U-shaped thread<br />
Self-drilling tip<br />
27
Asnis III Screw Fixation<br />
The Asnis III Cannulated Screw Systems have been designed to optimize surgical outcomes while simplifying procedures.<br />
The systems incorporate several features intended to enhance screw placement, insertion and removal.<br />
Features<br />
Low Profile Screw Head<br />
Stainless Steel (316LVM)<br />
Shaft and Core Diameter Equal<br />
Reverse Cutting Flute<br />
Self-drilling / self-tapping design<br />
Large diameter Guide Wires<br />
Percutaneous screw placement<br />
Partially threaded<br />
8mm Long screws<br />
Benefits<br />
Reduced potential for soft-tissue irritation.<br />
Improved strength.<br />
Added strength.<br />
To facilitate removal.<br />
Improves operating efficiency.<br />
More precise screw placement.<br />
Less surgical trauma.<br />
Interfragmentary compression.<br />
Improved stability and bilateral fixation.<br />
28
Asnis<br />
Asnis III <strong>Pelvic</strong> Screws<br />
8.0mm Cannulated Screws<br />
25mm Partial Thread<br />
6.5mm Cannulated Screws<br />
20mm Partial Thread<br />
REF. Description<br />
326725 Asnis III Cannulated Screw 8.0 x 125mm<br />
326730 Asnis III Cannulated Screw 8.0 x 130mm<br />
326735 Asnis III Cannulated Screw 8.0 x 135mm<br />
326740 Asnis III Cannulated Screw 8.0 x 140mm<br />
326745 Asnis III Cannulated Screw 8.0 x 145mm<br />
326750 Asnis III Cannulated Screw 8.0 x 150mm<br />
326755 Asnis III Cannulated Screw 8.0 x 155mm<br />
326760 Asnis III Cannulated Screw 8.0 x 160mm<br />
326765 Asnis III Cannulated Screw 8.0 x 165mm<br />
326770 Asnis III Cannulated Screw 8.0 x 170mm<br />
326775 Asnis III Cannulated Screw 8.0 x 175mm<br />
326780 Asnis III Cannulated Screw 8.0 x 180mm<br />
REF. Description<br />
326040 Asnis III Cannulated Screw 6.5 x 40mm<br />
326045 Asnis III Cannulated Screw 6.5 x 45mm<br />
326050 Asnis III Cannulated Screw 6.5 x 50mm<br />
326055 Asnis III Cannulated Screw 6.5 x 55mm<br />
326060 Asnis III Cannulated Screw 6.5 x 60mm<br />
326065 Asnis III Cannulated Screw 6.5 x 65mm<br />
326070 Asnis III Cannulated Screw 6.5 x 70mm<br />
326075 Asnis III Cannulated Screw 6.5 x 75mm<br />
326080 Asnis III Cannulated Screw 6.5 x 80mm<br />
326085 Asnis III Cannulated Screw 6.5 x 85mm<br />
326090 Asnis III Cannulated Screw 6.5 x 90mm<br />
326095 Asnis III Cannulated Screw 6.5 x 95mm<br />
326100 Asnis III Cannulated Screw 6.5 x 100mm<br />
326105 Asnis III Cannulated Screw 6.5 x 105mm<br />
326110 Asnis III Cannulated Screw 6.5 x 110mm<br />
326115 Asnis III Cannulated Screw 6.5 x 115mm<br />
326120 Asnis III Cannulated Screw 6.5 x 120mm<br />
Note:<br />
For Sterile screws add ‘S’ to REF<br />
29
<strong>Acetabular</strong> Articular Fragments Augmentation<br />
with HydroSet<br />
<strong>Fracture</strong>s of the posterior wall of the acetabulum comprise one-fourth to one-third<br />
of all acetabular fractures, representing the most common pattern of fracture of the<br />
acetabulum.*<br />
In fractures with intra-articular comminution and intercalary osteochondral<br />
fragments, one can use HydroSet calcium phosphate cement, an injectable,<br />
sculptable bone substitute to maintain the anatomical reduction of these small<br />
articular fragments before definitive fixation of the overlying posterior-wall<br />
fragment is completed.<br />
It is recommended that the femoral head is used as a template to orientate and to<br />
reduce the different articular fragments.<br />
Features<br />
Excellent Wet-Field Characteristics<br />
Fast Setting<br />
Isothermic<br />
Injectable or Manual Implantation<br />
Osteoconductive<br />
Radiopaque<br />
Benefits<br />
Decreases potential for waiting time.<br />
Limited waiting time.<br />
No damaging heat is released to the<br />
surrounding tissue.<br />
Greater number of options for the<br />
surgeon and the opportunity to sculpt<br />
HydroSet.<br />
A biologically compatible scaffold<br />
that promotes healthy in-growth, later<br />
remodels to the bone.<br />
Impenetrable by X-ray. Visible under<br />
fluroscopy.<br />
* Baumgaertner MR. <strong>Fracture</strong>s of the posterior wall of the acetabulum. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1999;7:54–65.<br />
Aho AJ, Isberg UK, Katevuo VK. <strong>Acetabular</strong> posterior wall fractures: 38 cases followed for 5 years. Acta Orthop Scand. 1986;57:101–5<br />
Letournel E, Judet R. <strong>Fracture</strong>s of the Acetabulum. 2nd ed. Berlin, Germany: Springer Verlag;1993.<br />
30
HydroSet<br />
Ordering Information – MPS Plates<br />
MPS Curved R108 Plate<br />
Stainless Plate Holes Titanium<br />
Steel Length REF<br />
REF mm<br />
425604 58.5 4 4 N/A<br />
425605 74.5 5 4 N/A<br />
425606 90.5 6 4 N/A<br />
425607 106.5 7 N/A<br />
425608 122.5 8 4 N/A<br />
425609 138.5 9 N/A<br />
425610 154.5 10 4 N/A<br />
425611 170.5 11 N/A<br />
425612 186.5 12 4 N/A<br />
425613 202.5 13 N/A<br />
425614 218.5 14 4 N/A<br />
425615 234.5 15 N/A<br />
425616 250.5 16 4 N/A<br />
425618 282.5 18 N/A<br />
425620 314.5 20 N/A<br />
MPS Straight Plate<br />
Stainless Plate Holes Titanium<br />
Steel Length REF<br />
REF mm<br />
425702 26.5 2 N/A<br />
425703 42.5 3 4 N/A<br />
425704 58.5 4 4 N/A<br />
425705 74.5 5 N/A<br />
425706 90.5 6 4 N/A<br />
425707 106.5 7 N/A<br />
425708 122.5 8 4 N/A<br />
425709 138.5 9 N/A<br />
425710 154.5 10 4 N/A<br />
425711 170.5 11 N/A<br />
425712 186.5 12 4 N/A<br />
425713 202.5 13 N/A<br />
425714 218.5 14 4 N/A<br />
425715 234.5 15 N/A<br />
425716 250.5 16 4 N/A<br />
425718 282.5 18 N/A<br />
425720 314.5 20 N/A<br />
MPS Curved R88 Plate<br />
Stainless Plate Holes Titanium<br />
Steel Length REF<br />
REF mm<br />
425654 58.5 4 4 N/A<br />
425655 74.5 5 4 N/A<br />
425656 90.5 6 4 N/A<br />
425657 106.5 7 N/A<br />
425658 122.5 8 4 N/A<br />
425659 138.5 9 N/A<br />
425660 154.5 10 4 N/A<br />
425661 170.5 11 N/A<br />
425662 186.5 12 4 N/A<br />
425663 202.5 13 N/A<br />
425664 218.5 14 4 N/A<br />
425665 234.5 15 N/A<br />
425666 250.5 16 4 N/A<br />
425668 282.5 18 N/A<br />
425670 314.5 20 N/A<br />
MPS Flex Plate (annealed)<br />
Stainless Plate Holes Titanium<br />
Steel Length REF<br />
REF mm<br />
425754 46.5 4 4 N/A<br />
425755 58.5 5 N/A<br />
425756 70.5 6 4 N/A<br />
425757 82.5 7 N/A<br />
425758 94.5 8 4 N/A<br />
425759 106.5 9 N/A<br />
425760 118.5 10 4 N/A<br />
425761 130.5 11 N/A<br />
425762 142.5 12 4 N/A<br />
425763 154.5 13 N/A<br />
425764 166.5 14 4 N/A<br />
425765 178.5 15 N/A<br />
425766 190.5 16 4 N/A<br />
425767 202.5 17 N/A<br />
425768 214.5 18 4 N/A<br />
425770 238.5 20 N/A<br />
425772 262.5 22 N/A<br />
MPS Symphysis Plate, R75<br />
Stainless Plate Holes Titanium<br />
Steel Length REF<br />
REF mm<br />
425794 58.5 4 4 N/A<br />
425796 90.5 6 4 N/A<br />
31<br />
4 Recommended set item
Ordering Information – MPS Screws<br />
3.5mm Cortical Screw, Self–Tapping<br />
Stainless Screw Titanium<br />
Steel Length REF<br />
REF<br />
mm<br />
338610 10 N/A<br />
338612 12 4 N/A<br />
338614 14 4 N/A<br />
338616 16 4 N/A<br />
338618 18 4 N/A<br />
338620 20 4 N/A<br />
338622 22 4 N/A<br />
338624 24 4 N/A<br />
338626 26 4 N/A<br />
338628 28 4 N/A<br />
338630 30 4 N/A<br />
338632 32 4 N/A<br />
338634 34 4 N/A<br />
338636 36 4 N/A<br />
338638 38 4 N/A<br />
338640 40 4 N/A<br />
338642 42 N/A<br />
338644 44 N/A<br />
338645 45 4 N/A<br />
338646 46 N/A<br />
338648 48 N/A<br />
338650 50 4 N/A<br />
338655 55 4 N/A<br />
338660 60 4 N/A<br />
338665 65 4 N/A<br />
338670 70 4 N/A<br />
338675 75 4 N/A<br />
338680 80 4 N/A<br />
338685 85 4 N/A<br />
338690 90 4 N/A<br />
338695 95 4 N/A<br />
338700 100 4 N/A<br />
338705 105 4 N/A<br />
338710 110 4 N/A<br />
338715 115 N/A<br />
338720 120 N/A<br />
4.5mm Cortical Screw, Self-Tapping<br />
Stainless Screw Titanium<br />
Steel Length REF<br />
REF<br />
mm<br />
340614 14 4 N/A<br />
340616 16 4 N/A<br />
340618 18 4 N/A<br />
340620 20 4 N/A<br />
340622 22 4 N/A<br />
340624 24 4 N/A<br />
340626 26 4 N/A<br />
340628 28 4 N/A<br />
340630 30 4 N/A<br />
340632 32 4 N/A<br />
340634 34 4 N/A<br />
340636 36 4 N/A<br />
340638 38 4 N/A<br />
340640 40 4 N/A<br />
340642 42 4 N/A<br />
340644 44 4 N/A<br />
340646 46 4 N/A<br />
340648 48 4 N/A<br />
340650 50 4 N/A<br />
340652 52 4 N/A<br />
340654 54 4 N/A<br />
340655 55 N/A<br />
340656 56 4 N/A<br />
340658 58 4 N/A<br />
340660 60 4 N/A<br />
340662 62 N/A<br />
340664 64 N/A<br />
340665 65 4 N/A<br />
340666 66 N/A<br />
340668 68 N/A<br />
340670 70 4 N/A<br />
340672 72 N/A<br />
340675 75 4 N/A<br />
340676 76 N/A<br />
340680 80 4 N/A<br />
340685 85 4 N/A<br />
340690 90 4 N/A<br />
340695 95 4 N/A<br />
340700 100 4 N/A<br />
340705 105 4 N/A<br />
340710 110 4 N/A<br />
340715 115 4 N/A<br />
340720 120 4 N/A<br />
340725 125 N/A<br />
340730 130 N/A<br />
340735 135 N/A<br />
340740 140 N/A<br />
340745 145 N/A<br />
340750 150 N/A<br />
32<br />
4 Recommended set item
Ordering Information – MPS Screws<br />
6.5mm CANCELLOUS Screw, 16mm Thread<br />
Stainless Screw Titanium<br />
Steel Length REF<br />
REF<br />
mm<br />
341030 30 N/A<br />
341035 35 N/A<br />
341040 40 N/A<br />
341045 45 N/A<br />
341050 50 4 N/A<br />
341055 55 4 N/A<br />
341060 60 4 N/A<br />
341065 65 4 N/A<br />
341070 70 4 N/A<br />
341075 75 4 N/A<br />
341080 80 4 N/A<br />
341085 85 4 N/A<br />
341090 90 4 N/A<br />
341095 95 4 N/A<br />
341100 100 4 N/A<br />
341105 105 4 N/A<br />
341110 110 4 N/A<br />
341115 115 4 N/A<br />
341120 120 4 N/A<br />
341125 125 4 N/A<br />
341130 130 4 N/A<br />
341135 135 N/A<br />
341140 140 N/A<br />
341145 145 N/A<br />
341150 150 N/A<br />
6.5mm CANCELLOUS Screw, 32mm Thread<br />
Stainless Screw Titanium<br />
Steel Length REF<br />
REF<br />
mm<br />
342045 45 N/A<br />
342050 50 4 N/A<br />
342055 55 4 N/A<br />
342060 60 4 N/A<br />
342065 65 4 N/A<br />
342070 70 4 N/A<br />
342075 75 4 N/A<br />
342080 80 4 N/A<br />
342085 85 4 N/A<br />
342090 90 4 N/A<br />
342095 95 4 N/A<br />
342100 100 4 N/A<br />
342105 105 4 N/A<br />
342110 110 4 N/A<br />
342115 115 4 N/A<br />
342120 120 4 N/A<br />
342125 125 4 N/A<br />
342130 130 4 N/A<br />
342135 135 N/A<br />
342140 140 N/A<br />
342145 145 N/A<br />
342150 150 N/A<br />
Washer<br />
Stainless Diameter Thickness Titanium<br />
Steel mm mm REF<br />
REF<br />
390016 13.0 4 1.5 N/A<br />
390019 9.0 4 1.0 N/A<br />
For the full range of standard non-self-tapping screws,<br />
please refer to the <strong>Stryker</strong> Osteosynthesis Product Catalog<br />
33<br />
4 Recommended set item
Ordering Information – MPS Instruments<br />
REF<br />
Description<br />
REF<br />
Description<br />
700351 4 Calibrated Drill Bit ø2.5mm x<br />
180mm, AO Fitting<br />
700355 4 Calibrated Drill Bit ø2.5mm x<br />
230mm, AO Fitting<br />
700353 4 Drill Bit ø3.5mm x 180mm,<br />
AO Fitting<br />
700356 4 Calibrated Drill Bit ø3.2mm x<br />
180mm, AO Fitting<br />
700357 4 Calibrated Drill Bit ø3.2mm x<br />
230mm, AO Fitting<br />
700354 4 Drill Bit ø4.5mm x 180mm,<br />
AO Fitting<br />
702804 4 Tap ø3.5mm x 180mm,<br />
AO Fitting<br />
702806 4 Tap ø4.5mm x 180mm,<br />
AO Fitting<br />
702807 4 Tap ø6.5mm x 180mm,<br />
AO Fitting<br />
702811 4 Countersink ø6.0mm x<br />
100mm,AO Fitting<br />
702812 4 Countersink ø8.0mm x<br />
100mm,AO Fitting<br />
702842 4 Screwdriver Hex 2.5mm,<br />
L280mm<br />
702843 4 Screwdriver Hex 3.5mm,<br />
L300mm<br />
702851 4 Screwdriver Hex 2.5mm,<br />
L165mm, AO Fitting<br />
702853 4 Screwdriver Hex 3.5mm,<br />
L165mm, AO Fitting<br />
702861 4 Screwdriver Holding Sleeve for<br />
Screws ø3.5mm<br />
702862 4 Screwdriver Holding Sleeve for<br />
Screws ø4.5/6.5mm<br />
702417 4 Double Drill Guide ø3.2/4.5mm<br />
702418 4 Double Drill Guide ø2.5/3.5mm<br />
702876 4 Depth Gauge 0-110mm,<br />
for Screws ø2.7/3.5/4.0mm,<br />
Titanium<br />
702877 4 Depth Gauge 0-150mm, for<br />
Screws ø4.5/6.5mm, Titanium<br />
702911 4 Straight Ball Spike<br />
702912 4 Straight Ball Spike, AO Fitting<br />
702923 4 Spiked Disk<br />
702427 4 T-handle small, AO Quick<br />
Coupling<br />
702428 4 Small Teardrop-Handle,<br />
AO Quick Coupling<br />
702429 4 Large Teardrop-Handle,<br />
AO Quick Coupling<br />
702915 4 Small Sciatic Nerve Retractor<br />
702916 4 Large Sciatic Nerve Retractor<br />
390083 4 Reduction Pin ø5.0mm L150mm,<br />
AO Fitting<br />
390084 4 Reduction Pin ø5.0mm L180mm,<br />
AO Fitting<br />
900106 4 Screw Forceps<br />
710312 4 Template MPS Flex plate, 8 H<br />
710313 4 Template MPS Flex plate, 18 H<br />
710315 4 Template MPS Straight plate, 8 H<br />
710316 4 Template MPS Straight plate, 18 H<br />
710318 4 Template MPS Curved R108 plate, 8 H<br />
710319 4 Template MPS Curved R108 plate, 18 H<br />
710321 4 Template MPS Curved R88 plate, 8 H<br />
710322 4 Template MPS Curved R88 plate, 18 H<br />
702902 4 Bending Iron for <strong>Pelvic</strong> plates<br />
702903 4 Bending Plier<br />
702921 4 Small Repositioning Forceps,<br />
type Matta<br />
702922 4 Large Repositioning Forceps,<br />
type Matta<br />
702924 4 Repositioning Forceps for Screws<br />
ø4.5mm<br />
702925 4 Repositioning Forceps for Screws<br />
ø3.5mm, Right<br />
702947 4 Repositioning Forceps for Screws<br />
ø3.5mm, Left<br />
702926 4 Small Reduction Forceps with Points<br />
L130mm<br />
702927 4 Large Reduction Forceps with Points<br />
L200mm<br />
702928 4 Faraboef Forceps L190mm<br />
702929 4 Faraboef Forceps L250mm<br />
702930 4 Repositioning Forceps, 2x1 Jaws<br />
702948 4 Repositioning Forceps, 1x1 Jaws<br />
702932 4 Repositioning Forceps with Serrated<br />
Jaws L140mm<br />
700641 4 Modified Verbrugge Forceps<br />
700647 4 Curved Chisel<br />
Optional Instruments<br />
390086 Reduction Pin ø6.0mm x 150mm,<br />
AO Fitting<br />
390087 Reduction Pin ø6.0mm x 180mm,<br />
AO Fitting<br />
700367 Large T-Handle, AO Quick Coupling<br />
702845 Screwdriver Hex. 2.5mm, L280, with<br />
Canevasit Handle<br />
702846 Screwdriver Hex. 3.5mm, L300,<br />
with Canevasit Handle<br />
702847 Straight Ball Spike L300mm,<br />
with Canevasit Handle<br />
702848 Canevasit Handle Small,<br />
AO Coupling<br />
702849 Canevasit Handle Large,<br />
AO Coupling<br />
710311 Template MPS Flex plate, 5 H<br />
710314 Template MPS Straight plate, 5 H<br />
710317 Template MPS Curved R108 plate, 5 H<br />
710320 Template MPS Curved R88 plate, 5 H<br />
34<br />
4 Recommended set item
Ordering Information – MPS Cases and Trays<br />
REF<br />
Description<br />
REF<br />
Description<br />
901557 4 Plastic Base<br />
(Implant Case Plates)<br />
901557 4 Plastic Base<br />
(Implant Case Screws)<br />
901686 4 Screw Rack with Lids<br />
(Implant Case Screws)<br />
901591 Metal Base Optional<br />
(Implant Case Plates)<br />
901591 Metal Base Optional<br />
(Implant Case Screws)<br />
901618 4 Plastic Base<br />
(Basic Instruments)<br />
901681 4 Plastic Lid<br />
(Implant Case Plates)<br />
901619 Metal Base Optional<br />
(Basic Instruments)<br />
901682 4 Tray Insert<br />
(Implant Case Plates)<br />
901687 4 Plastic Lid<br />
(Basic Instruments)<br />
901683 4 Rack with Lid # 1<br />
(Implant Case Plates)<br />
901688 4 Upper Tray Insert<br />
(Basic Instruments)<br />
901684 4 Rack with Lid # 2<br />
(Implant Case Plates)<br />
901689 4 Lower Tray Insert<br />
(Basic Instruments)<br />
901685 4 Plastic Lid<br />
(Implant Case Screws)<br />
901690 4 Plastic Base<br />
(Reduction Instruments)<br />
901691 4 Plastic Lid<br />
35<br />
4 Recommended set item
Ordering Information – Hoffmann II MRI Components<br />
REF Description<br />
Hoffmann II MRI Components<br />
4921-2-020 Five-Hole Pin Clamp for ø4, ø5, and ø6mm pins<br />
4921-2-060 10-Hole Pin Clamp for ø4, ø5, and ø6mm pins<br />
4921-2-080 <strong>Pelvic</strong> Clamp for ø4, ø5, and ø6mm pins<br />
4921-1-010 Rod to Rod Coupling for ø8mm rods or posts<br />
4921-1-020 Pin to Rod Coupling for ø4-5mm pins/ø8mm rods or posts<br />
4921-1-030 Inverted Pin to Rod Coupling for ø8mm rods or posts/ø4-5mm pins<br />
4921-2-140 30° Angled Post ø8mm<br />
4921-2-120 Straight Post ø8mm<br />
ø8mm Rods<br />
5028-8-065 Carbon Connecting Rod 65mm<br />
5028-8-100 Carbon Connecting Rod 100mm<br />
5028-8-150 Carbon Connecting Rod 150mm<br />
5028-8-200 Carbon Connecting Rod 200mm<br />
5028-8-250 Carbon Connecting Rod 250mm<br />
5028-8-300 Carbon Connecting Rod 300mm<br />
5028-8-350 Carbon Connecting Rod 350mm<br />
5028-8-400 Carbon Connecting Rod 400mm<br />
5028-8-450 Carbon Connecting Rod 450mm<br />
5028-8-500 Carbon Connecting Rod 500mm<br />
174mm (L)<br />
5028-7-030 Semi-Circular Carbon Rod 174mm (L)<br />
36
Ordering Information – Hoffmann II MRI<br />
Instruments<br />
REF<br />
Description<br />
Hoffmann II Instruments for MRI System (not for use in the MRI suite)<br />
4920-9-010 Stabilization/Reduction Wrench<br />
4920-9-020 Thumbwheel<br />
4920-9-030 7mm T-Wrench/ø5-6mm Pin Inserter<br />
4920-9-036 7mm Spanner Wrench<br />
4921-9-984 Storage Case Lid<br />
4921-9-983 Storage Case Upper Insert<br />
4921-9-982 Storage Case Lower Insert<br />
4921-9-981 Storage Case Base<br />
37
Ordering Information – Hoffmann<br />
REF<br />
Description<br />
Hoffmann Xpress Components<br />
4980-1-010S Universal Coupling Ø15/15mm 4-5/15mm<br />
For Tubes and Curved Rod<br />
15mm Ø, Pins 4mm, 5mm<br />
and 6mm cancellous<br />
(shaft Ø5mm)<br />
4980-2-020S 5 Pin Clamp 2 Posts<br />
For Pins Ø4mm, 5mm and<br />
6mm and to connect with<br />
Universal Coupling<br />
4980-2-010S 5 Pin Clamp 1 Post<br />
For Ø4, Ø5 and Ø6mm pins<br />
REF Description Length mm<br />
Hoffmann Xpress Components<br />
4980-3-150S Aluminium Tube<br />
4980-3-210S Aluminium Tube<br />
4980-3-260S Aluminium Tube<br />
4980-3-330S Aluminium Tube<br />
4980-3-440S Aluminium Tube<br />
4980-3-500S Aluminium Tube<br />
150mm<br />
210mm<br />
260mm<br />
330mm<br />
440mm<br />
500mm<br />
4980-3-020S Semi Circular Curved Tube Ø15mm 160 x 235<br />
38
Ordering Information – Apex <strong>Pelvic</strong> Pins<br />
Self Drilling/Self Tapping<br />
Stainless Steel Diameter Total Thread<br />
REF mm Length Length<br />
Thread/Shaft mm mm<br />
5018-6-150 5.0 150 50<br />
5018-3-180 5.0 180 35<br />
5018-6-180 5.0 180 50<br />
5018-8-180 5.0 180 60<br />
5018-5-200 5.0 200 50<br />
5018-6-200 5.0 200 60<br />
5018-5-250 5.0 250 50<br />
5018-7-250 5.0 250 70<br />
5021-7-150 6.0 150 50<br />
5021-6-180 6.0 180 60<br />
5021-8-200 6.0 200 70<br />
5021-8-250 6.0 250 80<br />
Cancellous<br />
Stainless Steel Diameter Total Thread<br />
REF mm Length Length<br />
Thread/Shaft mm mm<br />
5015-3-120 6.0/5.0 120 35<br />
5015-4-150 6.0/5.0 150 40<br />
5015-5-150 6.0/5.0 150 50<br />
5015-6-180 6.0/5.0 180 60<br />
5015-7-250 6.0/5.0 250 70<br />
39
Ordering Information - Asnis III<br />
6.5mm Implants - 20mm Thread Length<br />
Stainless Steel Diameter Total Titanium<br />
REF mm Length REF<br />
mm<br />
326040 6.5 40 602640<br />
326045 6.5 45 602645<br />
326050 6.5 50 602650<br />
326055 6.5 55 602655<br />
326060 6.5 60 602660<br />
326065 6.5 65 602665<br />
326070 6.5 70 602670<br />
326075 6.5 75 602675<br />
326080 6.5 80 602680<br />
326085 6.5 85 602685<br />
326090 6.5 90 602690<br />
326095 6.5 95 602695<br />
326100 6.5 100 602700<br />
326105 6.5 105 602705<br />
326110 6.5 110 602710<br />
326115 6.5 115 602715<br />
326120 6.5 120 602720<br />
6.5mm Implants - 40mm Thread Length<br />
Stainless Steel Diameter Total Titanium<br />
REF mm Length REF<br />
mm<br />
326255 6.5 55 602855<br />
326260 6.5 60 602860<br />
326265 6.5 65 602865<br />
326270 6.5 70 602870<br />
326275 6.5 75 602875<br />
326280 6.5 80 602880<br />
326285 6.5 85 602885<br />
326290 6.5 90 602890<br />
326295 6.5 95 602895<br />
326300 6.5 100 602900<br />
326305 6.5 105 602905<br />
326310 6.5 110 602910<br />
326315 6.5 115 602915<br />
326320 6.5 120 602920<br />
326325 6.5 125 602925<br />
326330 6.5 130 602930<br />
8.0mm Implants - 25mm Thread LENGTH<br />
Stainless Steel Diameter Total Titanium<br />
REF mm Length REF<br />
mm<br />
326725 8.0 125 N/A<br />
326730 8.0 130 N/A<br />
326735 8.0 135 N/A<br />
326740 8.0 140 N/A<br />
326745 8.0 145 N/A<br />
326750 8.0 150 N/A<br />
326755 8.0 155 N/A<br />
326760 8.0 160 N/A<br />
326765 8.0 165 N/A<br />
326770 8.0 170 N/A<br />
326775 8.0 175 N/A<br />
326780 8.0 180 N/A<br />
Instruments and Case<br />
*Optional<br />
Note:<br />
For Sterile screws add ‘S’ to REF<br />
702462S Asnis III Threaded Guide Wire ø3.2 x 300mm<br />
*702463 Asnis III Guide Wire without Thread ø3.2 x 300mm<br />
*702627 Asnis III Guide Wire with Calibrations and<br />
Quick Release Fitting ø3.2 x 300mm<br />
702626 Asnis III 6.5/8.0mm,Drill Bit ø3.2 x 300mm<br />
702495 Asnis III 8.0mm Direct Measuring Gauge for ø3.2mm Guide Wires<br />
702629 Asnis III 6.5/8.0mm,Cannulated Screwdriver with<br />
Elastosil Handle – Hex 5.0mm<br />
901596 Asnis III 8.0mm Plastic Base with Lid<br />
40
Ordering Information – HydroSet Injectable HA<br />
Bone Substitute<br />
REF<br />
Description<br />
397003 3cc HydroSet Bone Substitute<br />
397005 5cc HydroSet Bone Substitute<br />
397010 10cc HydroSet Bone Substitute<br />
397015 15cc HydroSet Bone Substitute<br />
41
Notes<br />
42
Notes<br />
43
<strong>Stryker</strong> Trauma AG<br />
Bohnackerweg 1<br />
CH-2545 Selzach<br />
Switzerland<br />
www.osteosynthesis.stryker.com<br />
This document is intended solely for the use of healthcare professionals. A surgeon must always rely on his or her own<br />
professional clinical judgment when deciding whether to use a particular product when treating a particular patient.<br />
<strong>Stryker</strong> does not dispense medical advice and recommends that surgeons be trained in the use of any particular product<br />
before using it in surgery. The information presented in this brochure is intended to demonstrate a <strong>Stryker</strong> product.<br />
Always refer to the package insert, product label and/or user instructions including the instructions for Cleaning and<br />
Sterilization (if applicable) before using any <strong>Stryker</strong> products. Products may not be available in all markets.<br />
Product availability is subject to the regulatory or medical practices that govern individual markets.<br />
Please contact your <strong>Stryker</strong> representative if you have questions about the availability of <strong>Stryker</strong> products in your area.<br />
<strong>Stryker</strong> Corporation or its divisions or other corporate affiliated entities own, use or have applied for the following<br />
trademarks or service marks: <strong>Stryker</strong>, Apex, Hoffmann Xpress, Hoffmann II, Asnis, Hydroset, Matta.<br />
All other trademarks are trademarks of their respective owners or holders.<br />
The products listed above are CE marked.<br />
Literature Number: 982350<br />
LOT A3309<br />
REF NO.<br />
982350<br />
Copyright © 2009 <strong>Stryker</strong><br />
44<br />
A3309