Cereal Rust Diseases - Plant Management Network
Cereal Rust Diseases - Plant Management Network
Cereal Rust Diseases - Plant Management Network
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
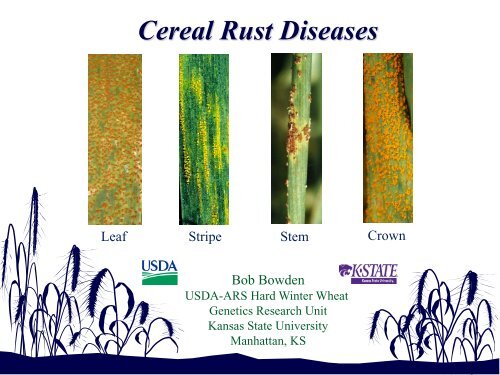
<strong>Cereal</strong> <strong>Rust</strong> <strong>Diseases</strong><br />
Leaf<br />
Stripe<br />
Stem<br />
Crown<br />
Bob Bowden<br />
USDA-ARS Hard Winter Wheat<br />
Genetics Research Unit<br />
Kansas State University<br />
Manhattan, KS
Castroville <strong>Rust</strong> Nursery
Ug99 Stem <strong>Rust</strong> in the Headlines
Percent of Acres<br />
Wheat Leaf <strong>Rust</strong>: Boom & Bust<br />
Karl Wheat Cultivar Succumbs to Leaf <strong>Rust</strong><br />
25<br />
20<br />
15<br />
10<br />
5<br />
0<br />
1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000<br />
Year
% Loss<br />
Stripe <strong>Rust</strong> Losses - Kansas<br />
12<br />
10<br />
8<br />
6<br />
4<br />
2<br />
0<br />
Year<br />
Jon Appel, Erick DeWolf, Bill Bockus
Oat Crown <strong>Rust</strong><br />
Eric Jackson, ARS, Aberdeen, ID
Erick DeWolf, 2011
Disease Resistance<br />
Highly Resistant<br />
Highly Susceptible<br />
Matthew Rouse
How Many Resistance Genes?<br />
• Lr1 to Lr68 for wheat leaf rust<br />
• Yr1 to Yr49 for wheat stripe rust<br />
• Sr1 to Sr53 for wheat stem rust<br />
• Pc-1 to Pc-96 for oat crown rust
Wheat Stem <strong>Rust</strong> Resistance Loci<br />
Sr1A.1R<br />
SrTm4<br />
1A 2A 3A 4A 5A 6A 7A<br />
Sr31<br />
Sr14<br />
Sr39<br />
Sr19<br />
Sr23<br />
Sr10<br />
Sr40<br />
Sr36 Sr20<br />
SrGabo56<br />
Sr9 SrWeb<br />
Sr28<br />
Sr16<br />
Sr32<br />
1B 2B 3B 4B 5B 6B 7B<br />
SrR<br />
Sr33<br />
Sr45<br />
Sr18<br />
Sr38<br />
Sr34<br />
Sr21<br />
Sr6<br />
Sr27<br />
Sr35<br />
Sr2<br />
Sr12<br />
SrB<br />
Sr24<br />
SrSha7<br />
Sr5<br />
Sr42<br />
SrCad<br />
1D 2D 3D 4D 5D 6D 7D<br />
Sr7<br />
Sr37<br />
SrNing<br />
Sr41<br />
Sr30<br />
SrC<br />
Sr8<br />
Sr26<br />
Sr13<br />
Sr11<br />
Sr29<br />
Sr22<br />
Sr15<br />
Sr17<br />
Lr34<br />
Sr44<br />
Sr43<br />
Sr25<br />
Mike Pumphrey, WSU
Stakman Infection Types<br />
Leonard and Szabo
Adult IT Rating Scale<br />
Xianming Chen
Race Specificity<br />
Isolate 1 Isolate 2
How Many Races?<br />
• Dozens for wheat leaf rust<br />
• Dozens for wheat stripe rust<br />
• Few (mostly just QFCSC) for wheat<br />
stem rust<br />
• Huge number for oat crown rust
Race Identification
Where do new races come from?
Yue Jin, <strong>Cereal</strong> Disease Lab<br />
Life Cycle of<br />
Puccinia graminis<br />
Macrocyclic, heteroecious
Buckthorn Nursery for Oat Crown <strong>Rust</strong><br />
<strong>Cereal</strong> Disease Lab
Xianming Chen, USDA
Long Distance Migration<br />
The Puccinia Pathway<br />
<strong>Cereal</strong> Disease Lab
Leaf<br />
Stripe<br />
Stem<br />
Crown<br />
Race Diversity Med Med Low* High<br />
Genotypic Diversity Low Low Low* High<br />
Sexual Recombination No No? No* Yes<br />
(spring oat region)<br />
Annual Bottlenecks No Yes* Yes* No<br />
R-gene durability Low-Med Low-Med High* Low<br />
* Except in PNW
Mean Virulence of P. coronata f.sp.<br />
avenae in Spring Oat Region<br />
Virulence in Oat Crown <strong>Rust</strong> (Puccinia coronata f. sp. avenae) in the United States from 2006 through 2009.<br />
M. L. Carson. 2011. <strong>Plant</strong> Disease 95:1528-1534
Cytogenetics to Reduce Linkage Drag<br />
Bernd Friebe, KSU
Major Gene Strategies<br />
• Use only gene combinations (pyramids).<br />
– Prob(virulence to one gene) = 10 -6<br />
– Prob(virulence to two genes) = 10 -12<br />
– Prob(virulence to three genes) = 10 -18<br />
– Prob(virulence to four genes) = 10 -24<br />
– Must have control of all the genes<br />
• Get smarter about finding durable combinations<br />
– Negative associations between virulences<br />
– Clone the effectors and targets and find and<br />
eliminate redundancies
Resistance Types<br />
• Major gene<br />
• Seedling or all-stage<br />
• Hypersensitive<br />
• Race-specific<br />
• Qualitative<br />
• Non-durable resistance<br />
• R-gene<br />
• NBS-LRR gene<br />
• Minor gene resistance<br />
• Adult plant resistance<br />
• Slow rusting resistance<br />
• Race-nonspecific<br />
• Quantitative resistance<br />
• Durable resistance<br />
• QTL<br />
• Non-NBS-LRR
Slow <strong>Rust</strong>ing Genes Identified<br />
• Lr34/Yr18 (7DS)<br />
• Lr46/Yr29 (1BL)<br />
• Lr67/Yr46 (4DL)<br />
• Lr68 (7BL)<br />
• Sr2/Yr30 (3BS)
Lr34 Phenotype<br />
Photo by Bob Bowden<br />
•Lr34/Yr18 was cloned and turned out to be ABC transporter<br />
(Krattinger et al. 2009)
Roelfs F2007 Mexican Variety<br />
Photo by Bob Bowden
Genetic basis of durable resistance to rust diseases of<br />
% <strong>Rust</strong><br />
wheat<br />
100<br />
Susceptible<br />
80<br />
60<br />
1 to 2 minor<br />
genes<br />
40<br />
20<br />
0<br />
0 10 20 30 40 50<br />
Days data recorded<br />
2 to 3 minor genes<br />
Munal, Picaflor,<br />
Francolin, Pauraque<br />
4 to 5 minor genes<br />
Kingbird<br />
Ravi Singh, CIMMYT<br />
Relatively few additive genes, each having small to<br />
intermediate effects, required for satisfactory disease control<br />
Near-immunity (trace to 5% severity) can be achieved even<br />
under high disease pressure by combining 4-5 minor genes<br />
with additive effects
Ug99-Resistant Varieties Released or in<br />
Advanced stages of Variety Registration<br />
Singh et al, 2011. Ann Rev Phytopathol
Acknowledgements<br />
• Xianming Chen<br />
• Erick De Wolf<br />
• Bernd Friebe<br />
• Eric Jackson<br />
• Yue Jin<br />
• Jim Kolmer<br />
• Mike Pumphrey<br />
• Matthew Rouse<br />
• Ravi Singh