Global Tuberculosis Report -- 2012.pdf
Global Tuberculosis Report -- 2012.pdf
Global Tuberculosis Report -- 2012.pdf
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
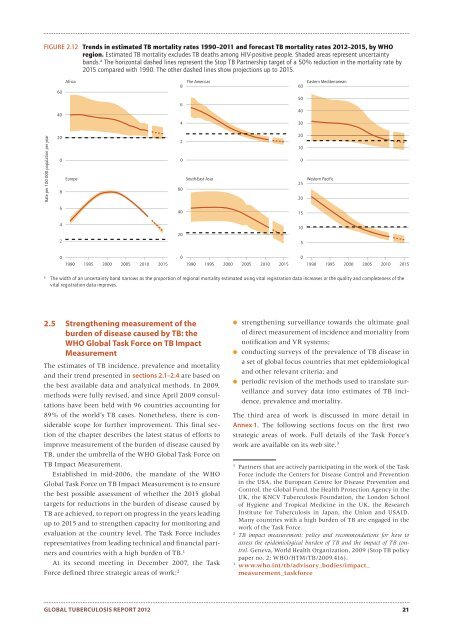
FIGURE 2.12 Trends in estimated TB mortality rates 1990–2011 and forecast TB mortality rates 2012–2015, by WHO<br />
region. Estimated TB mortality excludes TB deaths among HIV-positive people. Shaded areas represent uncertainty<br />
bands. a The horizontal dashed lines represent the Stop TB Partnership target of a 50% reduction in the mortality rate by<br />
2015 compared with 1990. The other dashed lines show projections up to 2015.<br />
60<br />
40<br />
Africa<br />
8<br />
6<br />
The Americas<br />
60<br />
50<br />
40<br />
Eastern Mediterranean<br />
4<br />
30<br />
Rate per 100 000 population per year<br />
20<br />
0<br />
8<br />
Europe<br />
2<br />
0<br />
60<br />
South-East Asia<br />
20<br />
10<br />
0<br />
25<br />
20<br />
Western Pacific<br />
6<br />
40<br />
15<br />
4<br />
2<br />
20<br />
10<br />
5<br />
0<br />
0<br />
1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 2015 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 2015 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 2015<br />
0<br />
a<br />
The width of an uncertainty band narrows as the proportion of regional mortality estimated using vital registration data increases or the quality and completeness of the<br />
vital registration data improves.<br />
2.5 Strengthening measurement of the<br />
burden of disease caused by TB: the<br />
WHO <strong>Global</strong> Task Force on TB Impact<br />
Measurement<br />
The estimates of TB incidence, prevalence and mortality<br />
and their trend presented in sections 2.1–2.4 are based on<br />
the best available data and analytical methods. In 2009,<br />
methods were fully revised, and since April 2009 consultations<br />
have been held with 96 countries accounting for<br />
89% of the world’s TB cases. Nonetheless, there is considerable<br />
scope for further improvement. This final section<br />
of the chapter describes the latest status of efforts to<br />
improve measurement of the burden of disease caused by<br />
TB, under the umbrella of the WHO <strong>Global</strong> Task Force on<br />
TB Impact Measurement.<br />
Established in mid-2006, the mandate of the WHO<br />
<strong>Global</strong> Task Force on TB Impact Measurement is to ensure<br />
the best possible assessment of whether the 2015 global<br />
targets for reductions in the burden of disease caused by<br />
TB are achieved, to report on progress in the years leading<br />
up to 2015 and to strengthen capacity for monitoring and<br />
evaluation at the country level. The Task Force includes<br />
representatives from leading technical and financial partners<br />
and countries with a high burden of TB. 1<br />
At its second meeting in December 2007, the Task<br />
Force defined three strategic areas of work: 2<br />
● strengthening surveillance towards the ultimate goal<br />
of direct measurement of incidence and mortality from<br />
notification and VR systems;<br />
● conducting surveys of the prevalence of TB disease in<br />
a set of global focus countries that met epidemiological<br />
and other relevant criteria; and<br />
● periodic revision of the methods used to translate surveillance<br />
and survey data into estimates of TB incidence,<br />
prevalence and mortality.<br />
The third area of work is discussed in more detail in<br />
Annex 1. The following sections focus on the first two<br />
strategic areas of work. Full details of the Task Force’s<br />
work are available on its web site. 3<br />
1<br />
Partners that are actively participating in the work of the Task<br />
Force include the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention<br />
in the USA, the European Centre for Disease Prevention and<br />
Control, the <strong>Global</strong> Fund, the Health Protection Agency in the<br />
UK, the KNCV <strong>Tuberculosis</strong> Foundation, the London School<br />
of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine in the UK, the Research<br />
Institute for <strong>Tuberculosis</strong> in Japan, the Union and USAID.<br />
Many countries with a high burden of TB are engaged in the<br />
work of the Task Force.<br />
2<br />
TB impact measurement: policy and recommendations for how to<br />
assess the epidemiological burden of TB and the impact of TB control.<br />
Geneva, World Health Organization, 2009 (Stop TB policy<br />
paper no. 2; WHO/HTM/TB/2009.416).<br />
3<br />
www.who.int/tb/advisory_bodies/impact_<br />
measurement_taskforce<br />
GLOBAL TUBERCULOSIS REPORT 2012 21