The Basics of Newtonian Mechanics - the Scientia Review
The Basics of Newtonian Mechanics - the Scientia Review
The Basics of Newtonian Mechanics - the Scientia Review
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
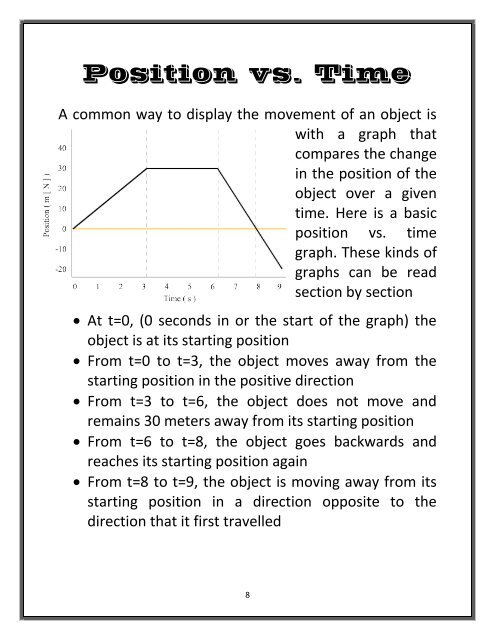
Position vs. Time<br />
A common way to display <strong>the</strong> movement <strong>of</strong> an object is<br />
with a graph that<br />
compares <strong>the</strong> change<br />
in <strong>the</strong> position <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong><br />
object over a given<br />
time. Here is a basic<br />
position vs. time<br />
graph. <strong>The</strong>se kinds <strong>of</strong><br />
graphs can be read<br />
section by section<br />
At t=0, (0 seconds in or <strong>the</strong> start <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> graph) <strong>the</strong><br />
object is at its starting position<br />
From t=0 to t=3, <strong>the</strong> object moves away from <strong>the</strong><br />
starting position in <strong>the</strong> positive direction<br />
From t=3 to t=6, <strong>the</strong> object does not move and<br />
remains 30 meters away from its starting position<br />
From t=6 to t=8, <strong>the</strong> object goes backwards and<br />
reaches its starting position again<br />
From t=8 to t=9, <strong>the</strong> object is moving away from its<br />
starting position in a direction opposite to <strong>the</strong><br />
direction that it first travelled<br />
8