Survey of Blunt Body Dynamic Stability in Supersonic Flow
Survey of Blunt Body Dynamic Stability in Supersonic Flow
Survey of Blunt Body Dynamic Stability in Supersonic Flow
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
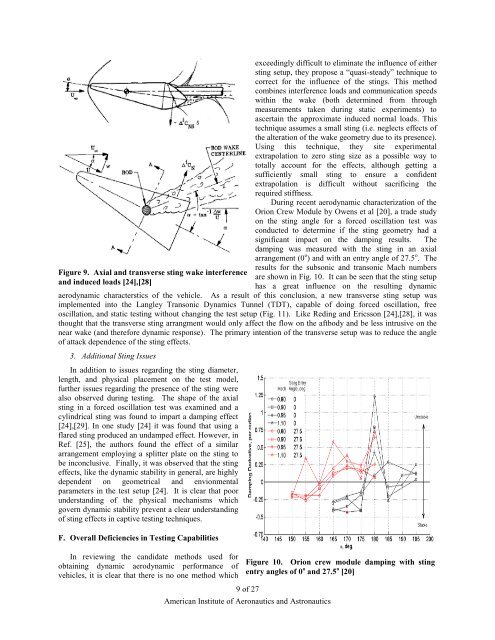
Figure 9. Axial and transverse st<strong>in</strong>g wake <strong>in</strong>terference<br />
and <strong>in</strong>duced loads [24],[28]<br />
9 <strong>of</strong> 27<br />
American Institute <strong>of</strong> Aeronautics and Astronautics<br />
exceed<strong>in</strong>gly difficult to elim<strong>in</strong>ate the <strong>in</strong>fluence <strong>of</strong> either<br />
st<strong>in</strong>g setup, they propose a “quasi-steady” technique to<br />
correct for the <strong>in</strong>fluence <strong>of</strong> the st<strong>in</strong>gs. This method<br />
comb<strong>in</strong>es <strong>in</strong>terference loads and communication speeds<br />
with<strong>in</strong> the wake (both determ<strong>in</strong>ed from through<br />
measurements taken dur<strong>in</strong>g static experiments) to<br />
ascerta<strong>in</strong> the approximate <strong>in</strong>duced normal loads. This<br />
technique assumes a small st<strong>in</strong>g (i.e. neglects effects <strong>of</strong><br />
the alteration <strong>of</strong> the wake geometry due to its presence).<br />
Us<strong>in</strong>g this technique, they site experimental<br />
extrapolation to zero st<strong>in</strong>g size as a possible way to<br />
totally account for the effects, although gett<strong>in</strong>g a<br />
sufficiently small st<strong>in</strong>g to ensure a confident<br />
extrapolation is difficult without sacrific<strong>in</strong>g the<br />
required stiffness.<br />
Dur<strong>in</strong>g recent aerodynamic characterization <strong>of</strong> the<br />
Orion Crew Module by Owens et al [20], a trade study<br />
on the st<strong>in</strong>g angle for a forced oscillation test was<br />
conducted to determ<strong>in</strong>e if the st<strong>in</strong>g geometry had a<br />
significant impact on the damp<strong>in</strong>g results. The<br />
damp<strong>in</strong>g was measured with the st<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> an axial<br />
arrangement (0 o ) and with an entry angle <strong>of</strong> 27.5 o . The<br />
results for the subsonic and transonic Mach numbers<br />
are shown <strong>in</strong> Fig. 10. It can be seen that the st<strong>in</strong>g setup<br />
has a great <strong>in</strong>fluence on the result<strong>in</strong>g dynamic<br />
aerodynamic characterstics <strong>of</strong> the vehicle. As a result <strong>of</strong> this conclusion, a new transverse st<strong>in</strong>g setup was<br />
implemented <strong>in</strong>to the Langley Transonic <strong>Dynamic</strong>s Tunnel (TDT), capable <strong>of</strong> do<strong>in</strong>g forced oscillation, free<br />
oscillation, and static test<strong>in</strong>g without chang<strong>in</strong>g the test setup (Fig. 11). Like Red<strong>in</strong>g and Ericsson [24],[28], it was<br />
thought that the transverse st<strong>in</strong>g arrangment would only affect the flow on the aftbody and be less <strong>in</strong>trusive on the<br />
near wake (and therefore dynamic response). The primary <strong>in</strong>tention <strong>of</strong> the transverse setup was to reduce the angle<br />
<strong>of</strong> attack dependence <strong>of</strong> the st<strong>in</strong>g effects.<br />
3. Additional St<strong>in</strong>g Issues<br />
In addition to issues regard<strong>in</strong>g the st<strong>in</strong>g diameter,<br />
length, and physical placement on the test model,<br />
further issues regard<strong>in</strong>g the presence <strong>of</strong> the st<strong>in</strong>g were<br />
also observed dur<strong>in</strong>g test<strong>in</strong>g. The shape <strong>of</strong> the axial<br />
st<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> a forced oscillation test was exam<strong>in</strong>ed and a<br />
cyl<strong>in</strong>drical st<strong>in</strong>g was found to impart a damp<strong>in</strong>g effect<br />
[24],[29]. In one study [24] it was found that us<strong>in</strong>g a<br />
flared st<strong>in</strong>g produced an undamped effect. However, <strong>in</strong><br />
Ref. [25], the authors found the effect <strong>of</strong> a similar<br />
arrangement employ<strong>in</strong>g a splitter plate on the st<strong>in</strong>g to<br />
be <strong>in</strong>conclusive. F<strong>in</strong>ally, it was observed that the st<strong>in</strong>g<br />
effects, like the dynamic stability <strong>in</strong> general, are highly<br />
dependent on geometrical and envionmental<br />
parameters <strong>in</strong> the test setup [24]. It is clear that poor<br />
understand<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> the physical mechanisms which<br />
govern dynamic stability prevent a clear understand<strong>in</strong>g<br />
<strong>of</strong> st<strong>in</strong>g effects <strong>in</strong> captive test<strong>in</strong>g techniques.<br />
F. Overall Deficiencies <strong>in</strong> Test<strong>in</strong>g Capabilities<br />
In review<strong>in</strong>g the candidate methods used for<br />
obta<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g dynamic aerodynamic performance <strong>of</strong><br />
vehicles, it is clear that there is no one method which<br />
Figure 10. Orion crew module damp<strong>in</strong>g with st<strong>in</strong>g<br />
entry angles <strong>of</strong> 0 o and 27.5 o [20]