Recent Advances in DNA Biosensor - International Frequency ...
Recent Advances in DNA Biosensor - International Frequency ...
Recent Advances in DNA Biosensor - International Frequency ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Sensors & Transducers Journal, Vol. 92, Issue 5, May 2008, pp. 122-133<br />
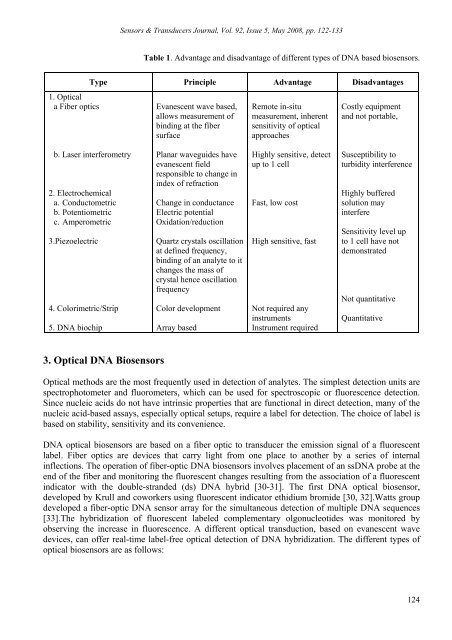
Table 1. Advantage and disadvantage of different types of <strong>DNA</strong> based biosensors.<br />
1. Optical<br />
a Fiber optics<br />
Type Pr<strong>in</strong>ciple Advantage Disadvantages<br />
Evanescent wave based,<br />
allows measurement of<br />
b<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g at the fiber<br />
surface<br />
Remote <strong>in</strong>-situ<br />
measurement, <strong>in</strong>herent<br />
sensitivity of optical<br />
approaches<br />
Costly equipment<br />
and not portable,<br />
b. Laser <strong>in</strong>terferometry<br />
2. Electrochemical<br />
a. Conductometric<br />
b. Potentiometric<br />
c. Amperometric<br />
3.Piezoelectric<br />
4. Colorimetric/Strip<br />
5. <strong>DNA</strong> biochip<br />
Planar waveguides have<br />
evanescent field<br />
responsible to change <strong>in</strong><br />
<strong>in</strong>dex of refraction<br />
Change <strong>in</strong> conductance<br />
Electric potential<br />
Oxidation/reduction<br />
Quartz crystals oscillation<br />
at def<strong>in</strong>ed frequency,<br />
b<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g of an analyte to it<br />
changes the mass of<br />
crystal hence oscillation<br />
frequency<br />
Color development<br />
Array based<br />
Highly sensitive, detect<br />
up to 1 cell<br />
Fast, low cost<br />
High sensitive, fast<br />
Not required any<br />
<strong>in</strong>struments<br />
Instrument required<br />
Susceptibility to<br />
turbidity <strong>in</strong>terference<br />
Highly buffered<br />
solution may<br />
<strong>in</strong>terfere<br />
Sensitivity level up<br />
to 1 cell have not<br />
demonstrated<br />
Not quantitative<br />
Quantitative<br />
3. Optical <strong>DNA</strong> <strong>Biosensor</strong>s<br />
Optical methods are the most frequently used <strong>in</strong> detection of analytes. The simplest detection units are<br />
spectrophotometer and fluorometers, which can be used for spectroscopic or fluorescence detection.<br />
S<strong>in</strong>ce nucleic acids do not have <strong>in</strong>tr<strong>in</strong>sic properties that are functional <strong>in</strong> direct detection, many of the<br />
nucleic acid-based assays, especially optical setups, require a label for detection. The choice of label is<br />
based on stability, sensitivity and its convenience.<br />
<strong>DNA</strong> optical biosensors are based on a fiber optic to transducer the emission signal of a fluorescent<br />
label. Fiber optics are devices that carry light from one place to another by a series of <strong>in</strong>ternal<br />
<strong>in</strong>flections. The operation of fiber-optic <strong>DNA</strong> biosensors <strong>in</strong>volves placement of an ss<strong>DNA</strong> probe at the<br />
end of the fiber and monitor<strong>in</strong>g the fluorescent changes result<strong>in</strong>g from the association of a fluorescent<br />
<strong>in</strong>dicator with the double-stranded (ds) <strong>DNA</strong> hybrid [30-31]. The first <strong>DNA</strong> optical biosensor,<br />
developed by Krull and coworkers us<strong>in</strong>g fluorescent <strong>in</strong>dicator ethidium bromide [30, 32].Watts group<br />
developed a fiber-optic <strong>DNA</strong> sensor array for the simultaneous detection of multiple <strong>DNA</strong> sequences<br />
[33].The hybridization of fluorescent labeled complementary olgonucleotides was monitored by<br />
observ<strong>in</strong>g the <strong>in</strong>crease <strong>in</strong> fluorescence. A different optical transduction, based on evanescent wave<br />
devices, can offer real-time label-free optical detection of <strong>DNA</strong> hybridization. The different types of<br />
optical biosensors are as follows:<br />
124