Guidelines for constructing and maintaining aquaculture ...
Guidelines for constructing and maintaining aquaculture ...
Guidelines for constructing and maintaining aquaculture ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
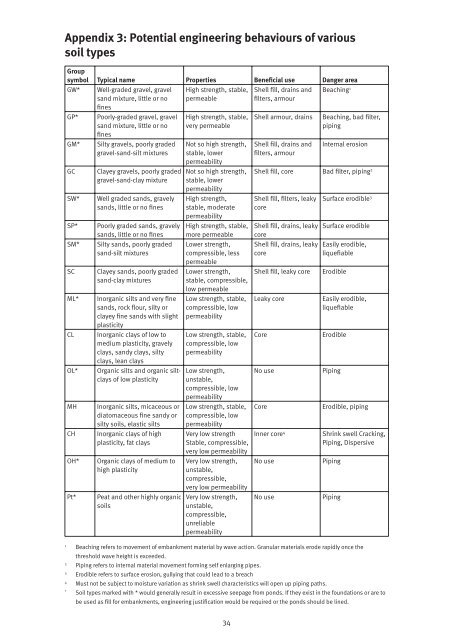
Appendix 3: Potential engineering behaviours of various<br />
soil types<br />
Group<br />
symbol Typical name Properties Beneficial use Danger area<br />
GW*<br />
GP*<br />
GM*<br />
GC<br />
SW*<br />
SP*<br />
SM*<br />
SC<br />
ML*<br />
CL<br />
OL*<br />
MH<br />
CH<br />
OH*<br />
Pt*<br />
Well-graded gravel, gravel<br />
s<strong>and</strong> mixture, little or no<br />
fines<br />
Poorly-graded gravel, gravel<br />
s<strong>and</strong> mixture, little or no<br />
fines<br />
Silty gravels, poorly graded<br />
gravel-s<strong>and</strong>-silt mixtures<br />
Clayey gravels, poorly graded<br />
gravel-s<strong>and</strong>-clay mixture<br />
Well graded s<strong>and</strong>s, gravely<br />
s<strong>and</strong>s, little or no fines<br />
Poorly graded s<strong>and</strong>s, gravely<br />
s<strong>and</strong>s, little or no fines<br />
Silty s<strong>and</strong>s, poorly graded<br />
s<strong>and</strong>-silt mixtures<br />
Clayey s<strong>and</strong>s, poorly graded<br />
s<strong>and</strong>-clay mixtures<br />
Inorganic silts <strong>and</strong> very fine<br />
s<strong>and</strong>s, rock flour, silty or<br />
clayey fine s<strong>and</strong>s with slight<br />
plasticity<br />
Inorganic clays of low to<br />
medium plasticity, gravely<br />
clays, s<strong>and</strong>y clays, silty<br />
clays, lean clays<br />
Organic silts <strong>and</strong> organic siltclays<br />
of low plasticity<br />
Inorganic silts, micaceous or<br />
diatomaceous fine s<strong>and</strong>y or<br />
silty soils, elastic silts<br />
Inorganic clays of high<br />
plasticity, fat clays<br />
Organic clays of medium to<br />
high plasticity<br />
Peat <strong>and</strong> other highly organic<br />
soils<br />
High strength, stable,<br />
permeable<br />
High strength, stable,<br />
very permeable<br />
Not so high strength,<br />
stable, lower<br />
permeability<br />
Not so high strength,<br />
stable, lower<br />
permeability<br />
High strength,<br />
stable, moderate<br />
permeability<br />
High strength, stable,<br />
more permeable<br />
Lower strength,<br />
compressible, less<br />
permeable<br />
Lower strength,<br />
stable, compressible,<br />
low permeable<br />
Low strength, stable,<br />
compressible, low<br />
permeability<br />
Low strength, stable,<br />
compressible, low<br />
permeability<br />
Low strength,<br />
unstable,<br />
compressible, low<br />
permeability<br />
Low strength, stable,<br />
compressible, low<br />
permeability<br />
Very low strength<br />
Stable, compressible,<br />
very low permeability<br />
Very low strength,<br />
unstable,<br />
compressible,<br />
very low permeability<br />
Very low strength,<br />
unstable,<br />
compressible,<br />
unreliable<br />
permeability<br />
Shell fill, drains <strong>and</strong><br />
filters, armour<br />
Shell armour, drains<br />
Shell fill, drains <strong>and</strong><br />
filters, armour<br />
Beaching 1<br />
Beaching, bad filter,<br />
piping<br />
Internal erosion<br />
Shell fill, core Bad filter, piping 2<br />
Shell fill, filters, leaky<br />
core<br />
Shell fill, drains, leaky<br />
core<br />
Shell fill, drains, leaky<br />
core<br />
Shell fill, leaky core<br />
Leaky core<br />
Core<br />
No use<br />
Core<br />
Inner core 4<br />
No use<br />
No use<br />
Surface erodible 3<br />
Surface erodible<br />
Easily erodible,<br />
liquefiable<br />
Erodible<br />
Easily erodible,<br />
liquefiable<br />
Erodible<br />
Piping<br />
Erodible, piping<br />
Shrink swell Cracking,<br />
Piping, Dispersive<br />
Piping<br />
Piping<br />
1<br />
Beaching refers to movement of embankment material by wave action. Granular materials erode rapidly once the<br />
threshold wave height is exceeded.<br />
2<br />
Piping refers to internal material movement <strong>for</strong>ming self enlarging pipes.<br />
3<br />
Erodible refers to surface erosion, gullying that could lead to a breach<br />
4<br />
Must not be subject to moisture variation as shrink swell characteristics will open up piping paths.<br />
*<br />
Soil types marked with * would generally result in excessive seepage from ponds. If they exist in the foundations or are to<br />
be used as fill <strong>for</strong> embankments, engineering justification would be required or the ponds should be lined.<br />
34