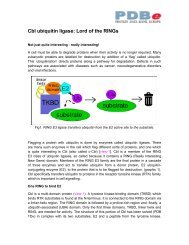
Automatic functional annotation of predicted active sites - European ...
Automatic functional annotation of predicted active sites - European ...
Automatic functional annotation of predicted active sites - European ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Side chain interaction model.<br />
The determination <strong>of</strong> residue interactions requires a<br />
transformation <strong>of</strong> a full atom model into a simpler representation. This is because the<br />
mathematical model, that needs to describe all combinations <strong>of</strong> atom interactions <strong>of</strong> two<br />
residues, would be too complex. The solution is to replace the all-atom structure model<br />
with a coarse grained model, by reducing each residue to a single point. In principle,<br />
a residue point can be calculated either by the centre <strong>of</strong> mass, or the geometric centre<br />
(centroid). Each representation can be calculated from main chain atoms, main and side<br />
chain atoms, or side chain atoms only.<br />
The focus in this study is the side chain interactions within residue triplet configuration.<br />
For this reason, a protein structure is represented as a point spread <strong>of</strong> side chain<br />
centroids.<br />
Protein structure triangulation.<br />
The extraction <strong>of</strong> residue triplets from a protein is<br />
based on triangulation <strong>of</strong> structures. Here structures are triangulated on the basis <strong>of</strong> three<br />
criteria. The first is the compositional constraint. Each residue in a triplet must be an<br />
element <strong>of</strong> the 20 natural amino acids, while hetero atoms are excluded. One prominent<br />
reason is that there are not many examples <strong>of</strong> residue-hetero atom interactions in the<br />
dataset that would support a statistical analysis.<br />
The second condition <strong>of</strong> triplet extraction requires that none <strong>of</strong> the residues are direct<br />
neighbours in the protein sequence. The assumption made here is, that any covalently<br />
bonded residues have a higher likelihood than any other two residues being next to each<br />
other in space that are not bonded. Similarly, the probability <strong>of</strong> finding three residues in<br />
space that are connected, is higher than finding unconnected triplets <strong>of</strong> residues. Consequently,<br />
the distribution <strong>of</strong> interacting residues in space would be over-represented. The<br />
definition <strong>of</strong> residue neighbourhood affects the data mining result, e.g. by requiring a<br />
pair interaction in the triplet to have a distance <strong>of</strong> more than one residue, patches <strong>of</strong><br />
residues at one side <strong>of</strong> a beta-sheet may not be discovered. While tuning this parameter<br />
can modify the result <strong>of</strong> the data mining, the objective here is to discover new knowledge<br />
45