deva.metal Handbuch EN für GGB - Supresores
deva.metal Handbuch EN für GGB - Supresores
deva.metal Handbuch EN für GGB - Supresores
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
4<br />
Counter materials<br />
Counter<br />
materials<br />
The <strong>deva</strong>.<strong>metal</strong> ® sliding materials can<br />
only be used with counter material<br />
hardness of at least 180 HB. If an<br />
additional lubricant is introduced into<br />
the sliding contact, hardness values<br />
of >130 HB are also admissible. In<br />
abrasive environments, a hardened 35<br />
HRC/45 HRC surface should be used.<br />
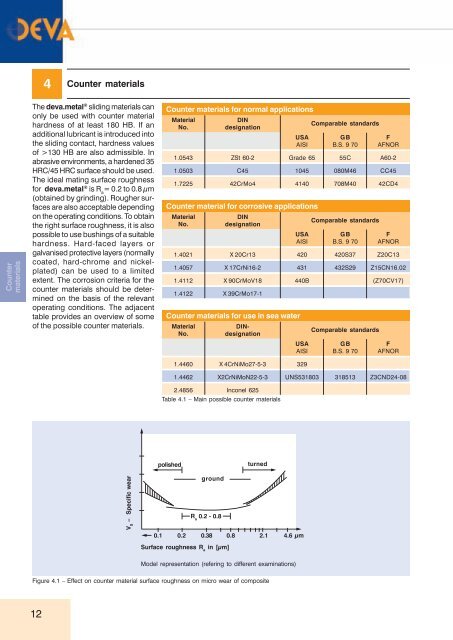
The ideal mating surface roughness<br />
for <strong>deva</strong>.<strong>metal</strong> ® is R a<br />
= 0.2 to 0.8 μm<br />
(obtained by grinding). Rougher surfaces<br />
are also acceptable depending<br />
on the operating conditions. To obtain<br />
the right surface roughness, it is also<br />
possible to use bushings of a suitable<br />
hardness. Hard-faced layers or<br />
galvanised protective layers (normally<br />
coated, hard-chrome and nickelplated)<br />
can be used to a limited<br />
extent. The corrosion criteria for the<br />
counter materials should be determined<br />
on the basis of the relevant<br />
operating conditions. The adjacent<br />
table provides an overview of some<br />
of the possible counter materials.<br />
Counter materials for normal applications<br />
Material<br />
No.<br />
1.0543<br />
1.0503<br />
1.7225<br />
DIN<br />
designation<br />
ZSt 60-2<br />
C45<br />
42CrMo4<br />
USA<br />
AISI<br />
Grade 65<br />
1045<br />
4140<br />
Counter material for corrosive applications<br />
Material<br />
No.<br />
1.4021<br />
1.4057<br />
1.4112<br />
1.4122<br />
DIN<br />
designation<br />
X 20Cr13<br />
X 17CrNi16-2<br />
X 90CrMoV18<br />
X 39CrMo17-1<br />
Counter materials for use in sea water<br />
Material<br />
No.<br />
DINdesignation<br />
USA<br />
AISI<br />
420<br />
431<br />
440B<br />
USA<br />
AISI<br />
Comparable standards<br />
GB<br />
B.S. 9 70<br />
55C<br />
080M46<br />
708M40<br />
Comparable standards<br />
GB<br />
B.S. 9 70<br />
420S37<br />
432S29<br />
Comparable standards<br />
GB<br />
B.S. 9 70<br />
F<br />
AFNOR<br />
A60-2<br />
CC45<br />
42CD4<br />
F<br />
AFNOR<br />
Z20C13<br />
Z15CN16.02<br />
(Z70CV17)<br />
F<br />
AFNOR<br />
1.4460<br />
1.4462<br />
X 4CrNiMo27-5-3<br />
X2CrNiMoN22-5-3<br />
329<br />
UNS531803 318513 Z3CND24-08<br />
2.4856<br />
Inconel 625<br />
Table 4.1 – Main possible counter materials<br />
polished<br />
turned<br />
V S<br />
– Specific wear<br />
ground<br />
R a<br />
0.2 - 0.8<br />
0.1 0.2 0.38 0.8 2.1 4.6 μm<br />
Surface roughness R a<br />
in [μm]<br />
Model representation (refering to different examinations)<br />
Figure 4.1 – Effect on counter material surface roughness on micro wear of composite<br />
12