Science Focus 2 TEST Chapter 4 - Pearson Australia Media ...
Science Focus 2 TEST Chapter 4 - Pearson Australia Media ...
Science Focus 2 TEST Chapter 4 - Pearson Australia Media ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 <strong>TEST</strong><br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 4: Body systems<br />
Name: _______________________ Class: __________ Date: _______<br />
Instructions: Write answers in the right-hand column.<br />
Score: ___________ / 109 marks<br />
Section A − Multiple choice (30 marks)<br />
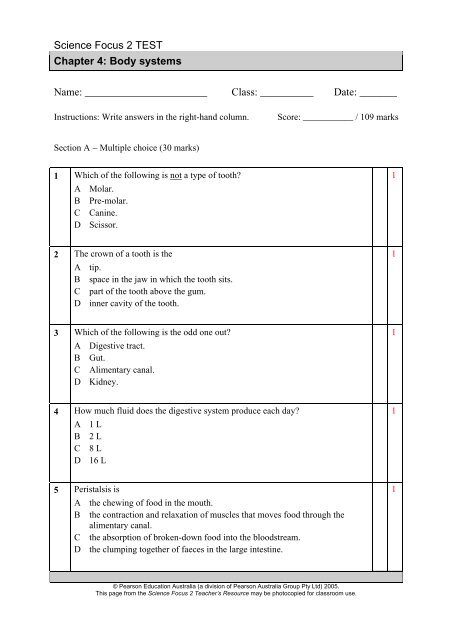
1 Which of the following is not a type of tooth?<br />
A Molar.<br />
B Pre-molar.<br />
C Canine.<br />
D Scissor.<br />
1<br />
2 The crown of a tooth is the<br />
A tip.<br />
B space in the jaw in which the tooth sits.<br />
C part of the tooth above the gum.<br />
D inner cavity of the tooth.<br />
1<br />
3 Which of the following is the odd one out?<br />
A Digestive tract.<br />
B Gut.<br />
C Alimentary canal.<br />
D Kidney.<br />
1<br />
4 How much fluid does the digestive system produce each day?<br />
A 1 L<br />
B 2 L<br />
C 8 L<br />
D 16 L<br />
1<br />
5 Peristalsis is<br />
A the chewing of food in the mouth.<br />
B the contraction and relaxation of muscles that moves food through the<br />
alimentary canal.<br />
C the absorption of broken-down food into the bloodstream.<br />
D the clumping together of faeces in the large intestine.<br />
1<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 <strong>TEST</strong><br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 4: Body systems<br />
6 Which of the following is/are not found in the digestive system?<br />
A Perpoofer valve.<br />
B Sphincters.<br />
C Villi.<br />
D Chyme.<br />
1<br />
7 The liver may be described as<br />
A a J-shaped organ.<br />
B a chemical factory.<br />
C the smallest digestive organ.<br />
D the longest organ.<br />
1<br />
8 The scientific name for released digestive gases is<br />
A sulfur dioxide.<br />
B flatus.<br />
C fartus.<br />
D odourus unpleasantus.<br />
1<br />
9 When matter is moved more slowly than usual through the digestive system,<br />
which of the following is more likely to occur?<br />
A Diarrhoea.<br />
B Heartburn.<br />
C Constipation.<br />
D Vomiting.<br />
1<br />
10 The tiny filtration units in your kidneys are called<br />
A nephrons.<br />
B filtrons.<br />
C urinators.<br />
D ureters.<br />
1<br />
11 Dialysis is the medical term for<br />
A a kidney transplant.<br />
B kidney failure.<br />
C filtering of blood by a machine.<br />
D a build-up of poisonous wastes in the blood.<br />
1<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 <strong>TEST</strong><br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 4: Body systems<br />
12 Kidney stones can cause extreme pain. A recently developed method to<br />
eliminate kidney stones uses<br />
A ultrasound.<br />
B lasers.<br />
C chemicals.<br />
D surgery.<br />
1<br />
13 The function of plasma is to<br />
A fight infection.<br />
B carry carbon dioxide.<br />
C carry the red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets around the body.<br />
D determine blood type.<br />
1<br />
14 The pulmonary vein carries<br />
A deoxygenated blood to the lungs.<br />
B newly oxygenated blood to the lungs.<br />
C deoxygenated blood to the rest of the body (not the lungs).<br />
D newly oxygenated blood to the heart.<br />
1<br />
15 Which of the following refers to a lower heart chamber?<br />
A Atrium.<br />
B Septum.<br />
C Ventricle.<br />
D Valve.<br />
1<br />
16 Which of the following is closest to a normal ECG?<br />
1<br />
A<br />
B<br />
C<br />
D<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 <strong>TEST</strong><br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 4: Body systems<br />
17 An artery may become narrowed due to a build-up of<br />
A dead blood cells.<br />
B cholesterol.<br />
C angina.<br />
D polyunsaturates.<br />
1<br />
18 What two recent scientific developments have helped heart sufferers?<br />
A Ultrasonic treatment.<br />
B Chemicals to lower cholesterol.<br />
C Heart valves and pacemakers.<br />
D Polyunsaturates.<br />
1<br />
19 What fraction of the human body is made up of water?<br />
1<br />
A<br />
B<br />
C<br />
D<br />
1<br />
10<br />
1<br />
3<br />
1<br />
2<br />
2<br />
3<br />
20 Which of the following shows the approximate percentages of three major gases<br />
in inhaled air?<br />
A 50% nitrogen, 49% oxygen, 1% carbon dioxide.<br />
B 79% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, 0.04% carbon dioxide.<br />
C 79% nitrogen, 14% oxygen, 6% carbon dioxide.<br />
D 59% nitrogen, 41% oxygen, 0.04% carbon dioxide.<br />
1<br />
21 Which of the following is not a property of alveoli?<br />
A Their cell walls are only one cell thick.<br />
B They lie close to the walls of capillaries.<br />
C They have a dry surface to allow efficient diffusion.<br />
D They are shaped to give maximum surface area.<br />
1<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 <strong>TEST</strong><br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 4: Body systems<br />
22 Most oxygen is transported in the bloodstream<br />
A bound to haemoglobin.<br />
B as gaseous oxygen molecules.<br />
C bound to platelets.<br />
D as dissolved carbon dioxide molecules and hydrogen carbonate ions.<br />
1<br />
23 We need fibre because<br />
A it contains large amounts of vitamins and minerals.<br />
B it provides bulk which helps move substances through the digestive system.<br />
C it is the major source of energy in foods.<br />
D it is used for growth and repair.<br />
1<br />
24 Pasta, bread and rice are foods that are all rich in<br />
A carbohydrates.<br />
B proteins.<br />
C fats.<br />
D vitamin C.<br />
1<br />
25 Which of the following diseases is caused by a lack of vitamins?<br />
A Hepatitis C.<br />
B AIDS.<br />
C Scurvy.<br />
D Polio.<br />
1<br />
26 Which two of the following are minerals?<br />
A Calcium.<br />
B Potassium.<br />
C Folic acid.<br />
D Riboflavin.<br />
1<br />
27 From which one of the following categories should you have most serves each<br />
day for a healthy diet?<br />
A Vegetables.<br />
B Meat and meat alternatives.<br />
C Breads and cereals.<br />
D Milk and milk products.<br />
1<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 <strong>TEST</strong><br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 4: Body systems<br />
28 Which food item is high in kilojoules and high in calcium?<br />
A Ice-cream.<br />
B Can of soft drink.<br />
C Hamburger.<br />
D Margarine.<br />
1<br />
29 Obesity<br />
A is an eating disorder in which sufferers unrealistically perceive they need to<br />
lose weight.<br />
B involves binge eating followed by purging.<br />
C is a condition in which a person is more than 24 per cent overweight.<br />
D is a town where a large number of OBE recipients reside.<br />
1<br />
30 Respiration is a chemical reaction which<br />
A occurs only in the body cells of animals.<br />
B always has oxygen as a reactant.<br />
C involves a sequence of reactions.<br />
D is endothermic (absorbs energy).<br />
1<br />
Section B − Written answers (79 marks)<br />
1 Identify the tooth type for the function<br />
of<br />
a biting.<br />
b grinding.<br />
c cutting.<br />
3<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 <strong>TEST</strong><br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 4: Body systems<br />
2 Label the tooth diagram below with the<br />
tooth type and function where indicated.<br />
4<br />
3 Explain how acid is created in the<br />
mouth, and what can it cause.<br />
2<br />
4 Identify the parts of the digestive<br />
system on the following diagram.<br />
5<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 <strong>TEST</strong><br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 4: Body systems<br />
5 Identify the location in the digestive<br />
system where<br />
a stools form.<br />
b insulin is produced.<br />
c nutrients pass through villi.<br />
d considerable heat energy is<br />
produced.<br />
e saliva produced.<br />
f peristalsis occurs.<br />
g you find hydrochloric acid.<br />
h digestion begins.<br />
4<br />
6 a Identify the end-product of<br />
digestion that provides energy to<br />
cells.<br />
b How is this substance transported<br />
around the body?<br />
c Give two ways this end-product<br />
is stored in the body.<br />
7 Explain<br />
a a stomach ulcer.<br />
b a possible cause of cirrhosis.<br />
4<br />
2<br />
8 Identify two waste products produced<br />
by cells in your body.<br />
1<br />
9 Classify the following in the order in<br />
which fluid flows, starting with the first<br />
stage.<br />
bladder, kidney, urethra, ureter.<br />
2<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 <strong>TEST</strong><br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 4: Body systems<br />
10 Explain the main function of<br />
a red blood cells.<br />
b white blood cells.<br />
c platelets.<br />
d antigens.<br />
4<br />
11 Assess whether a person with type B+<br />
blood could safely<br />
a donate blood to a person with<br />
type B− blood.<br />
b donate to a person with type O+<br />
blood.<br />
c receive blood from a donor with<br />
type O+ blood.<br />
12 Label the heart diagram below. 4<br />
3<br />
13 Identify the type of blood tubes that<br />
a are one cell thick.<br />
b carry blood at low pressure.<br />
c have the thickest outer layer.<br />
3<br />
14 Describe the role of the lungs in the<br />
circulatory system.<br />
2<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 <strong>TEST</strong><br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 4: Body systems<br />
15 Identify four structures which air<br />
passes through on its journey from the<br />
atmosphere to the alveoli in your lungs.<br />
4<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 <strong>TEST</strong><br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 4: Body systems<br />
16 The questions that follow refer to the<br />
diagram below of the human respiratory<br />
system.<br />
6<br />
Identify the structure shown (use the<br />
numbers 1 to 8 to answer) that<br />
a prevents food from entering the<br />
trachea.<br />
b contracts and flattens when you<br />
breathe in.<br />
c filters, warms and humidifies air.<br />
d contracts to raise the rib cage<br />
when you breathe in.<br />
e is the site of gaseous exchange<br />
between the lungs and the<br />
bloodstream.<br />
f is a bronchus.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 <strong>TEST</strong><br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 4: Body systems<br />
17 Describe what happens to each of the<br />
following structures during expiration<br />
(breathing out).<br />
a Ribs (raised or lowered?).<br />
b Diaphragm (flattens or is domeshaped?)<br />
c Pressure in the chest cavity<br />
(increases or decreases?).<br />
d Intercostal muscles (contract or<br />
relax?).<br />
18 Identify five types of nutrients, and<br />
give an example of a food rich in each<br />
one.<br />
4<br />
5<br />
19 Identify the part of food or nutrient that<br />
a assists chemical reactions in the<br />
body.<br />
b repairs body tissue.<br />
c is required in small amounts for<br />
good health.<br />
d provides a rich source of energy.<br />
20 Classify the following in order from<br />
least required each day to most required<br />
each day for a healthy diet.<br />
fruits, indulgence items, milk and milk<br />
products, breads and cereals,<br />
vegetables, meat and alternatives.<br />
21 a Describe the process of aerobic<br />
respiration by writing a chemical<br />
equation.<br />
b State whether the reaction is<br />
exothermic or endothermic.<br />
c Define the process of aerobic<br />
respiration.<br />
4<br />
3<br />
4<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 <strong>TEST</strong><br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 4: Body systems<br />
22 Describe the function of an enzyme. 2<br />
23 Identify<br />
a the two products of anaerobic<br />
respiration in yeast cells.<br />
b two industrial uses of the<br />
anaerobic respiration reaction in<br />
yeast cells.<br />
c the product of anaerobic<br />
respiration in human muscle<br />
cells.<br />
24 Recall two reasons why a person at rest<br />
would need energy.<br />
3<br />
2<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.