Cracking the Coding Interview, 4 Edition - 150 Programming Interview Questions and Solutions
Cracking the Coding Interview, 4 Edition - 150 Programming Interview Questions and Solutions
Cracking the Coding Interview, 4 Edition - 150 Programming Interview Questions and Solutions
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Solutions</strong> to Chapter 14 | Java<br />
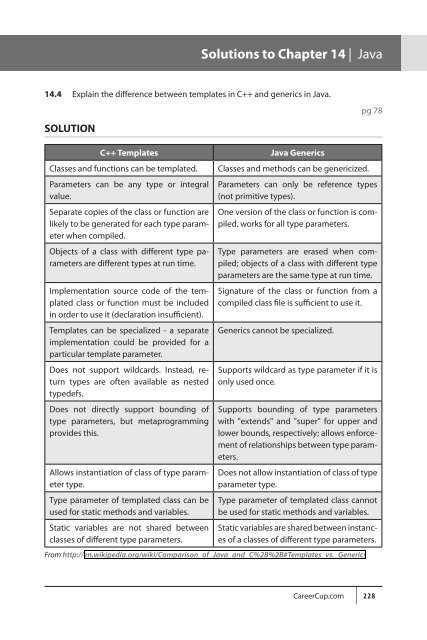
14.4 Explain <strong>the</strong> difference between templates in C++ <strong>and</strong> generics in Java.<br />
SOLUTION<br />
pg 78<br />
C++ Templates<br />
Classes <strong>and</strong> functions can be templated.<br />
Parameters can be any type or integral<br />
value.<br />
Separate copies of <strong>the</strong> class or function are<br />
likely to be generated for each type parameter<br />
when compiled.<br />
Objects of a class with different type parameters<br />
are different types at run time.<br />
Implementation source code of <strong>the</strong> templated<br />
class or function must be included<br />
in order to use it (declaration insufficient).<br />
Templates can be specialized - a separate<br />
implementation could be provided for a<br />
particular template parameter.<br />
Does not support wildcards. Instead, return<br />
types are often available as nested<br />
typedefs.<br />
Does not directly support bounding of<br />
type parameters, but metaprogramming<br />
provides this.<br />
Allows instantiation of class of type parameter<br />
type.<br />
Type parameter of templated class can be<br />
used for static methods <strong>and</strong> variables.<br />
Static variables are not shared between<br />
classes of different type parameters.<br />
Java Generics<br />
Classes <strong>and</strong> methods can be genericized.<br />
Parameters can only be reference types<br />
(not primitive types).<br />
One version of <strong>the</strong> class or function is compiled,<br />
works for all type parameters.<br />
Type parameters are erased when compiled;<br />
objects of a class with different type<br />
parameters are <strong>the</strong> same type at run time.<br />
Signature of <strong>the</strong> class or function from a<br />
compiled class file is sufficient to use it.<br />
Generics cannot be specialized.<br />
Supports wildcard as type parameter if it is<br />
only used once.<br />
Supports bounding of type parameters<br />
with "extends" <strong>and</strong> "super" for upper <strong>and</strong><br />
lower bounds, respectively; allows enforcement<br />
of relationships between type parameters.<br />
Does not allow instantiation of class of type<br />
parameter type.<br />
Type parameter of templated class cannot<br />
be used for static methods <strong>and</strong> variables.<br />
Static variables are shared between instances<br />
of a classes of different type parameters.<br />
From http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Comparison_of_Java_<strong>and</strong>_C%2B%2B#Templates_vs._Generics<br />
CareerCup.com<br />
2 2 8