A Sharp Interface Cartesian Grid Method for Simulating Flows with ...
A Sharp Interface Cartesian Grid Method for Simulating Flows with ...
A Sharp Interface Cartesian Grid Method for Simulating Flows with ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
368 UDAYKUMAR ET AL.<br />
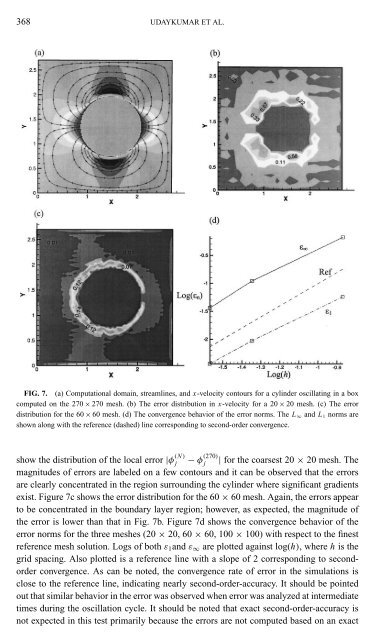
FIG. 7. (a) Computational domain, streamlines, and x-velocity contours <strong>for</strong> a cylinder oscillating in a box<br />
computed on the 270 × 270 mesh. (b) The error distribution in x-velocity <strong>for</strong> a 20 × 20 mesh. (c) The error<br />
distribution <strong>for</strong> the 60 × 60 mesh. (d) The convergence behavior of the error norms. The L ∞ and L 1 norms are<br />
shown along <strong>with</strong> the reference (dashed) line corresponding to second-order convergence.<br />
show the distribution of the local error |φ (N)<br />
j − φ (270)<br />
j | <strong>for</strong> the coarsest 20 × 20 mesh. The<br />
magnitudes of errors are labeled on a few contours and it can be observed that the errors<br />
are clearly concentrated in the region surrounding the cylinder where significant gradients<br />
exist. Figure 7c shows the error distribution <strong>for</strong> the 60 × 60 mesh. Again, the errors appear<br />
to be concentrated in the boundary layer region; however, as expected, the magnitude of<br />
the error is lower than that in Fig. 7b. Figure 7d shows the convergence behavior of the<br />
error norms <strong>for</strong> the three meshes (20 × 20, 60 × 60, 100 × 100) <strong>with</strong> respect to the finest<br />
reference mesh solution. Logs of both ε 1 and ε ∞ are plotted against log(h), where h is the<br />
grid spacing. Also plotted is a reference line <strong>with</strong> a slope of 2 corresponding to secondorder<br />
convergence. As can be noted, the convergence rate of error in the simulations is<br />
close to the reference line, indicating nearly second-order-accuracy. It should be pointed<br />
out that similar behavior in the error was observed when error was analyzed at intermediate<br />
times during the oscillation cycle. It should be noted that exact second-order-accuracy is<br />
not expected in this test primarily because the errors are not computed based on an exact