u x u u)a ′ ∂ ′ ∂ ′ xxxx )b ∂ ∂ ω′ ∂ ∂ ∂ ω′ ∂ U x U)c ∂ ω ...
u x u u)a ′ ∂ ′ ∂ ′ xxxx )b ∂ ∂ ω′ ∂ ∂ ∂ ω′ ∂ U x U)c ∂ ω ...
u x u u)a ′ ∂ ′ ∂ ′ xxxx )b ∂ ∂ ω′ ∂ ∂ ∂ ω′ ∂ U x U)c ∂ ω ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
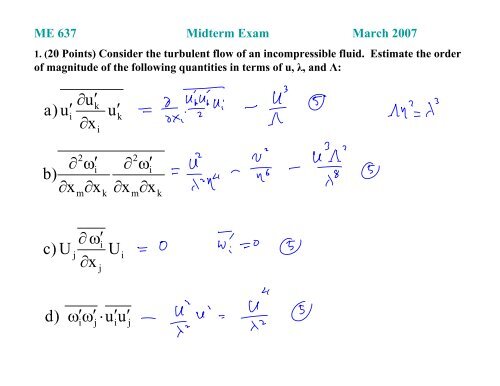
ME 637 Midterm Exam March 2007<br />
1. (20 Points) Consider the turbulent flow of an incompressible fluid. Estimate the order<br />
of magnitude of the following quantities in terms of u, λ, and Λ:<br />
<strong>∂</strong>u<strong>′</strong><br />
k<br />
a ) u<strong>′</strong><br />
i<br />
u<strong>′</strong><br />
k<br />
<strong>∂</strong>xi<br />
<strong>∂</strong><br />
b)<br />
<strong>∂</strong>x<br />
2<br />
m<br />
<strong>ω</strong><strong>′</strong><br />
i<br />
<strong>∂</strong>x<br />
k<br />
<strong>∂</strong><br />
<strong>∂</strong>x<br />
2<br />
m<br />
<strong>ω</strong><strong>′</strong><br />
i<br />
<strong>∂</strong>x<br />
k<br />
c) U<br />
j<br />
<strong>∂</strong> <strong>ω</strong><strong>′</strong><br />
i<br />
<strong>∂</strong>x<br />
j<br />
U<br />
i<br />
d ) <strong>ω</strong><strong>′</strong><strong>ω</strong><strong>′</strong> ⋅u<strong>′</strong><br />
u<strong>′</strong><br />
i<br />
j<br />
i<br />
j
2. (20 Points) Determine the contribution of eddies of size r to the correlations a) and b) in problem 1.<br />
For evaluate these correlations, compare the contribution of large, and small eddies.
3. (30 Point) Consider that case of a viscous Newtonian fluid between two long parallel walls. The lower<br />
wall is set suddenly in motion at time zero while the upper wall is stationary as shown in the figure.<br />
The fluid is initially at rest and there is no pressure gradient.<br />
a. State the unsteady momentum and continuity equations for parallel the flow shown in its<br />
simplest form.<br />
b. State the boundary and initial conditions.<br />
c. Find the velocity field.<br />
d. Find the steady velocity profile in the duct.<br />
y<br />
h<br />
u=0<br />
Newtonian<br />
Viscous Fluid<br />
U o<br />
x
4. (30 Points) Pollutant concentration and heat transport equations are given by<br />
Let<br />
<strong>∂</strong>c<br />
<strong>∂</strong>t<br />
+ u<br />
j<br />
<strong>∂</strong>c<br />
<strong>∂</strong>x<br />
j<br />
c = C +<br />
2<br />
<strong>∂</strong> c<br />
= α<br />
<strong>∂</strong>x<br />
<strong>∂</strong>x<br />
c'<br />
j<br />
j<br />
T = T +<br />
T'<br />
<strong>∂</strong>T<br />
<strong>∂</strong>t<br />
+ u<br />
j<br />
<strong>∂</strong>T<br />
<strong>∂</strong>x<br />
u = U + u<br />
a. Find the equation governing the average concentration C and average temperature .<br />
b. Find the transport equation for concentration-temperature correlation c' T'<br />
c. Identify the terms in the equation for .<br />
i<br />
c' T'<br />
j<br />
2<br />
<strong>∂</strong> T<br />
= α<br />
<strong>∂</strong>x<br />
<strong>∂</strong>x<br />
i<br />
'<br />
i<br />
j<br />
j<br />
T