Polymer Identification Symbols For Packaging
Polymer Identification Symbols For Packaging
Polymer Identification Symbols For Packaging
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Polymer</strong> <strong>Identification</strong> <strong>Symbols</strong> <strong>For</strong> <strong>Packaging</strong><br />
✎<br />
The legislation<br />
The European Directive 94/62/EC on<br />
packaging and packaging waste sets<br />
out targets for the recovery of used<br />
packaging. Article 8 of this Directive,<br />
‘Marking and <strong>Identification</strong>’ states:<br />
“ to facilitate collection, reuse and<br />
recovery including recycling, packaging<br />
shall indicate for purposes of its<br />
identification and classification by the<br />
industry concerned the nature of the<br />
packaging material(s) used”<br />
The subsequent Commission Decision<br />
97/129/EC provides numeric and<br />
abbreviation identifications for<br />
packaging materials. In Article 3, the<br />
Decision states that “their use shall be<br />
voluntary”.<br />
APME fully supports the use of marking<br />
where the marking will effectively help in<br />
the recovery of used packaging.<br />
There are two key points:<br />
☞<br />
☞<br />
The application of the marking<br />
shall be voluntary<br />
The symbol is a means of<br />
material identification and is not a<br />
claim for recyclability<br />
✎<br />
What symbol<br />
Industry and consumers have become<br />
aware of the key symbols used for<br />
identifying the various materials used for<br />
packaging and any action for<br />
identification should build on this<br />
established awareness.<br />
<strong>Packaging</strong> and packed products are<br />
traded on an international basis and any<br />
symbol should have a wide as possible<br />
recognition.<br />
The American Society of the Plastics<br />
Industry (SPI) introduced a symbol and<br />
numbering system in 1988 (the Resin<br />
<strong>Identification</strong> Code – RIC) specifically<br />
for rigid plastic packaging over 200cc, or<br />
50gm. The symbol and numbering code<br />
have become mandatory in a majority of<br />
USA states and widely adopted in<br />
Australia, Canada, Japan as well as in<br />
Europe. It is important to build on this<br />
awareness.<br />
The APME position is that when<br />
marking for the identification of the<br />
plastic material is beneficial, the SPI<br />
symbol should be used.<br />
The detailed examples of the symbol,<br />
numbering and acronyms are shown on<br />
the reverse of this document. The size<br />
and location of such marking should be<br />
compatible with the objective of the<br />
intended identification. Additional<br />
polymer coding can only be adopted by<br />
international agreement.<br />
✎<br />
Why Use It<br />
As a voluntary action and when the<br />
symbol and material code are assessed<br />
to effectively support the recovery of<br />
used packaging by identification of the<br />
plastic at any stage of the operations<br />
from sorting through to recycling.<br />
✎<br />
Where to use it<br />
On any plastic packaging.<br />
It should not be used for non-packaging<br />
plastic parts, such as automotive or<br />
electrical/electronic equipment. <strong>For</strong><br />
such components, the ISO 11469 and<br />
ISO 1043 should be used. (Copies<br />
obtainable through National Standards<br />
Bodies). These identifications should<br />
never be used in conjunction with the<br />
SPI code.
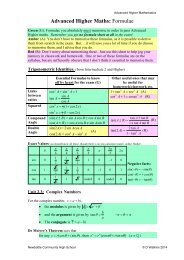
<strong>Polymer</strong> Type<br />
CEN<br />
Recommendation<br />
CEN WI 261 070<br />
EU Commission<br />
Decision<br />
97/129/EC<br />
APME Position<br />
Polyethylene<br />
Terephthalate<br />
01<br />
PET<br />
1<br />
PET<br />
1<br />
PET<br />
High Density<br />
Polyethylene<br />
02<br />
PE-HD<br />
2<br />
HDPE<br />
2<br />
HDPE<br />
Polyvinyl Chloride<br />
03<br />
PVC<br />
3<br />
PVC<br />
3<br />
PVC<br />
Low density<br />
Polyethylene<br />
04<br />
PE-LD<br />
4<br />
LDPE<br />
4<br />
LDPE<br />
Polypropylene<br />
05<br />
PP<br />
5<br />
PP<br />
5<br />
PP<br />
Polystyrene<br />
06<br />
PS<br />
6<br />
PS<br />
6<br />
PS<br />
Unallocated<br />
references<br />
07-20<br />
7-19<br />
7-19<br />
ASSOCIATION OF PLASTICS MANUFACTURERS IN EUROPE (APME)<br />
APME’S TECHNICAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL CENTRE<br />
Avenue E. Van Nieuwenhuyse 4 Box 3 B-1160 Brussels<br />
Telephone (32-2) 676 17 50 Facsimile (32-2) 675 40 02 E-mail info.apme@apme.org Web site http://www.apme.org<br />
October 2001