REVERSE OPG - A REVIVAL. C. Pravda, D. Koteeswaran. - Aosr.co.in
REVERSE OPG - A REVIVAL. C. Pravda, D. Koteeswaran. - Aosr.co.in
REVERSE OPG - A REVIVAL. C. Pravda, D. Koteeswaran. - Aosr.co.in
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
C. <strong>Pravda</strong> et al.<br />
College, Chennai to demonstrate the normal anatomy<br />
as well as the osteoarthitic changes of the <strong>co</strong>ndyle. The<br />
mach<strong>in</strong>e that was used for the study was Rotograph<br />
230 of 1992 model. * Despite the advent of new<br />
technological advancement and <strong>in</strong>novation this unit<br />
is still <strong>in</strong> use to take <strong>OPG</strong>s and reverse <strong>OPG</strong>s. Certa<strong>in</strong><br />
modifications were made <strong>in</strong> the mach<strong>in</strong>e. The ch<strong>in</strong> rest<br />
was removed so that the patient can be positioned<br />
posteriorly such that the <strong>co</strong>ndylar region is moved<br />
closer to the lateral centre of rotation with<strong>in</strong> a fixed<br />
distance between the X ray source and the cassette. The<br />
procedure was expla<strong>in</strong>ed to the patients regard<strong>in</strong>g the<br />
movement of the tube around the patient’s head. Patient<br />
was asked to remove the eyeglasses, earr<strong>in</strong>gs, dentures,<br />
hairp<strong>in</strong>s, etc. Patient can sit or stand erectly <strong>in</strong> the mach<strong>in</strong>e<br />
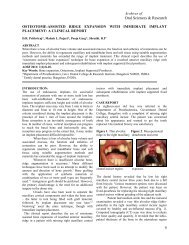
<strong>in</strong> the reverse position (Figure 1). The head was aligned<br />
with the mid sagittal plane perpendicular to the floor.<br />
The ch<strong>in</strong> was slightly tilted down so that the Frankfort<br />
l<strong>in</strong>e is parallel to the floor. Lateral head stabilizers<br />
are used to ensure that the patient’s head is central.<br />
Exposure is made with both mouth opened and<br />
closed position. It should be remembered that if the<br />
left and right markers are built-<strong>in</strong> the cassette, they will<br />
be <strong>in</strong><strong>co</strong>rrect. So the film mark<strong>in</strong>g has to be altered.<br />
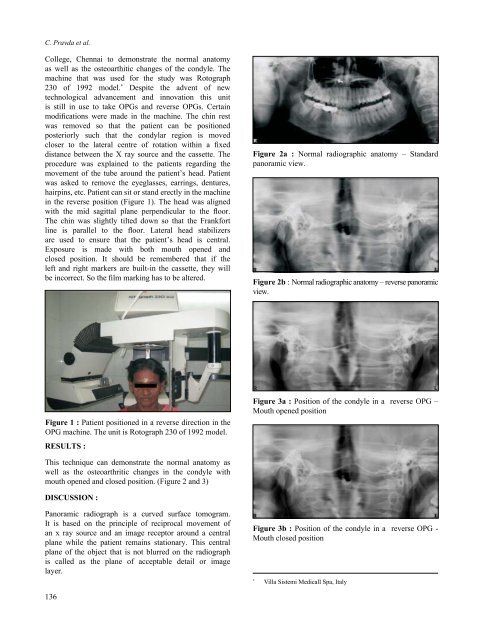
Figure 2a : Normal radiographic anatomy – Standard<br />
panoramic view.<br />
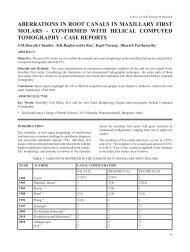
Figure 2b : Normal radiographic anatomy – reverse panoramic<br />
view.<br />
Figure 1 : Patient positioned <strong>in</strong> a reverse direction <strong>in</strong> the<br />
<strong>OPG</strong> mach<strong>in</strong>e. The unit is Rotograph 230 of 1992 model.<br />
RESULTS :<br />
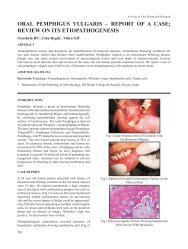
Figure 3a : Position of the <strong>co</strong>ndyle <strong>in</strong> a reverse <strong>OPG</strong> –<br />
Mouth opened position<br />
This technique can demonstrate the normal anatomy as<br />
well as the osteoarthritic changes <strong>in</strong> the <strong>co</strong>ndyle with<br />
mouth opened and closed position. (Figure 2 and 3)<br />
DISCUSSION :<br />
Panoramic radiograph is a curved surface tomogram.<br />
It is based on the pr<strong>in</strong>ciple of reciprocal movement of<br />
an x ray source and an image receptor around a central<br />
plane while the patient rema<strong>in</strong>s stationary. This central<br />
plane of the object that is not blurred on the radiograph<br />
is called as the plane of acceptable detail or image<br />
layer.<br />
Figure 3b : Position of the <strong>co</strong>ndyle <strong>in</strong> a reverse <strong>OPG</strong> -<br />
Mouth closed position<br />
*<br />
Villa Sistemi Medicall Spa, Italy<br />
136