You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
PHYSICS FUNDAMENTAL FOR <strong>IIT</strong>-<strong>JEE</strong><br />
Reflection at plane & curved surfaces<br />
KEY CONCEPTS & PROBLEM SOLVING STRATEGY<br />
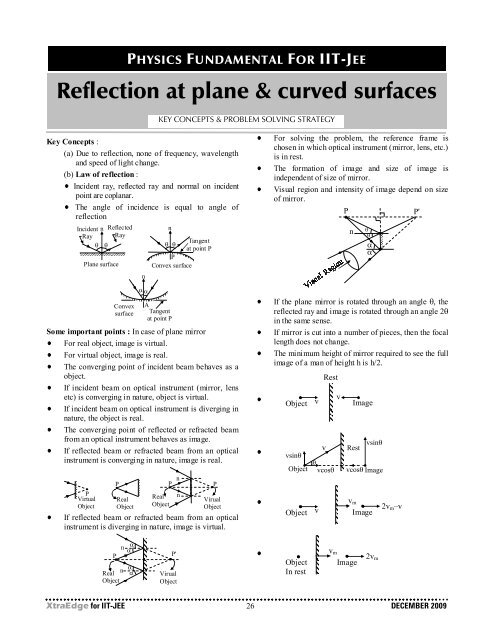
Key Concepts :<br />
(a) Due to reflection, none of frequency, wavelength<br />
and speed of light change.<br />
(b) Law of reflection :<br />
Incident ray, reflected ray and normal on incident<br />
point are coplanar.<br />
The angle of incidence is equal to angle of<br />
reflection<br />
Incident n Reflected<br />
Ray Ray<br />
θ θ<br />
Plane surface<br />
Convex<br />
surface<br />
n<br />
α α<br />
n<br />
Tangent<br />
θ θ<br />
at point P<br />
P<br />
Convex surface<br />
A<br />
Tangent<br />
at point P<br />
Some important points : In case of plane mirror<br />
For real object, image is virtual.<br />
For virtual object, image is real.<br />
The converging point of incident beam behaves as a<br />
object.<br />
If incident beam on optical instrument (mirror, lens<br />
etc) is converging in nature, object is virtual.<br />
If incident beam on optical instrument is diverging in<br />
nature, the object is real.<br />
The converging point of reflected or refracted beam<br />
from an optical instrument behaves as image.<br />
If reflected beam or refracted beam from an optical<br />
instrument is converging in nature, image is real.<br />
P<br />
Virtual<br />
Object<br />
P<br />
Real<br />
Object<br />
P<br />
Real<br />
Object<br />
n<br />
n<br />
P<br />
Virual<br />
Object<br />
If reflected beam or refracted beam from an optical<br />
instrument is diverging in nature, image is virtual.<br />
For solving the problem, the reference frame is<br />
chosen in which optical instrument (mirror, lens, etc.)<br />
is in rest.<br />
The formation of image and size of image is<br />
independent of size of mirror.<br />
Visual region and intensity of image depend on size<br />
of mirror.<br />
P<br />
n<br />
If the plane mirror is rotated through an angle θ, the<br />
reflected ray and image is rotated through an angle 2θ<br />
in the same sense.<br />
If mirror is cut into a number of pieces, then the focal<br />
length does not change.<br />
The minimum height of mirror required to see the full<br />
image of a man of height h is h/2.<br />
Object<br />
vsinθ<br />
Object<br />
Object<br />
v<br />
Rest<br />
v<br />
θ<br />
vcosθ<br />
v<br />
v<br />
θ<br />
θ<br />
α<br />
α<br />
Image<br />
Rest<br />
vsinθ<br />
vcosθ Image<br />
v m<br />
2v m –v<br />
Image<br />
P'<br />
P<br />
n<br />
Real<br />
n<br />
Object<br />
α<br />
α<br />
α<br />
α<br />
P'<br />
Virual<br />
Object<br />
Object<br />
In rest<br />
v m<br />
Image<br />
2v m<br />
XtraEdge for <strong>IIT</strong>-<strong>JEE</strong> 26 DECEMBER 2009