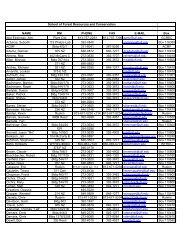
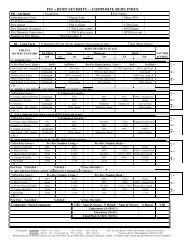
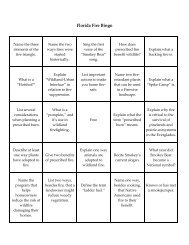
as pdf
as pdf
as pdf
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Soil Water Evaporation<br />
• Stage 1. For soils saturated to the surface, the evaporation<br />
rate is similar to surface water evaporation.<br />
• Stage 2. As the surface dries out, evaporation slows to a rate<br />
dependent on the capillary conductivity of the soil.<br />
• Stage 3. Once pore spaces dry, water loss occurs in the form<br />
of vapor diffusion. Vapor diffusion requires more energy input<br />
than capillary conduction and is much, much, slower.<br />
Note that for soils under a forest canopy, R net , vapor pressure<br />
deficit, and turbulent transport (wind) are lower than for<br />
exposed soils.