Fasteners - hdgasa
Fasteners - hdgasa
Fasteners - hdgasa
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Contribution from South America<br />
Bob’s BANTER:<br />
What readers have<br />
to say...<br />
Hello Bob,<br />
I wrote to you last year re using<br />
your “Cleaner Fish” article in the<br />
GALVANIZING magazine. I have<br />
spoken to Terry Smith, the editor.<br />
He is delighted to hear we read<br />
his magazine! He said I may send<br />
it on to others. Obviously with<br />
your email details.<br />
Coincidentally our sons were<br />
friends at school and still<br />
maintain contact.<br />
Please send me a copy.<br />
Thanks a lot.<br />
George Savage<br />
Picasso Digital Graphics<br />
Hi Bob<br />
After 15 years’ of retirement I find<br />
that the pure scientific articles are<br />
getting less interesting, or is it<br />
understandable. Your Bob’s Banter,<br />
with its often philosophic slant, is<br />
however always great reading. I<br />
especially enjoyed your latest one<br />
based on Darwin’s evolution<br />
theory. Thanks. Best wishes for a<br />
lovely 2012 and many more to<br />
come.<br />
Regards<br />
Wim Skinner<br />
Hi Bob,<br />
Just read your article “Bob’s<br />
Banter” in HD Galvanizing Today<br />
no. 47 – what an inspirational way<br />
to start my day.<br />
Hope to see more of your<br />
writings in the magazine in the<br />
future.<br />
tx<br />
Conrad Hubbe<br />
for STATIC Structural Engineers<br />
cc (In association with Geni<br />
Consulting Engineers cc)<br />
Motivation and methodology<br />
of hot dip galvanizing steel<br />
railway sleepers for Vale Do<br />
Rio Doce, Brazil<br />
Introduction<br />
Due to thermodynamic laws, steel<br />
when left unprotected will in time<br />
return to its natural state of iron ore.<br />
This means that insufficient corrosion<br />
protection, will result in premature<br />
corrosion, ultimately reducing the<br />
mechanical properties and strength of<br />
the steel.<br />
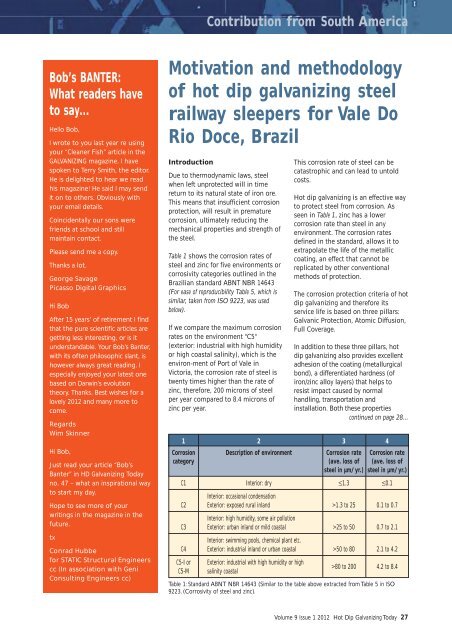
Table 1 shows the corrosion rates of<br />
steel and zinc for five environments or<br />
corrosivity categories outlined in the<br />
Brazilian standard ABNT NBR 14643<br />
(For ease of reproducibility Table 5, which is<br />
similar, taken from ISO 9223, was used<br />
below).<br />
If we compare the maximum corrosion<br />
rates on the environment "C5"<br />
(exterior: industrial with high humidity<br />
or high coastal salinity), which is the<br />
environ-ment of Port of Vale in<br />
Victoria, the corrosion rate of steel is<br />
twenty times higher than the rate of<br />
zinc, therefore, 200 microns of steel<br />
per year compared to 8.4 microns of<br />
zinc per year.<br />
This corrosion rate of steel can be<br />
catastrophic and can lead to untold<br />
costs.<br />
Hot dip galvanizing is an effective way<br />
to protect steel from corrosion. As<br />
seen in Table 1, zinc has a lower<br />
corrosion rate than steel in any<br />
environment. The corrosion rates<br />
defined in the standard, allows it to<br />
extrapolate the life of the metallic<br />
coating, an effect that cannot be<br />
replicated by other conventional<br />
methods of protection.<br />
The corrosion protection criteria of hot<br />
dip galvanizing and therefore its<br />
service life is based on three pillars:<br />
Galvanic Protection, Atomic Diffusion,<br />
Full Coverage.<br />
In addition to these three pillars, hot<br />
dip galvanizing also provides excellent<br />
adhesion of the coating (metallurgical<br />
bond), a differentiated hardness (of<br />
iron/zinc alloy layers) that helps to<br />
resist impact caused by normal<br />
handling, transportation and<br />
installation. Both these properties<br />
continued on page 28...<br />
1 2 3 4<br />
Corrosion Description of environment Corrosion rate Corrosion rate<br />
category (ave. loss of (ave. loss of<br />
steel in µm/yr.) steel in µm/yr.)<br />
C1 Interior: dry ≤1.3 ≤0.1<br />
Interior: occasional condensation<br />
C2 Exterior: exposed rural inland >1.3 to 25 0.1 to 0.7<br />
Interior: high humidity, some air pollution<br />
C3 Exterior: urban inland or mild coastal >25 to 50 0.7 to 2.1<br />
Interior: swimming pools, chemical plant etc.<br />
C4 Exterior: industrial inland or urban coastal >50 to 80 2.1 to 4.2<br />
C5-I or<br />
C5-M<br />
Exterior: industrial with high humidity or high<br />
salinity coastal<br />
>80 to 200 4.2 to 8.4<br />
Table 1: Standard ABNT NBR 14643 (Similar to the table above extracted from Table 5 in ISO<br />
9223, (Corrosivity of steel and zinc).<br />
Volume 9 Issue 1 2012 Hot Dip Galvanizing Today 27