Substances, Mixtures, and Solubility - McGraw-Hill Higher Education
Substances, Mixtures, and Solubility - McGraw-Hill Higher Education
Substances, Mixtures, and Solubility - McGraw-Hill Higher Education
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
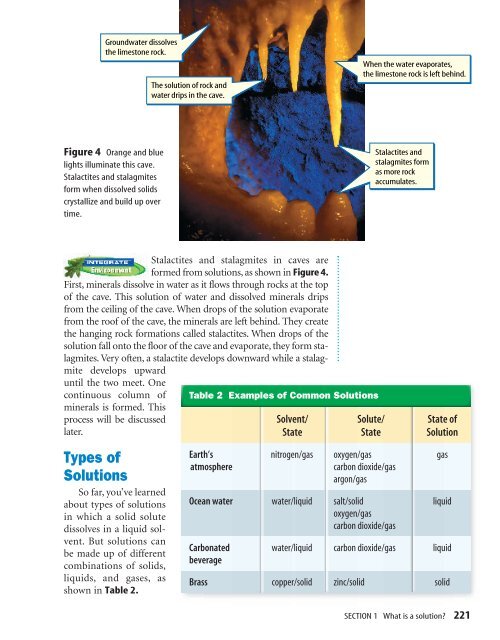
Groundwater dissolves<br />
the limestone rock.<br />
The solution of rock <strong>and</strong><br />
water drips in the cave.<br />
When the water evaporates,<br />
the limestone rock is left behind.<br />
Figure 4 Orange <strong>and</strong> blue<br />
lights illuminate this cave.<br />
Stalactites <strong>and</strong> stalagmites<br />
form when dissolved solids<br />
crystallize <strong>and</strong> build up over<br />
time.<br />
Stalactites <strong>and</strong><br />
stalagmites form<br />
as more rock<br />
accumulates.<br />
Stalactites <strong>and</strong> stalagmites in caves are<br />
formed from solutions, as shown in Figure 4.<br />
First, minerals dissolve in water as it flows through rocks at the top<br />
of the cave. This solution of water <strong>and</strong> dissolved minerals drips<br />
from the ceiling of the cave. When drops of the solution evaporate<br />
from the roof of the cave, the minerals are left behind. They create<br />
the hanging rock formations called stalactites. When drops of the<br />
solution fall onto the floor of the cave <strong>and</strong> evaporate, they form stalagmites.<br />
Very often, a stalactite develops downward while a stalagmite<br />
develops upward<br />
until the two meet. One<br />
continuous column of<br />
minerals is formed. This<br />
process will be discussed<br />
later.<br />
Types of<br />
Solutions<br />
So far, you’ve learned<br />
about types of solutions<br />
in which a solid solute<br />
dissolves in a liquid solvent.<br />
But solutions can<br />
be made up of different<br />
combinations of solids,<br />
liquids, <strong>and</strong> gases, as<br />
shown in Table 2.<br />
Table 2 Examples of Common Solutions<br />
Solvent/ Solute/ State of<br />
State State Solution<br />
Earth’s nitrogen/gas oxygen/gas gas<br />
atmosphere<br />
carbon dioxide/gas<br />
argon/gas<br />
Ocean water water/liquid salt/solid liquid<br />
oxygen/gas<br />
carbon dioxide/gas<br />
Carbonated water/liquid carbon dioxide/gas liquid<br />
beverage<br />
Brass copper/solid zinc/solid solid<br />
SECTION 1 What is a solution 221