Job Hazard Analysis (JHA) - MCCS Camp Lejeune
Job Hazard Analysis (JHA) - MCCS Camp Lejeune
Job Hazard Analysis (JHA) - MCCS Camp Lejeune
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Job</strong> <strong>Hazard</strong> <strong>Analysis</strong><br />
(<strong>JHA</strong>)<br />
In support of OSHA’s Voluntary Protection Program (VPP)<br />
And<br />
Marine Corps Base <strong>Camp</strong> <strong>Lejeune</strong>’ s desire to Improve<br />
workplace safety, a <strong>JHA</strong> shall be conducted on all job<br />
tasks to identify and control common hazards.<br />
This lesson will assist you with establishing a <strong>JHA</strong> for all<br />
job tasks.
WHAT’s a <strong>JHA</strong><br />
A <strong>Job</strong> <strong>Hazard</strong> <strong>Analysis</strong> is a technique that focuses on<br />
job tasks as a way to identify hazards before they<br />
result in injury, illness, property damage, or worse<br />
It focuses on the relationship between the worker,<br />
the task, the tools, and the work environment<br />
Ideally, after you identify uncontrolled hazards, you<br />
will take steps to eliminate or reduce them to an<br />
acceptable risk level
How do I know that I’m doing my job safely<br />
1. Prior to performing any work, review the <strong>JHA</strong> for that<br />
job task.<br />
• It identifies safety hazards in the workplace.<br />
• Each job is broken down into process steps making<br />
it easier to identify, eliminate, & control hazards.<br />
2. <strong>JHA</strong> identifies required training for each task<br />
• SOPs, Training guides, Operational Manuals, etc<br />
listed for required qualifications to perform task.
How do I know that I’m doing my job safely<br />
Cont.<br />
3. <strong>JHA</strong> identifies required Personal Protective<br />
Equipment (PPE) for the job task.<br />
• Standardizes operations based on appropriate<br />
PPE based on the acceptable risk level.<br />
Employees must understand <strong>Job</strong> hazard analysis is a<br />
VPP (Voluntary Protection Program) recognition<br />
Requirement!
<strong>Job</strong> <strong>Hazard</strong> <strong>Analysis</strong><br />
(<strong>JHA</strong>)
Who Should Perform a <strong>JHA</strong><br />
• A <strong>Job</strong> <strong>Hazard</strong> <strong>Analysis</strong> should<br />
be conducted and documented<br />
by a team, supervisors &<br />
employees, who are familiar<br />
with and knowledgeable of the<br />
process.<br />
• This team should be<br />
knowledgeable, but objective.<br />
People who work frequently on<br />
the task tend to get<br />
comfortable, and can overlook<br />
hazards others would spot.<br />
Conducting a <strong>JHA</strong>
Conducting a <strong>JHA</strong> cont.<br />
<strong>JHA</strong>s written based on PRIORITIES<br />
Consider giving priority to:<br />
• jobs with the highest injury or illness rates<br />
• jobs where there have been “Near Miss” –where an<br />
incident occurred but no one got hurt<br />
• jobs where OSHA standards might have been<br />
identified<br />
• jobs with the potential to cause serious injuries or<br />
illness, even if there is no history of such problems<br />
• jobs in which one simple human mistake could lead<br />
to severe injury<br />
• jobs that are new to your operation or have been<br />
changed<br />
• jobs complex enough to require written instructions
Conducting a <strong>JHA</strong> cont.<br />
HOW TO START <br />
• The <strong>JHA</strong> is a five step process which includes;<br />
– Employee Involvement<br />
• <strong>JHA</strong> is not an employee evaluation but a Task<br />
evaluation<br />
• Employees are involved in the entire process<br />
• Supervisors & employees discuss the steps involved<br />
with a particular job task and why
Identify <strong>Hazard</strong>ous Conditions –Step 1<br />
After Tasks are broken into steps, the next step is to<br />
identify the hazards<br />
HOW TO DO IT<br />
Identify the hazards of each step by asking :<br />
• What can go wrong<br />
• What are the consequences<br />
• How could it happen<br />
• What are other contributing factors<br />
• How likely is it that the hazard will occur
Identify <strong>Hazard</strong>ous Conditions<br />
Review the list of hazards with employees who do the<br />
job. Discuss what could be done to eliminate or<br />
reduce them.
Determine Root Causes –Step 2<br />
Root Cause ‐ failure, or fault from which a chain of effects or<br />
failures originates.<br />
Example : Employee cut hand with a box cutter.<br />
Contributing factor: Employee used excess force<br />
Contributing factor : hand in path of blade<br />
Contributing factor:: Lack of training from supervisor<br />
Root Cause : Dull blade and lack of training<br />
• Potential causes of injuries include:<br />
– Lack of knowledge<br />
– Lack of physical ability<br />
– Prior training that included unsafe<br />
practices<br />
– Previously unidentified hazard<br />
– Newly introduced hazard resulting from process or equipment change.
Eliminate the <strong>Hazard</strong>s –Step 3<br />
After <strong>Hazard</strong>s are identified they must be mitigated<br />
using one or a combination of these techniques
Engineering Controls<br />
• Engineering controls eliminate<br />
exposure to the hazard by:<br />
• 1. Isolating the employee from the<br />
hazard<br />
• 2. Improving (redesign) work area<br />
layout<br />
• 3. Substituting less hazardous<br />
product<br />
• 4. Modifying equipment
Administrative Controls<br />
• Administrative controls<br />
reduce employee<br />
exposure to a hazard by:<br />
1. Reducing the frequency of<br />
performing the hazardous task<br />
2. Rotating employees to<br />
reduce exposure time<br />
3. Training employees to<br />
recognize hazards and employ<br />
safety practices.
Administrative Controls<br />
• Accountability for carrying out actions should<br />
be clearly assigned, understood, and initialed<br />
by the respective person indicating their<br />
personal commitment and accountability for<br />
that action.
PPE<br />
• OSHA requires employers to provide<br />
PPE to reduce employee exposure to<br />
hazards when engineering and<br />
administrative controls are not feasible<br />
or effective<br />
• PPE alone should not be relied on to<br />
protect against hazards; other uses<br />
include guards, engineering controls,<br />
and sound manufacturing practices.
Control Measures –Step 4<br />
What do I do next <br />
Correct the unsafe conditions and processes.<br />
• Train all employees on the new conditions and<br />
updated process<br />
• Ensure employees understand these changes
Control Measures<br />
What do I do next <br />
Use the <strong>JHA</strong>s!<br />
• Annual Review<br />
• With new equipment<br />
• Train new employees
Evaluation of Effectiveness –Step 5<br />
• Once the <strong>JHA</strong> is completed, it<br />
should be reviewed by someone<br />
with authority to implement<br />
changes.<br />
• Supervisors should follow up to<br />
make sure that the<br />
recommendations have been acted<br />
upon.<br />
• The <strong>JHA</strong>’s should be logged and filed<br />
for future reference.
Evaluation of Effectiveness<br />
• Assess how well the <strong>JHA</strong> process is “fixing” hazardous<br />
conditions by:<br />
– Updating <strong>JHA</strong>s for routine and non‐routine task<br />
– Ensuring <strong>JHA</strong>s were developed for all new processes<br />
– Conducting routine self‐inspections<br />
– Examining Industrial Hygiene reports<br />
–Reviewing investigation findings for injuries and near<br />
misses<br />
– Following up on employee concerns.<br />
• Incorporate evaluation into Annual Program Evaluation<br />
process.
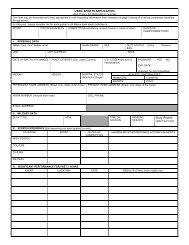
Blank <strong>JHA</strong><br />
Organization:<br />
<strong>MCCS</strong><br />
Task:<br />
JOB HAZARD ANALYSIS WORKSHEET<br />
Division:<br />
Section/Shop:<br />
Conducted By:<br />
David<br />
Reviewed By:<br />
Approved By:<br />
Date: Date: Date:<br />
Sequence of Steps<br />
1. Get/Drive/park <strong>MCCS</strong><br />
vehicle<br />
2. Sort merchandise<br />
3. Working environment<br />
4. Product destruction<br />
Potential Accidents or<br />
<strong>Hazard</strong>s<br />
1. Driving hazards.<br />
2a. Cuts/lacerations from<br />
broken glass.<br />
2b. Chemical irritation<br />
from broken containers.<br />
3a. Too hot/too cold.<br />
3b. Inadequate lighting.<br />
3c. Trip hazards from<br />
crowded room.<br />
3d. Head injuries from<br />
overhead obstacles.<br />
4a. Laceration from box<br />
cutters.<br />
4b. Lower back injury from<br />
lifting surveyed items.<br />
Preventative Measures<br />
1. Wear seat belt. Pay<br />
attention to road<br />
signs.<br />
Drive defensively.<br />
2a & b. Wear gloves,<br />
mask, and eye<br />
protection.<br />
3a. Dress appropriately<br />
for the stores<br />
condition.<br />
3b. Relocate survey<br />
items to a well lit<br />
area.<br />
3c & 3d. Be aware of<br />
environment and<br />
surroundings. Take your<br />
time when walking into<br />
crowded area.<br />
4a. Wear leather gloves<br />
and ensure you know<br />
where both hands are<br />
before using cutter.<br />
4b. Use proper lifting<br />
techniques and<br />
mechanical devices when<br />
necessary.
DOCUMENTING a <strong>JHA</strong><br />
• <strong>JHA</strong>s can be written & saved in ESAMS<br />
• Approved <strong>JHA</strong>s in ESAMS provide excellent examples of<br />
specific job tasks<br />
• For detailed steps for creating & inputting <strong>JHA</strong>s into ESAMS<br />
contact <strong>MCCS</strong> Safety.
DOCUMENTING a <strong>JHA</strong><br />
• Review Recent/Approved <strong>JHA</strong>
QUIZ<br />
1. Employees are not involved in the <strong>JHA</strong> process.<br />
a. True<br />
b. False<br />
2. Step 1 in doing a <strong>JHA</strong> is<br />
a. Determine the root cause<br />
b. Identify <strong>Hazard</strong>s<br />
c. Eliminate hazards<br />
3. Name three mitigation techniques to eliminate hazards.<br />
a. ______________<br />
b. ______________<br />
c. ______________
Summary<br />
• The information provided was intended to<br />
assist Directors, Department heads,<br />
Supervisors and Managers by;<br />
1. Using the 5 step process in conducting your<br />
<strong>JHA</strong><br />
2. Reducing the occurrence of workplace<br />
injuries by using the <strong>JHA</strong><br />
3. Increasing worker productivity and morale<br />
4. Maintaining compliance with regulatory<br />
agencies.
QUIZ Answers<br />
1. Employees are not involved in the <strong>JHA</strong> process.<br />
b. False<br />
2. The first step in doing a <strong>JHA</strong> is<br />
b. Identify <strong>Hazard</strong>s<br />
3. Name three mitigation techniques to eliminate hazards.<br />
a. Engineering<br />
b. Administrative<br />
c. PPE