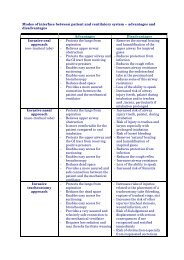
Pyrexia - PACT - ESICM
Pyrexia - PACT - ESICM
Pyrexia - PACT - ESICM
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Task 1. Assessing and measuring fever in ICU<br />
Stavem K, Saxholm H, Smith-Erichsen N. Accuracy of infrared ear thermometry<br />
in adult patients. Intensive Care Med 1997; 23(1): 100–105. PMID<br />
9037647<br />
Giuliano KK, Scott SS, Elliot S, Giuliano AJ. Temperature measurement in<br />
critically ill orally intubated adults: a comparison of pulmonary artery<br />
core, tympanic, and oral methods. Crit Care Med 1999; 27(10): 2188–<br />
2193. PMID 10548205<br />
Bridges E, Thomas K. Noninvasive measurement of body temperature in critically<br />
ill patients. Crit Care Nurse 2009; 29(3): 94–97. PMID 19487784<br />
An 86-year-old lady with multiple trauma receiving mechanical<br />
ventilation for two weeks develops fever (green line, °C), without tachycardia<br />
(blue line, b/min). The recording is from the bedside computer monitor,<br />
visualising continuous measurements (vertical lines are days). There is a diurnal<br />
pattern. The diagnosis made was ventilator-associated pneumonia attributable<br />
to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The blue arrow indicates the day of starting<br />
piperacillin and tobramycin, and the ‘lytic’ resolution of the fever is illustrated.<br />
Heart rate b/min<br />
Body temperature C<br />
Laboratory appraisal<br />
The clinical assessment is supplemented by selected laboratory measurements.<br />
The commonest of these is the leukocyte and differential counts as signs of<br />
infection include leukocytosis and a ‘left shift’. Investigators have searched for<br />
specific ‘sepsis’ markers including circulating C-reactive protein, procalcitonin<br />
and the cytokine, interleukin-6. Although the exact predictive values remain<br />
uncertain, some of these plasma factors can help to forecast the likelihood of<br />
microbial infection in a patient with fever, before the results of Gram stains, and<br />
particularly microbiological cultures, are available. On day six after trauma or<br />
surgery, development of fever and persistently high circulating IL-6 and C-<br />
reactive protein levels may be predictive for nosocomial infection. Similarly, the<br />
detection of endotoxaemia by means of rapid assay techniques may be of some<br />
predictive value in Gram-negative infection/bacteraemia and its associated<br />
morbidity.<br />
The following papers address the (limited) value of surrogate indicators of<br />
microbial infection.<br />
[8]