2 End-of-chapter test - Macmillan Academy
2 End-of-chapter test - Macmillan Academy
2 End-of-chapter test - Macmillan Academy
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
2 <strong>End</strong>-<strong>of</strong>-<strong>chapter</strong> <strong>test</strong><br />
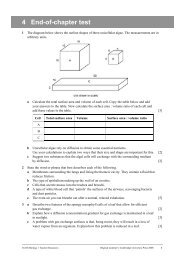
1 The diagram below shows part <strong>of</strong> the cell surface (plasma) membrane.<br />
B<br />
D<br />
E<br />
A<br />
C<br />
a Identify the structures labelled A, B, C, D and E. [5]<br />
b State one function <strong>of</strong> the structure labelled C. [1]<br />
c Cell membranes are said to have a fluid mosaic structure.<br />
Explain the meaning <strong>of</strong> fluid mosaic. [2]<br />
d Some <strong>of</strong> the fatty-acid tails <strong>of</strong> the phospholipids in the membrane are saturated,<br />
while others are unsaturated. What effect does the proportion <strong>of</strong> unsaturated fattyacid<br />
tails have on the properties <strong>of</strong> the membrane [1]<br />
e State two functions <strong>of</strong> membrane glycoproteins. [2]<br />
2 Copy and complete the following account about cell signalling.<br />
There are three main ways that receptors in the cell membrane are involved in cell signalling.<br />
The receptor may form an ion channel. For example, the transmitter substance acetylcholine is<br />
released by nerve cells at a ________________. At the membrane <strong>of</strong> the next nerve cell, it binds<br />
to a receptor and causes ________________ ions to flood into the second cell, starting a new<br />
nerve impulse.<br />
A second mechanism is when the receptor itself acts as an enzyme. For example, the hormone<br />
________________ binds with the enzyme tyrosine kinase, causing glucose to be changed into<br />
________________ in liver cells.<br />
A third mechanism involves a substance in the membrane called a ________________.<br />
When this is activated, it triggers a series <strong>of</strong> reactions. The hormone adrenaline is<br />
detected by liver cells in this way, causing the conversion <strong>of</strong> ________________<br />
into glucose. [6]<br />
3 a Explain the meaning <strong>of</strong> the term diffusion. [2]<br />
b Polar molecules such as glucose can cross membranes by facilitated diffusion.<br />
What are the differences between this mechanism and ordinary diffusion [2]<br />
4 In relation to plant cells, explain the meaning <strong>of</strong> the following terms:<br />
a osmosis<br />
b pressure potential<br />
c turgid<br />
d plasmolysis. [4]<br />
COAS Biology 1 Teacher Resources Original material © Cambridge University Press 2008 1
2 <strong>End</strong>-<strong>of</strong>-<strong>chapter</strong> <strong>test</strong><br />
5 What would happen if a plant cell with a water potential <strong>of</strong> –300 kPa were placed in the<br />
following:<br />
a distilled water<br />
b a sucrose solution with a water potential <strong>of</strong> –2000 kPa.<br />
Explain your answers. [4]<br />
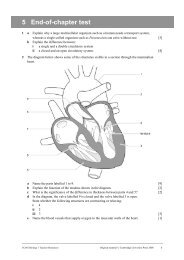
6 Three <strong>test</strong> tubes were labelled A, B and C. 10 cm 3 <strong>of</strong> distilled water was placed in tube A;<br />
10 cm 3 <strong>of</strong> a 0.85% salt solution was placed in tube B; 10 cm 3 <strong>of</strong> a 2% salt solution was placed<br />
in tube C. 1 cm 3 <strong>of</strong> fresh blood was then added to each <strong>of</strong> the tubes. The contents <strong>of</strong> the tubes<br />
were shaken and spun in a centrifuge for 5 minutes to separate any blood cells from the<br />
solutions. The results are shown in the diagram below.<br />
a Explain the appearance <strong>of</strong> the contents <strong>of</strong> tube A after centrifuging. [3]<br />
b Blood plasma has a salt concentration <strong>of</strong> about 0.85%. If you were to look through a<br />
microscope at red blood cells taken from the precipitates in tubes B and C, describe how<br />
they would differ in appearance. [2]<br />
c Patients who have suffered severe burns lose fluid through the damaged skin. To treat this,<br />
patients can be given transfusions <strong>of</strong> isotonic saline solution through a drip.<br />
i Explain the meaning <strong>of</strong> isotonic saline solution. [1]<br />
ii Explain why it is important that the solution is isotonic. [2]<br />
7 Describe one similarity and two differences between facilitated diffusion and<br />
active transport. [3]<br />
8 Digestive enzymes are secreted from the cells <strong>of</strong> the pancreas by exocytosis.<br />
Describe this process. [3]<br />
9 A pea plant was grown in a sample <strong>of</strong> soil. The concentration <strong>of</strong> nitrate ions (NO 3 – ) in the soil<br />
water was measured, and found to be 2 mmol dm –3 . The concentration <strong>of</strong> nitrate ions inside a<br />
root cell <strong>of</strong> the pea plant was 29 mmol dm –3 . The inside <strong>of</strong> the root cell was also found to be<br />
negatively charged compared with the outside <strong>of</strong> the cell. State the most likely mechanism that<br />
would account for the uptake <strong>of</strong> nitrate ions by the plant, giving two reasons for your answer. [3]<br />
Total:<br />
46<br />
Score: %<br />
Grade boundaries: 80% A, 70% B, 60% C, 50% D, 40% E<br />
COAS Biology 1 Teacher Resources Original material © Cambridge University Press 2008 2