Spirant approximants in Galician - ResearchGate
Spirant approximants in Galician - ResearchGate
Spirant approximants in Galician - ResearchGate
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
62 E. Martínez-Celdrán & X. L. Regueira<br />
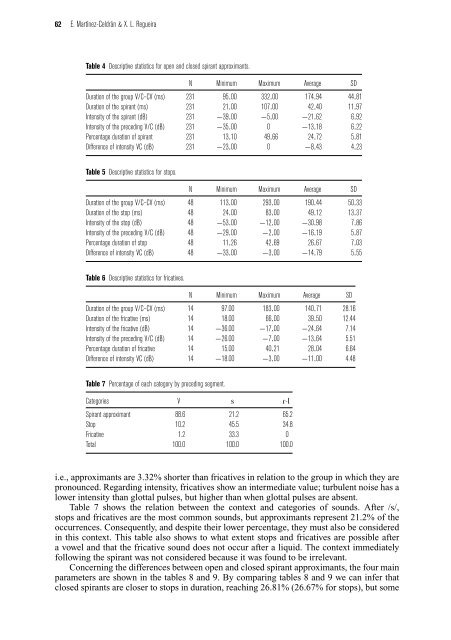
Table 4 Descriptive statistics for open and closed spirant <strong>approximants</strong>.<br />
N M<strong>in</strong>imum Maximum Average SD<br />
Duration of the group V/C–CV (ms) 231 95.00 332.00 174.94 44.81<br />
Duration of the spirant (ms) 231 21.00 107.00 42.40 11.97<br />
Intensity of the spirant (dB) 231 −39.00 −5.00 −21.62 6.92<br />
Intensity of the preced<strong>in</strong>g V/C (dB) 231 −35.00 0 −13.18 6.22<br />
Percentage duration of spirant 231 13.10 49.66 24.72 5.81<br />
Difference of <strong>in</strong>tensity VC (dB) 231 −23.00 0 −8.43 4.23<br />
Table 5 Descriptive statistics for stops.<br />
N M<strong>in</strong>imum Maximum Average SD<br />
Duration of the group V/C–CV (ms) 48 113.00 293.00 190.44 50.33<br />
Duration of the stop (ms) 48 24.00 83.00 49.12 13.37<br />
Intensity of the stop (dB) 48 −53.00 −12.00 −30.98 7.86<br />
Intensity of the preced<strong>in</strong>g V/C (dB) 48 −29.00 −2.00 −16.19 5.87<br />
Percentage duration of stop 48 11.26 42.69 26.67 7.03<br />
Difference of <strong>in</strong>tensity VC (dB) 48 −33.00 −3.00 −14.79 5.55<br />
Table 6 Descriptive statistics for fricatives.<br />
N M<strong>in</strong>imum Maximum Average SD<br />
Duration of the group V/C–CV (ms) 14 97.00 183.00 140.71 28.16<br />
Duration of the fricative (ms) 14 18.00 66.00 39.50 12.44<br />
Intensity of the fricative (dB) 14 −36.00 −17.00 −24.64 7.14<br />
Intensity of the preced<strong>in</strong>g V/C (dB) 14 −26.00 −7.00 −13.64 5.51<br />
Percentage duration of fricative 14 15.00 40.21 28.04 6.64<br />
Difference of <strong>in</strong>tensity VC (dB) 14 −18.00 −3.00 −11.00 4.48<br />
Table 7 Percentage of each category by preced<strong>in</strong>g segment.<br />
Categories V s |-l<br />
<strong>Spirant</strong> approximant 88.6 21.2 65.2<br />
Stop 10.2 45.5 34.8<br />
Fricative 1.2 33.3 0<br />
Total 100.0 100.0 100.0<br />
i.e., <strong>approximants</strong> are 3.32% shorter than fricatives <strong>in</strong> relation to the group <strong>in</strong> which they are<br />
pronounced. Regard<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>tensity, fricatives show an <strong>in</strong>termediate value; turbulent noise has a<br />
lower <strong>in</strong>tensity than glottal pulses, but higher than when glottal pulses are absent.<br />
Table 7 shows the relation between the context and categories of sounds. After /s/,<br />
stops and fricatives are the most common sounds, but <strong>approximants</strong> represent 21.2% of the<br />
occurrences. Consequently, and despite their lower percentage, they must also be considered<br />
<strong>in</strong> this context. This table also shows to what extent stops and fricatives are possible after<br />
a vowel and that the fricative sound does not occur after a liquid. The context immediately<br />
follow<strong>in</strong>g the spirant was not considered because it was found to be irrelevant.<br />
Concern<strong>in</strong>g the differences between open and closed spirant <strong>approximants</strong>, the four ma<strong>in</strong><br />
parameters are shown <strong>in</strong> the tables 8 and 9. By compar<strong>in</strong>g tables 8 and 9 we can <strong>in</strong>fer that<br />
closed spirants are closer to stops <strong>in</strong> duration, reach<strong>in</strong>g 26.81% (26.67% for stops), but some