CooCox CoOS User's Guide
CooCox CoOS User's Guide
CooCox CoOS User's Guide
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
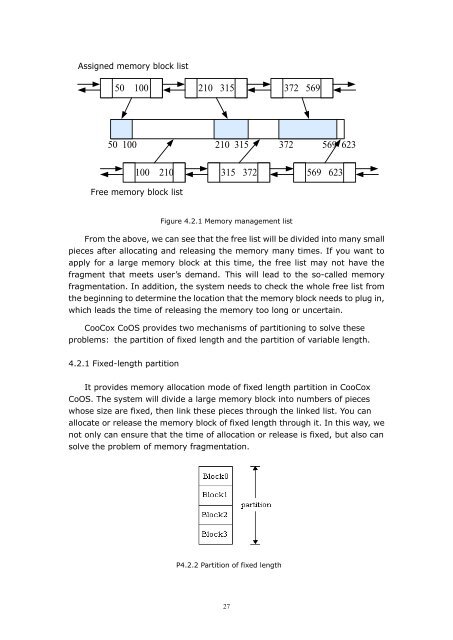
Assigned memory block list<br />
50 100 210 315 372 569<br />
50 100 210 315 372 569 623<br />
100 210 315 372 569 623<br />
Free memory block list<br />
Figure 4.2.1 Memory management list<br />
From the above, we can see that the free list will be divided into many small<br />
pieces after allocating and releasing the memory many times. If you want to<br />
apply for a large memory block at this time, the free list may not have the<br />
fragment that meets user’s demand. This will lead to the so-called memory<br />
fragmentation. In addition, the system needs to check the whole free list from<br />
the beginning to determine the location that the memory block needs to plug in,<br />
which leads the time of releasing the memory too long or uncertain.<br />
<strong>CooCox</strong> <strong>CoOS</strong> provides two mechanisms of partitioning to solve these<br />
problems: the partition of fixed length and the partition of variable length.<br />
4.2.1 Fixed-length partition<br />
It provides memory allocation mode of fixed length partition in <strong>CooCox</strong><br />
<strong>CoOS</strong>. The system will divide a large memory block into numbers of pieces<br />
whose size are fixed, then link these pieces through the linked list. You can<br />
allocate or release the memory block of fixed length through it. In this way, we<br />
not only can ensure that the time of allocation or release is fixed, but also can<br />
solve the problem of memory fragmentation.<br />
P4.2.2 Partition of fixed length<br />
27