Study Guide for James' AP1, Exam 1
Study Guide for James' AP1, Exam 1
Study Guide for James' AP1, Exam 1
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
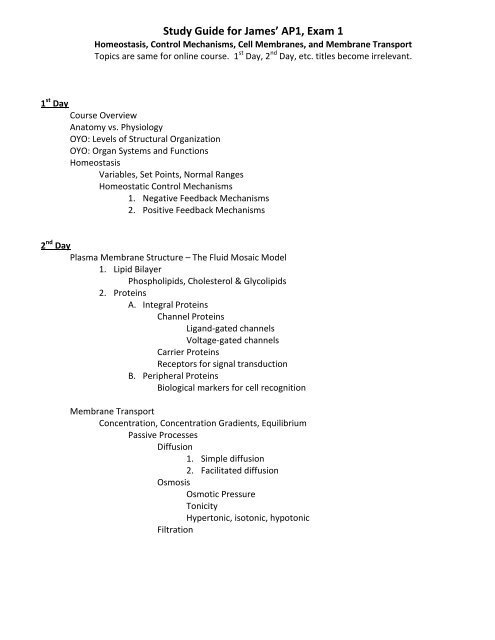
<strong>Study</strong> <strong>Guide</strong> <strong>for</strong> James’ <strong>AP1</strong>, <strong>Exam</strong> 1<br />
Homeostasis, Control Mechanisms, Cell Membranes, and Membrane Transport<br />
Topics are same <strong>for</strong> online course. 1 st Day, 2 nd Day, etc. titles become irrelevant.<br />
1 st Day<br />
Course Overview<br />
Anatomy vs. Physiology<br />
OYO: Levels of Structural Organization<br />
OYO: Organ Systems and Functions<br />
Homeostasis<br />
Variables, Set Points, Normal Ranges<br />
Homeostatic Control Mechanisms<br />
1. Negative Feedback Mechanisms<br />
2. Positive Feedback Mechanisms<br />
2 nd Day<br />
Plasma Membrane Structure – The Fluid Mosaic Model<br />
1. Lipid Bilayer<br />
Phospholipids, Cholesterol & Glycolipids<br />
2. Proteins<br />
A. Integral Proteins<br />
Channel Proteins<br />
Ligand-gated channels<br />
Voltage-gated channels<br />
Carrier Proteins<br />
Receptors <strong>for</strong> signal transduction<br />
B. Peripheral Proteins<br />
Biological markers <strong>for</strong> cell recognition<br />
Membrane Transport<br />
Concentration, Concentration Gradients, Equilibrium<br />
Passive Processes<br />
Diffusion<br />
1. Simple diffusion<br />
2. Facilitated diffusion<br />
Osmosis<br />
Osmotic Pressure<br />
Tonicity<br />
Hypertonic, isotonic, hypotonic<br />
Filtration
3 rd Day<br />
Membrane Transport (cont.)<br />
Active Processes<br />
Primary Active Transport<br />
Vesicular Active Transport<br />
Exocytosis<br />
Endocytosis<br />
a. Phagocytosis<br />
b. Pinocytosis<br />
Specificity<br />
Competition<br />
Saturation<br />
Transport Maximum<br />
4 th Day<br />
Organic Compounds<br />
OYO: from handout: Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins<br />
Tissue Types<br />
Epithelial<br />
Muscular<br />
Nervous<br />
Connective<br />
Chemical Reactions<br />
Synthesis<br />
Decomposition<br />
Exchange<br />
Oxidation-Reduction<br />
5 th Day – EXAM #1
Terminology – Having a good command of these terms enables you to speak intelligently about these<br />
topics. *This is NOT an all-inclusive list but it’s a good start. Please add more terms as you see fit.<br />
Anatomy<br />
Physiology Filtration<br />
Organelle Solutes<br />
Tissue<br />
Organ Active membrane transport processes<br />
Organ system Active transport (Primary active transport)<br />
Interdependency Vesicular transport<br />
Homeostasis Exocytosis<br />
Variables Endocytosis<br />
Negative feedback mechanism Vesicle<br />
Receptor Phagocytosis<br />
Effector Pinocytosis<br />
Control center<br />
Effector T-SNARE proteins<br />
Positive Feedback mechanism Clathrin proteins<br />
V-SNARE proteins<br />
Plasma membrane (cell membrane)<br />
Fluid mosaic model Specificity<br />
Lipid bilayer Competition<br />
Phospholipid Saturation<br />
Hydrophilic Transport Max<br />
Integral protein<br />
Peripheral protein Carbohydrates<br />
Carrier protein (transport Protein) Glucose<br />
Non-gated channel protein Lipids<br />
Gated channel protein Triglycerides<br />
Non-gated channel protein Proteins<br />
Gated channel protein Amino acids<br />
Voltage-gated channel protein Structural proteins<br />
Ligand-gated channel protein Functional proteins<br />
Receptor protein<br />
Glycoprotein Epithelial tissue<br />
Glycocalyx “free” body surfaces<br />
Muscle tissue<br />
Concentration Fibers<br />
Concentration as a percentage Myofilaments<br />
Concentration expressed as milliosmoles Actin & myosin<br />
Concentration gradient Nervous tissue<br />
Equilibrium Neuroglia<br />
Connective tissue<br />
Passive membrane transport processes<br />
Simple diffusion Reactants vs. End products vs. catalysts<br />
Facilitated diffusion Synthesis (anabolic) reaction)<br />
Net diffusion Decomposition (catabolic reaction)<br />
Osmosis Exchange reaction<br />
Osmotic pressure Oxidation-reduction reaction<br />
Tonicity<br />
Isotonic vs. Hypertonic vs. Hypotonic
Essays – You should be able to respond in a coherent and logical manner to each of the following. Pretend<br />
you’re explaining this topic to someone who was not in class. When you can do this without memorizing<br />
your answers and the listener/reader can make sense of it then you have truly learned and understand.<br />
1. Tell me all you know about NFBMs.<br />
2. Tell me all you know about PFBMs.<br />
3. Tell me all you know about homeostasis.<br />
4. Tell me all you know about osmosis.<br />
5. Tell me all you know about filtration.<br />
6. Tell me all you know about primary active transport.