Download PDF, 1'488 KB - COST Action 850
Download PDF, 1'488 KB - COST Action 850
Download PDF, 1'488 KB - COST Action 850
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Transcriptome analysis of nematode,<br />
Steinernema carpocapsae induced by<br />
insect haemolymph<br />
Y- J. Hao, R.Montiel, G. Nasimento, N. Simoes<br />
CIRN and Department of Biology,Univesity of the Azores<br />
Ponda Delgada, Portugal<br />
nkhyjin@yahoo.com.cn
Today’s outline<br />
~ 100 laboratories in<br />
more than 60 countries<br />
are currently involved<br />
in EPN-EPB research
Taxonomy<br />
Application<br />
Behavioral<br />
ecology<br />
Phylogenetics<br />
Biochemistry<br />
Biogeography<br />
Physiology<br />
Ecology<br />
Molecular<br />
biology<br />
Genetics
Life Cycle
Alternative of Insecticide<br />
Extraordinarily lethal for<br />
soil insect pests.<br />
Groundwater contamination,<br />
chemical trespass, and<br />
pollinators are not issues<br />
Safe for plants and animals.<br />
Unlike chemicals, nematode<br />
applications do not require<br />
masks or other safety<br />
equipment
Focal Spot
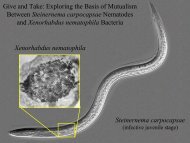
Steinernema carpocapsae<br />
Most studied, available<br />
versatile of all EPN<br />
Effective against lepidoterous<br />
larvae : various webworm,<br />
cutworm, armyworms, girdlers<br />
and wood-borers
"ambush" forager, standing<br />
on its tail in an upright position<br />
near the soil surface.<br />
Effective against highly<br />
mobile surface-adapted<br />
insects.<br />
Highly responsive to CO2:<br />
the spiracles are a key<br />
portal of host entry.
So ……<br />
HELP EACH OTHER<br />
Generally speaking,<br />
nematode can’t kill<br />
insect<br />
Symbiotic bacteria<br />
can kill and digest<br />
insects<br />
But- bacteria<br />
can’t penetrate<br />
insects…
Is nematode –bacteria complex necessary <br />
<br />
symbiotic
Free-living Nematode<br />
S. carpocapsae<br />
isolated from Azores<br />
can kill some insect<br />
species.
How can<br />
S. carpocapsae survive<br />
Multiply under<br />
continuously attacks of<br />
their host’s immune<br />
system What is their<br />
immune evasion<br />
strategies
OBJECTIVE<br />
Genes and gene<br />
products involved<br />
in nematode-host<br />
interaction<br />
Virulence mechanisms<br />
of gene products
APPROACH<br />
Molecular Biology<br />
Bioinformatics<br />
Biochemistry
BIOINFORMATICS<br />
cDNA Sequence<br />
Bioinformation analysis: ORF prediction<br />
Homology comparison<br />
Function prediction
PARTIAL RESULTS
Differencial expression<br />
EST database construction<br />
Select interesting EST<br />
Full length cDNA<br />
Gene expression<br />
Biochemistry assays
ACKNOWLEDMENTS<br />
This work was supported by the<br />
Grant of FCT (Fundacao para a<br />
Ciencia e a Tecnologia) of<br />
Portugal though BPD/21079/2004
THANKS