Pulpal Diagnosis - University at Buffalo
Pulpal Diagnosis - University at Buffalo
Pulpal Diagnosis - University at Buffalo
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Eugene A. Pantera, Jr., DDS, MS<br />
Department of Periodontics and Endodontics<br />
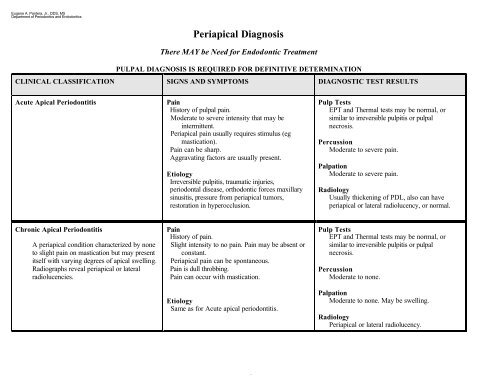
Periapical <strong>Diagnosis</strong><br />
There MAY be Need for Endodontic Tre<strong>at</strong>ment<br />
PULPAL DIAGNOSIS IS REQUIRED FOR DEFINITIVE DETERMINATION<br />
CLINICAL CLASSIFICATION SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS DIAGNOSTIC TEST RESULTS<br />
Acute Apical Periodontitis<br />
Pain<br />
History of pulpal pain.<br />
Moder<strong>at</strong>e to severe intensity th<strong>at</strong> may be<br />
intermittent.<br />
Periapical pain usually requires stimulus (eg<br />
mastic<strong>at</strong>ion).<br />
Pain can be sharp.<br />
Aggrav<strong>at</strong>ing factors are usually present.<br />
Etiology<br />
Irreversible pulpitis, traum<strong>at</strong>ic injuries,<br />
periodontal disease, orthodontic forces maxillary<br />
sinusitis, pressure from periapical tumors,<br />
restor<strong>at</strong>ion in hyperocclusion.<br />
Pulp Tests<br />
EPT and Thermal tests may be normal, or<br />
similar to irreversible pulpitis or pulpal<br />
necrosis.<br />
Percussion<br />
Moder<strong>at</strong>e to severe pain.<br />
Palp<strong>at</strong>ion<br />
Moder<strong>at</strong>e to severe pain.<br />
Radiology<br />
Usually thickening of PDL, also can have<br />
periapical or l<strong>at</strong>eral radiolucency, or normal.<br />
Chronic Apical Periodontitis<br />
A periapical condition characterized by none<br />
to slight pain on mastic<strong>at</strong>ion but may present<br />
itself with varying degrees of apical swelling.<br />
Radiographs reveal periapical or l<strong>at</strong>eral<br />
radiolucencies.<br />
Pain<br />
History of pain.<br />
Slight intensity to no pain. Pain may be absent or<br />
constant.<br />
Periapical pain can be spontaneous.<br />
Pain is dull throbbing.<br />
Pain can occur with mastic<strong>at</strong>ion.<br />
Etiology<br />
Same as for Acute apical periodontitis.<br />
Pulp Tests<br />
EPT and Thermal tests may be normal, or<br />
similar to irreversible pulpitis or pulpal<br />
necrosis.<br />
Percussion<br />
Moder<strong>at</strong>e to none.<br />
Palp<strong>at</strong>ion<br />
Moder<strong>at</strong>e to none. May be swelling.<br />
Radiology<br />
Periapical or l<strong>at</strong>eral radiolucency.<br />
4