Energy Minimization Methods
Energy Minimization Methods
Energy Minimization Methods
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
4<br />
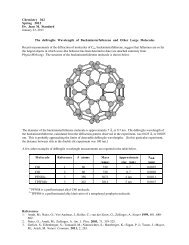
<strong>Energy</strong> <strong>Minimization</strong> Tolerances<br />
An energy minimization usually is carried out on a computer until the gradients (slopes) for all the coordinates are<br />
within some tolerance. For example, the default tolerance may be set so that the absolute value of the gradient must<br />
be less than or equal to 0.1 kcal/mol-Å. This means that in most cases, the computer will not find exactly the<br />
minimum (in the example below, at x=1.000 Å) but something very close.<br />
0.004<br />
<strong>Energy</strong> (kcal/mol)<br />
0.003<br />
0.002<br />
0.001<br />
0<br />
0.98 0.99 1 1.01 1.02<br />
x (angstroms)<br />
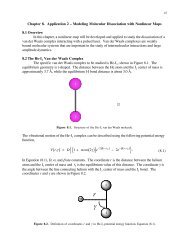
Figure 4. Example potential for bond stretching.<br />
For the example potential in Figure 4, suppose an energy minimization starts out with x=1.06 Å and after a few<br />
steps, it has reached the point x=1.01 Å. At each point in the minimization, the computer checks the gradients<br />
(slopes) to see if the tolerance has been reached. For the point x=1.01 Å in this example, we can estimate the slope<br />
by drawing a tangent line at that point and calculating the slope as Δy/Δx. For x=1.01Å, the slope of the tangent line<br />
comes out to about 0.21 kcal/mol-Å, so the minimization is not complete.<br />
If the minimization then continues for a few more steps and eventually reaches the point x=1.005 Å, an estimate of<br />
the slope of the tangent line at this point yields about –0.10 kcal/mol-Å. Therefore, since the absolute value of the<br />
slope is equal to the tolerance, the minimization would stop. For this example, the computer would find any<br />
geometry within the range of 0.995 – 1.005 Å as being numerically acceptable for the minimized geometry.<br />
If the range of geometries for which the gradient tolerance is satisfied (in this case, 0.005 Å) is too large, the<br />
tolerance can be made smaller in the software package and the minimization can be run again in order to find a<br />
geometry closer to the actual minimum.<br />
In addition to tolerance for the gradient, an energy minimization also usually includes tolerances for the energy.<br />
That is, a check is usually made to ensure that the energy of the minimized structure is the same as the previous step<br />
to within a certain tolerance. For example, a particular minimization might require the energy to be converged to<br />
within 0.01 kJ/mol.