- Page 3:
Network Warrior
- Page 6 and 7:
Network Warrior, Second Edition by
- Page 8 and 9:
Configuring Trunks 42 IOS 42 CatOS
- Page 10 and 11:
Nexus and HSRP 189 GLBP 189 Object
- Page 12 and 13:
Bipolar Violation 362 CRC6 363 Erro
- Page 14 and 15:
Configuring Contexts 486 Interfaces
- Page 16 and 17:
Nonpriority Queue Too Large 624 Def
- Page 18 and 19:
Environmental 729 Leadership and Me
- Page 20 and 21:
I faced a very tough decision when
- Page 22 and 23:
Using Code Examples This book is he
- Page 24 and 25:
would not be published today. Her d
- Page 27 and 28:
CHAPTER 1 What Is a Network Before
- Page 29:
WAN A WAN is a network that is used
- Page 32 and 33:
I was surprised to learn that there
- Page 34 and 35:
equired. Collisions are also limite
- Page 36 and 37:
Hubs have a lot of drawbacks, and m
- Page 38 and 39:
destination MAC address and checks
- Page 40 and 41:
Switch Types Cisco switches can be
- Page 42 and 43:
Planning a Chassis-Based Switch Ins
- Page 44 and 45:
Installing and removing modules Mod
- Page 46 and 47:
How Autonegotiation Works First, le
- Page 48 and 49:
Figure 3-2. Full duplex frames cons
- Page 50 and 51:
Once you’ve set the speed, you ca
- Page 52 and 53:
Figure 4-1. VLANs on a switch Figur
- Page 54 and 55:
Another way to route between VLANs
- Page 56 and 57:
There are a lot of options when cre
- Page 58 and 59:
To create a VLAN, give the vlan com
- Page 60 and 61:
1004 fddinet-default act/unsup 1005
- Page 62 and 63:
This automatically puts us into int
- Page 64 and 65:
How Trunks Work Figure 5-2 is a vis
- Page 66 and 67:
Which Protocol to Use Why are there
- Page 68 and 69:
The default mode for most Cisco swi
- Page 70 and 71:
The output of show interface trunk
- Page 72 and 73:
Switch-2# (enable)clear trunk 3/5 1
- Page 75 and 76:
CHAPTER 6 VLAN Trunking Protocol In
- Page 77 and 78:
Switches with mismatched VTP domain
- Page 79 and 80:
Figure 6-3. Broadcast sent to all s
- Page 81 and 82:
In larger, more dynamic environment
- Page 83 and 84:
3750-IOS(config)#vtp mode client S
- Page 85 and 86:
IOS VTP pruning is enabled with the
- Page 87:
NX-OS NX-OS does not support VTP pr
- Page 90 and 91:
Figure 7-1. EtherChannel on IOS and
- Page 92 and 93:
• The source and destination port
- Page 94 and 95:
The only solutions for this problem
- Page 96 and 97:
Switch-2-CatOS: (enable)sho channel
- Page 98 and 99:
Port-channel: Po1 ------------ Age
- Page 100 and 101:
Input flow-control is off, output f
- Page 102 and 103:
Figure 7-6. VSS MEC versus Nexus vP
- Page 104 and 105:
Technically, you could bond port ch
- Page 106 and 107:
5 Po14 up success success 3-7,9 6 P
- Page 108 and 109:
The computer on Switch A sends out
- Page 110 and 111:
The numbers on the left side of the
- Page 112 and 113:
0 input packets with dribble condit
- Page 114 and 115:
Preventing Loops with Spanning Tree
- Page 116 and 117:
Figure 8-4. BPDU format Every port
- Page 118 and 119:
Root ID Priority 24577 Address 0009
- Page 120 and 121:
Here is the same command as seen on
- Page 122 and 123:
To disable PortFast on an interface
- Page 124 and 125:
UplinkFast should be configured onl
- Page 126 and 127:
If BackboneFast is used, it must be
- Page 128 and 129:
Figure 8-9. Unidirectional link pro
- Page 130 and 131:
Designing to Prevent Spanning Tree
- Page 132 and 133:
outer. Router is the term I will ge
- Page 134 and 135:
When a packet arrives at a router,
- Page 136 and 137:
Gateway of last resort is 11.0.0.1
- Page 138 and 139:
Subnet Subnets are indented under t
- Page 140 and 141:
Supernet (Group of Major Networks)
- Page 142 and 143:
Now I’ll assign a different inter
- Page 145 and 146:
CHAPTER 10 Routing Protocols A rout
- Page 147 and 148:
There may be more than one type of
- Page 149 and 150:
Metrics and Protocol Types The job
- Page 151 and 152:
Figure 10-6. OSPF uses bandwidth to
- Page 153 and 154:
Looking at Table 10-1, you can see
- Page 155 and 156:
is learned on one permanent virtual
- Page 157 and 158:
By default, no interfaces are inclu
- Page 159 and 160:
• Updates in RIPv2 are sent using
- Page 161 and 162:
As with all IGPs, you list the inte
- Page 163 and 164:
D 192.168.3.0/24 [90/2195456] via 1
- Page 165 and 166:
Autonomous System External (ASE) LS
- Page 167 and 168:
outers are assumed to be connected
- Page 169 and 170:
OSPF Router with ID (192.168.1.116)
- Page 171 and 172:
Dampening enabled. 2687 history pat
- Page 173 and 174:
CHAPTER 11 Redistribution Redistrib
- Page 175 and 176:
Regardless of which protocol you re
- Page 177 and 178:
Gateway of last resort is not set C
- Page 179 and 180:
Here are the arguments required for
- Page 181 and 182:
If you do not specify a default met
- Page 183 and 184:
outer ospf 100 redistribute eigrp 1
- Page 185 and 186:
autonomous systems using the same r
- Page 187 and 188:
P 10.10.10.0/24, 1 successors, FD i
- Page 189 and 190:
Gateway of last resort is not set 5
- Page 191 and 192:
Gateway of last resort is not set 5
- Page 193 and 194:
CHAPTER 12 Tunnels A tunnel is a me
- Page 195 and 196:
Figure 12-1. Simple network Given t
- Page 197 and 198:
Keepalive not set Tunnel source 10.
- Page 199 and 200:
To prove that the tunnel is running
- Page 201 and 202:
Router D: interface Loopback0 ip ad
- Page 203 and 204:
down the tunnel. Unfortunately, it
- Page 205:
PIX firewalls also support the keyw
- Page 208 and 209:
The details of Cisco’s HSRP can b
- Page 210 and 211:
To enable this behavior, you must c
- Page 212 and 213:
On each router, we have added the s
- Page 214 and 215:
Figure 13-5. HSRP limitations Metro
- Page 216 and 217:
of 1,024 GLBP groups per router int
- Page 218 and 219:
Weighting is used both for load dis
- Page 220 and 221:
Another nice GLBP command is show g
- Page 222 and 223:
If we wanted GLBP to enable the for
- Page 224 and 225:
metric route-type tag Match metric
- Page 226 and 227:
We used to be able to do AND operat
- Page 228 and 229:
simply provides the best path to th
- Page 230 and 231:
Policy routing overrides the routin
- Page 233 and 234:
CHAPTER 15 Switching Algorithms in
- Page 235 and 236:
Process Switching The original meth
- Page 237 and 238:
a. Is the destination reachable b.
- Page 239 and 240:
The drawbacks of this implementatio
- Page 241 and 242:
The term trie comes from the word r
- Page 243 and 244:
IP fast switching on the same inter
- Page 245 and 246:
CEF 30 ****************************
- Page 247 and 248:
CHAPTER 16 Multilayer Switches Swit
- Page 249 and 250:
Ethernet ports on routers tend to b
- Page 251 and 252:
Queueing strategy: fifo Output queu
- Page 253 and 254:
Another way to get to the MSFC is w
- Page 255:
A quick word is in order about choo
- Page 258 and 259:
Figure 17-1. Individual versus inte
- Page 260 and 261:
Because it controls the crossbar fa
- Page 262 and 263:
Figure 17-3. Cisco 6509 backplanes
- Page 264 and 265:
the standard 6500 chassis (40 Gbps
- Page 266 and 267:
Supervisor-720 This model represent
- Page 268 and 269:
etween the different buses. Specifi
- Page 270 and 271: CSM for load-balancing needs, but t
- Page 272 and 273: Interface Vlan30 "inside", is up, l
- Page 274 and 275: Intrusion Detection System modules.
- Page 276 and 277: MSFC for Layer-3 functionality, the
- Page 278 and 279: Queueing strategy: fifo Output queu
- Page 280 and 281: Figure 17-9. VSS layout including P
- Page 282 and 283: If you change your mind, just negat
- Page 284 and 285: We can see the status of the VSS cl
- Page 286 and 287: activity interval and global aging
- Page 288 and 289: To reboot only the active switch an
- Page 291 and 292: CHAPTER 18 Cisco Nexus At the time
- Page 293 and 294: 6509 and 6509E had side-to-side air
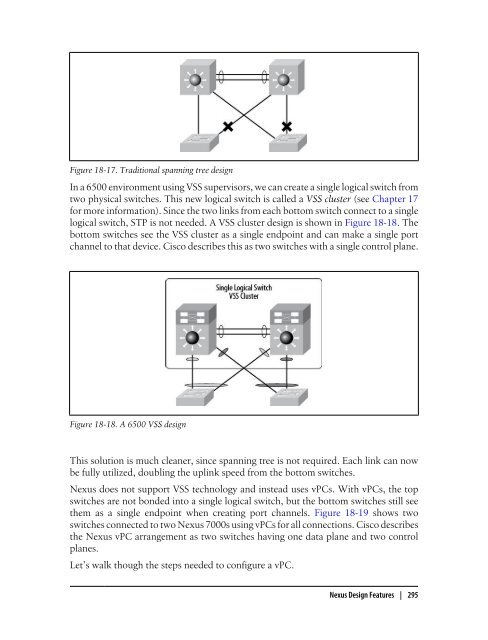
- Page 295 and 296: ports. When mounting switches in ra
- Page 297 and 298: Figure 18-6. Nexus 5010 with power
- Page 299 and 300: Figure 18-8. Nexus 2148 FEX with po
- Page 301 and 302: dhcp Enable/Disable DHCP Snooping d
- Page 303 and 304: No more write memory Cisco has been
- Page 305 and 306: on commands with big outputs, like
- Page 307 and 308: Scalability The Nexus 7000 chassis
- Page 309 and 310: The downside is that it makes the c
- Page 311 and 312: Next, I’ll allocate all 32 ports
- Page 313 and 314: Once I’m connected to the VDC, it
- Page 315 and 316: NX-7K-1-Cozy(config-if)# rate-mode
- Page 317 and 318: Figure 18-15. FEXs attached in cros
- Page 319: The FEX associate command is what d
- Page 323 and 324: And the vPC peer keepalive: NX-7K-2
- Page 325 and 326: Port Mode 1 access access Native Vl
- Page 327 and 328: Imagine two Nexus 5010s, with large
- Page 329 and 330: NX-5K-2(config-sync-sp)# sync-peers
- Page 331 and 332: Here it says that it verified local
- Page 333 and 334: spanning-tree port type edge trunk
- Page 335 and 336: NX-5K-1# config sync NX-5K-1(config
- Page 337 and 338: Name: GAD !Command: Checkpoint cmd
- Page 339 and 340: tell it that we’re using the mana
- Page 341 and 342: Install is in progress, please wait
- Page 343 and 344: CHAPTER 19 Catalyst 3750 Features T
- Page 345 and 346: As it says, I need to reboot, so I
- Page 347 and 348: You create macros are created with
- Page 349 and 350: An easier way to see where macros h
- Page 351 and 352: Storm Control Storm control prevent
- Page 353 and 354: Additionally, the latest releases o
- Page 355 and 356: that this is measured every 200 ms,
- Page 357 and 358: Protect When a violation occurs, th
- Page 359 and 360: 3750(config)#monitor session 1 des
- Page 361 and 362: 3750(config)#no monitor session S
- Page 363 and 364: command. The options are cos and tr
- Page 365 and 366: The interface’s configuration wil
- Page 367 and 368: CHAPTER 20 Telecom Nomenclature The
- Page 369 and 370: Digital refers to a signal that has
- Page 371 and 372:
CSU/DSU CSU stands for Channel Serv
- Page 373 and 374:
Designator Transmission rate Voice
- Page 375 and 376:
Figure 20-4. Different propagation
- Page 377 and 378:
POTS POTS is short for the clever p
- Page 379:
T-carrier T-carrier is the generic
- Page 382 and 383:
T1s are full-duplex links. Voice T1
- Page 384 and 385:
This allows for some interesting er
- Page 386 and 387:
Figure 21-4. One-channel sample T1s
- Page 388 and 389:
Performance Monitoring CSU/DSUs con
- Page 390 and 391:
though again, they are described fo
- Page 392 and 393:
Watch out for assumptions. Router D
- Page 394 and 395:
Not all models of CSU/DSU have all
- Page 396 and 397:
Figure 21-13. Integrated CSU/DSU lo
- Page 398 and 399:
Hardware revision is 0.112, Softwar
- Page 400 and 401:
(ninety-six 15-minute intervals), a
- Page 402 and 403:
clocking, framing, and encoding, wh
- Page 404 and 405:
sends a FEOOF signal back to the so
- Page 406 and 407:
You show the status of the interfac
- Page 408 and 409:
However, because this is a channeli
- Page 410 and 411:
Here, we can see the individual ser
- Page 413 and 414:
CHAPTER 23 Frame Relay Frame Relay
- Page 415 and 416:
dell-see). These DLCIs (and your da
- Page 417 and 418:
Figure 23-4. Frame Relay CIR and DE
- Page 419 and 420:
Figure 23-7. Six-node fully meshed
- Page 421 and 422:
ansi q933a Congestion Avoidance in
- Page 423 and 424:
out pkts dropped 0 out bytes droppe
- Page 425 and 426:
Router-B(config)#int s0/0 Router-B(
- Page 427 and 428:
Local IP addresses mapped to remote
- Page 429 and 430:
Figure 23-12. Three-node Frame Rela
- Page 431 and 432:
00:33:05: Serial0/0(in): Status, my
- Page 433:
Serial0/0.102 (up): point-to-point
- Page 436 and 437:
Because entire packets are prefixed
- Page 438 and 439:
So how do the branches communicate
- Page 440 and 441:
encapsulation ppp auto qos voip tru
- Page 442 and 443:
Wildcard Masks Wildcard masks (also
- Page 444 and 445:
Reflexive access lists, covered lat
- Page 446 and 447:
Here’s an actual example from a P
- Page 448 and 449:
access-list Inbound permit icmp any
- Page 450 and 451:
access-list Inbound line 8 permit i
- Page 452 and 453:
Or using named access lists: ip acc
- Page 454 and 455:
able to communicate only with the d
- Page 456 and 457:
to contain a permit appletalk inste
- Page 458 and 459:
Figure 25-4. Simple access list app
- Page 460 and 461:
Reflexive access lists can only be
- Page 463 and 464:
CHAPTER 26 Authentication in Cisco
- Page 465 and 466:
NX-OS switches work a little differ
- Page 467 and 468:
If you specify a command or menu th
- Page 469 and 470:
e used when minimal security is des
- Page 471 and 472:
CHAP CHAP is more secure than PAP b
- Page 473 and 474:
Two-way authentication. As with PAP
- Page 475 and 476:
Hostname ISP ! username Bob-01 pass
- Page 477 and 478:
Nexus switches seem to be more gear
- Page 479 and 480:
Creating Method Lists A method list
- Page 481 and 482:
If you’re relying on external ser
- Page 483:
interface Serial0/0/0:0 no ip addre
- Page 486 and 487:
high level of security, but like yo
- Page 488 and 489:
term referring to a zone created be
- Page 490 and 491:
Figure 27-2. DMZ connecting to a ve
- Page 492 and 493:
Figure 27-4 shows a simplified layo
- Page 495 and 496:
CHAPTER 28 ASA Firewall Configurati
- Page 497 and 498:
All model ASAs can be configured to
- Page 499 and 500:
In multicontext mode, interface cha
- Page 501 and 502:
Object Groups Object groups allow a
- Page 503 and 504:
access-list In line 1 extended perm
- Page 505 and 506:
Different inspects are enabled by d
- Page 507 and 508:
Figure 28-4. Context types within a
- Page 509 and 510:
Figure 28-6. Another no-shared-inte
- Page 511 and 512:
Figure 28-9. Multiple contexts shar
- Page 513 and 514:
We now find ourselves in the system
- Page 515 and 516:
Type help or '' for a list of avail
- Page 517 and 518:
Maximum VLANs : 200 Inside Hosts :
- Page 519 and 520:
For failover to work, each ASA must
- Page 521 and 522:
interface GigabitEthernet0/3 descri
- Page 523 and 524:
VPN CTCP upd 0 0 0 0 VPN SDI upd 0
- Page 525 and 526:
Be careful of this method of operat
- Page 527 and 528:
Group 2 State: Standby Ready Active
- Page 529 and 530:
global (outside) 1 interface nat (i
- Page 531 and 532:
Normally, the static command includ
- Page 533 and 534:
3191 bytes copied in 3.280 secs (10
- Page 535 and 536:
filters. For example, if you only w
- Page 537 and 538:
CHAPTER 29 Wireless Wireless networ
- Page 539 and 540:
consumer equipment will get nowhere
- Page 541 and 542:
TKIP The Temporal Key Integrity Pro
- Page 543 and 544:
The authentication open command tel
- Page 545 and 546:
Cisco-WAP(config)#int g0 Cisco-WAP(
- Page 547:
Troubleshooting Here are some usefu
- Page 550 and 551:
See Chapter 21 for more information
- Page 552 and 553:
equipment using slow-speed links, b
- Page 554 and 555:
hairpinning is generally frowned up
- Page 556 and 557:
Common Issues with VoIP When dealin
- Page 558 and 559:
Small-Office VoIP Example In a Cisc
- Page 560 and 561:
SW-3750(config-vlan)#vlan 901 SW-37
- Page 562 and 563:
mls qos trust device cisco-phone ml
- Page 564 and 565:
the right code, which minimizes pro
- Page 566 and 567:
Next, we’ll configure the phone s
- Page 568 and 569:
R1-PBX(config-telephony)#transfer-s
- Page 570 and 571:
Figure 30-4. Cisco 7970 phone; the
- Page 572 and 573:
I’m assigning the line number 111
- Page 574 and 575:
Different separator options may be
- Page 576 and 577:
To make the button work on the Cisc
- Page 578 and 579:
peers to send our calls there. Sinc
- Page 580 and 581:
If a call is destined for the numbe
- Page 582 and 583:
ACK Acknowledge a SIP message. CANC
- Page 584 and 585:
Key: 123456789 Trunk2 Number: 97355
- Page 586 and 587:
Here’s the rub. It only works gre
- Page 588 and 589:
sip-ua credentials number 608222222
- Page 590 and 591:
ephone-dn 22 dual-line number 97355
- Page 592 and 593:
that replaces anything that could a
- Page 594 and 595:
TFTP paging-dn 20 Preferred Codec:
- Page 596 and 597:
R1-PBX#sho dialplan number 92111111
- Page 598 and 599:
From: ;tag=383B4-0 To: Date: Thu,
- Page 600 and 601:
Figure 31-1. Simple two-building ne
- Page 602 and 603:
Assuming a FIFO (first in, first ou
- Page 604 and 605:
Figure 31-4. Simple two-building Vo
- Page 606 and 607:
ecame apparent as users began to wa
- Page 608 and 609:
WFQ WFQ is the default queuing mech
- Page 610 and 611:
Figure 31-8. Faster links are not b
- Page 612 and 613:
Common QoS Misconceptions There are
- Page 614 and 615:
Of course, QoS not resolving a need
- Page 616 and 617:
Record who is using each protocol a
- Page 618 and 619:
Removing the placeholder, we now ha
- Page 620 and 621:
• Voice control—30 Kbps • Tel
- Page 622 and 623:
Policy Maps Now that we have our cl
- Page 624 and 625:
Our final configuration is as follo
- Page 626 and 627:
Of course, you would need to have a
- Page 628 and 629:
0 packets, 0 bytes 5 minute rate 0
- Page 630 and 631:
Traffic-shaping terminology The fol
- Page 632 and 633:
In the Ethernet handoff example, I
- Page 634 and 635:
Internet address is 10.10.10.2/30 M
- Page 636 and 637:
819 input errors, 559 CRC, 227 fram
- Page 638 and 639:
more than 1 out of every 10 packets
- Page 641 and 642:
CHAPTER 34 The Converged Network In
- Page 643 and 644:
The HTTP class references access li
- Page 645 and 646:
Class-map: Voice-RTP (match-any) 19
- Page 647 and 648:
5 minute offered rate 255000 bps, d
- Page 649 and 650:
The drop rate in the first bold lin
- Page 651 and 652:
which can result in drops in lower-
- Page 653 and 654:
CHAPTER 35 Designing Networks There
- Page 655 and 656:
• Each user will have one phone s
- Page 657 and 658:
Another requirement that engineers
- Page 659 and 660:
If you have planned your network to
- Page 661 and 662:
Figure 35-6. Bay face layout Just b
- Page 663 and 664:
Keep it simple Take a look at any o
- Page 665 and 666:
Network Designs I can’t tell you
- Page 667 and 668:
stadium. The stadium was divided in
- Page 669 and 670:
• User VLANs Planning ahead of ti
- Page 671 and 672:
Figure 35-12. Bridged three-tier ec
- Page 673 and 674:
• Which interface is primary •
- Page 675 and 676:
CHAPTER 36 IP Design When a network
- Page 677 and 678:
the same network, so the packet wil
- Page 679 and 680:
Figure 36-2. Classful subnets of a
- Page 681 and 682:
Figure 36-4 shows how a single rout
- Page 683 and 684:
To make things even more interestin
- Page 685 and 686:
she would likely allocate them in t
- Page 687 and 688:
Figure 36-7. Divide-by-half IP subn
- Page 689 and 690:
IP Subnetting Made Easy IP subnetti
- Page 691 and 692:
Figure 36-11. Possible subnet octet
- Page 693 and 694:
Figure 36-15. Subnet worksheet step
- Page 695:
Figure 36-17. Horizontal format of
- Page 698 and 699:
If you’re not familiar with scien
- Page 700 and 701:
hexadecimal numbers separated by co
- Page 702 and 703:
Loopback address The loopback addre
- Page 704 and 705:
The following guidelines may be use
- Page 706 and 707:
To see the automatically configured
- Page 708 and 709:
The interface now has a link-local
- Page 710 and 711:
Success! Notice how we didn’t hav
- Page 712 and 713:
ND reachable time is 30000 millisec
- Page 714 and 715:
R4: L FF00::/8 [0/0] via ::, Null0
- Page 716 and 717:
60 cycles per second (60 Hz). 1080p
- Page 718 and 719:
The company ended up losing an enti
- Page 720 and 721:
~152.1.58.124 .INIT. 16 - 64 0 0.00
- Page 722 and 723:
=128.118.46.3 0.0.0.0 16 64 0 0.000
- Page 724 and 725:
configuration that caused the route
- Page 726 and 727:
ut the cables were not tied togethe
- Page 728 and 729:
everse the change, but make sure yo
- Page 730 and 731:
Escalate If you can’t figure out
- Page 732 and 733:
ead this, groaning, “I hate polit
- Page 734 and 735:
If your company is short on cash, y
- Page 736 and 737:
• Increase reliability Unless you
- Page 738 and 739:
On the other hand, devices that are
- Page 741 and 742:
CHAPTER 41 Avoiding Frustration I
- Page 743 and 744:
managers usually wake up, at which
- Page 745 and 746:
tension with my statement. The focu
- Page 747 and 748:
Understand the shortcomings of your
- Page 749 and 750:
What about upgrading something like
- Page 751 and 752:
To increase simplicity I’m a big
- Page 753 and 754:
of you Do you think you’ll be the
- Page 755 and 756:
Tell people that you’ve done some
- Page 757 and 758:
Index Symbols 802.xx standards (see
- Page 759 and 760:
computer jerks and, 727-730 selling
- Page 761 and 762:
trunk negotiation, 40 types of, 14
- Page 763 and 764:
Digital Signal Processors (DSPs), 5
- Page 765 and 766:
floating static route, 119 Foreign
- Page 767 and 768:
multicontext ASAs and, 482-484 PAT
- Page 769 and 770:
login method, 454 loopback addresse
- Page 771 and 772:
(see also NX-OS; specific Nexus dev
- Page 773 and 774:
plain-old telephone service (POTS),
- Page 775 and 776:
RFC 2281, 181, 184 RFC 2373, 676 RF
- Page 777 and 778:
show fabric switching-mode command,
- Page 779 and 780:
stacking GBICs, 317 stacking switch
- Page 781 and 782:
translation-profile command, 564 tr
- Page 783:
vtp password command, 57 VTP passwo