Solutions to Chapter 4 - Communication Networks
Solutions to Chapter 4 - Communication Networks
Solutions to Chapter 4 - Communication Networks
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Communication</strong> <strong>Networks</strong> (2 nd Edition)<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 4 <strong>Solutions</strong><br />
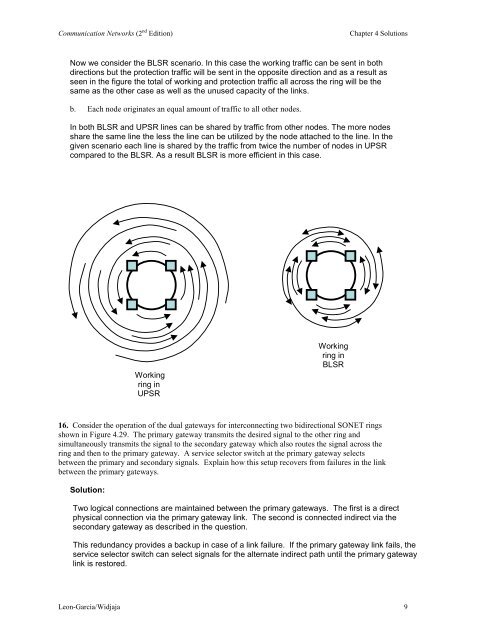
Now we consider the BLSR scenario. In this case the working traffic can be sent in both<br />
directions but the protection traffic will be sent in the opposite direction and as a result as<br />
seen in the figure the <strong>to</strong>tal of working and protection traffic all across the ring will be the<br />
same as the other case as well as the unused capacity of the links.<br />
b. Each node originates an equal amount of traffic <strong>to</strong> all other nodes.<br />
In both BLSR and UPSR lines can be shared by traffic from other nodes. The more nodes<br />
share the same line the less the line can be utilized by the node attached <strong>to</strong> the line. In the<br />
given scenario each line is shared by the traffic from twice the number of nodes in UPSR<br />
compared <strong>to</strong> the BLSR. As a result BLSR is more efficient in this case.<br />
Working<br />
ring in<br />
UPSR<br />
Working<br />
ring in<br />
BLSR<br />
16. Consider the operation of the dual gateways for interconnecting two bidirectional SONET rings<br />
shown in Figure 4.29. The primary gateway transmits the desired signal <strong>to</strong> the other ring and<br />
simultaneously transmits the signal <strong>to</strong> the secondary gateway which also routes the signal across the<br />
ring and then <strong>to</strong> the primary gateway. A service selec<strong>to</strong>r switch at the primary gateway selects<br />
between the primary and secondary signals. Explain how this setup recovers from failures in the link<br />
between the primary gateways.<br />
Solution:<br />
Two logical connections are maintained between the primary gateways. The first is a direct<br />
physical connection via the primary gateway link. The second is connected indirect via the<br />
secondary gateway as described in the question.<br />
This redundancy provides a backup in case of a link failure. If the primary gateway link fails, the<br />
service selec<strong>to</strong>r switch can select signals for the alternate indirect path until the primary gateway<br />
link is res<strong>to</strong>red.<br />
Leon-Garcia/Widjaja 9