Matlab code for damping identification using energy ... - CFD4Aircraft
Matlab code for damping identification using energy ... - CFD4Aircraft
Matlab code for damping identification using energy ... - CFD4Aircraft
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Analytical integration of experimental data<br />
A single frequency sinusoidal function has been used to curve-fit the experimental measurements<br />
in order to use an analytical integration of accelerations to obtain velocities and<br />
displacements and to obtain an analytical expression of the integrals present in eq. (11).<br />
Considering a single test with an excitation at frequency ω i , vector g i (t) takethe<strong>for</strong>m<br />
⎧<br />
⎪⎨<br />
g i (t) =<br />
⎪⎩<br />
0<br />
0<br />
g i (t)<br />
0<br />
0<br />
0<br />
0<br />
0<br />
0<br />
0<br />
⎫<br />
⎪⎬<br />
⎪⎭<br />
(13)<br />
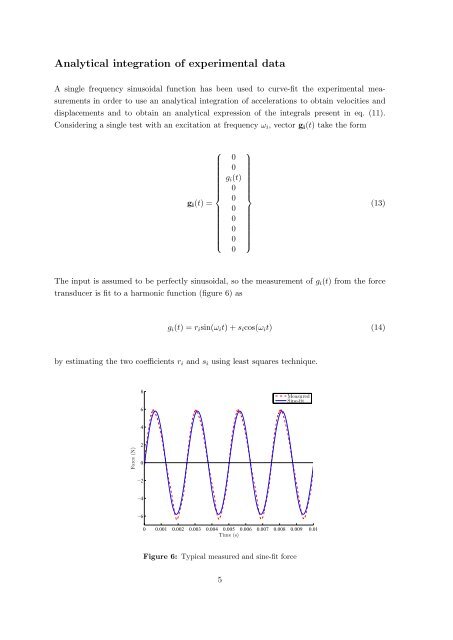
The input is assumed to be perfectly sinusoidal, so the measurement of g i (t) from the <strong>for</strong>ce<br />
transducer is fit to a harmonic function (figure 6) as<br />
g i (t) =r i sin(ω i t)+s i cos(ω i t) (14)<br />
by estimating the two coefficients r i and s i <strong>using</strong> least squares technique.<br />
8<br />
6<br />
Measured<br />
Sine-fit<br />
4<br />
Force (N)<br />
2<br />
0<br />
−2<br />
−4<br />
−6<br />
0 0.001 0.002 0.003 0.004 0.005 0.006 0.007 0.008 0.009 0.01<br />
Time (s)<br />
Figure 6: Typical measured and sine-fit <strong>for</strong>ce<br />
5