Nausea and vomiting - St Elizabeth Hospice
Nausea and vomiting - St Elizabeth Hospice
Nausea and vomiting - St Elizabeth Hospice
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Nausea</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>vomiting</strong><br />
Treat reversible causes if possible <strong>and</strong> appropriate e.g. drugs, hypercalcaemia, anxiety, constipation, cough,<br />
gastric irritation.<br />
Remember unrelated causes e.g. gastroenteritis<br />
If patient is <strong>vomiting</strong> or if oral absorption is in doubt→ use subcutaneous route (syringe driver) or rectal route<br />
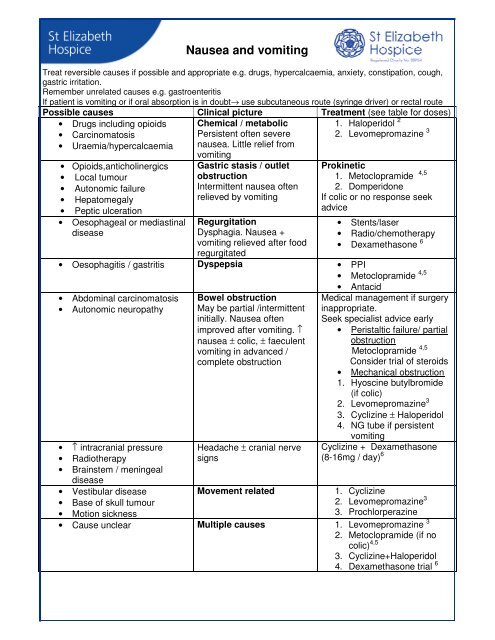
Possible causes Clinical picture Treatment (see table for doses)<br />
• Drugs including opioids<br />
• Carcinomatosis<br />
• Uraemia/hypercalcaemia<br />
• Opioids,anticholinergics<br />
• Local tumour<br />
• Autonomic failure<br />
• Hepatomegaly<br />
• Peptic ulceration<br />
• Oesophageal or mediastinal<br />
disease<br />
Chemical / metabolic<br />
Persistent often severe<br />
nausea. Little relief from<br />
<strong>vomiting</strong><br />
Gastric stasis / outlet<br />
obstruction<br />
Intermittent nausea often<br />
relieved by <strong>vomiting</strong><br />
Regurgitation<br />
Dysphagia. <strong>Nausea</strong> +<br />
<strong>vomiting</strong> relieved after food<br />
regurgitated<br />
1. Haloperidol 2<br />
2. Levomepromazine 3<br />
Prokinetic<br />
1. Metoclopramide 4,5<br />
2. Domperidone<br />
If colic or no response seek<br />
advice<br />
• <strong>St</strong>ents/laser<br />
• Radio/chemotherapy<br />
• Dexamethasone 6<br />
• Oesophagitis / gastritis Dyspepsia • PPI<br />
• Metoclopramide 4,5<br />
• Abdominal carcinomatosis<br />
• Autonomic neuropathy<br />
• ↑ intracranial pressure<br />
• Radiotherapy<br />
• Brainstem / meningeal<br />
disease<br />
• Vestibular disease<br />
• Base of skull tumour<br />
• Motion sickness<br />
Bowel obstruction<br />
May be partial /intermittent<br />
initially. <strong>Nausea</strong> often<br />
improved after <strong>vomiting</strong>. ↑<br />
nausea ± colic, ± faeculent<br />
<strong>vomiting</strong> in advanced /<br />
complete obstruction<br />
Headache ± cranial nerve<br />
signs<br />
• Antacid<br />
Medical management if surgery<br />
inappropriate.<br />
Seek specialist advice early<br />
• Peristaltic failure/ partial<br />
obstruction<br />
Metoclopramide 4,5<br />
Consider trial of steroids<br />
• Mechanical obstruction<br />
1. Hyoscine butylbromide<br />
(if colic)<br />
2. Levomepromazine 3<br />
3. Cyclizine ± Haloperidol<br />
4. NG tube if persistent<br />
<strong>vomiting</strong><br />
Cyclizine + Dexamethasone<br />
(8-16mg / day) 6<br />
Movement related<br />
1. Cyclizine<br />
2. Levomepromazine 3<br />
3. Prochlorperazine<br />
• Cause unclear Multiple causes 1. Levomepromazine 3<br />
2. Metoclopramide (if no<br />
colic) 4,5<br />
3. Cyclizine+Haloperidol<br />
4. Dexamethasone trial 6
5HT 3 antagonists e.g. Ondansetron are of proven value in chemotherapy / radiotherapy induced<br />
nausea <strong>and</strong> <strong>vomiting</strong> but are otherwise not recommended.<br />
Prescribing notes<br />
1<br />
Long term antiemetic use should be reviewed regularly. <strong>St</strong>op if underlying cause has resolved<br />
2<br />
Haloperidol may cause extrapyramidal side effects.<br />
3<br />
Levomepromazine is a potent, broad spectrum antiemetic. Use low doses to avoid sedation <strong>and</strong><br />
hypotension. A 6mg tablet is available on a named patient supply basis only (Link pharmaceuticals)<br />
The equivalent SC dose is half of the oral dose.<br />
4<br />
Metoclopramide may cause extrapyramidal side effects with prolonged use. Caution in patients under<br />
20 years.<br />
5<br />
Prokinetic action of metoclopramide is blocked by anticholinergics e.g. Cyclizine, Amitriptyline<br />
6<br />
Corticosteroids are best given before 2pm. Review <strong>and</strong> reduce to lowest effective dose. Give 5-7 day<br />
trial <strong>and</strong> withdraw if ineffective.<br />
7<br />
Dexamethasone 1mg is approximately equivalent to 7mg prednisolone<br />
DRUG<br />
ORAL DOSE<br />
(PR DOSE)<br />
DRUG DOSES<br />
STAT DOSE<br />
/ PRN DOSE<br />
SUBCUTANEOUS<br />
SYRINGE DRIVER /<br />
24HRS<br />
Cyclizine 50mg, 8hrly 50mg PO /SC 100-150mg (usually<br />
100mg)<br />
Domperidone<br />
10-20mg, 6-8hrly<br />
(30-60mg, 6-8hrly PR)<br />
with meals<br />
Haloperidol 1.5mg bd or 3mg nocte 1.5mg PO<br />
1.25-2.5mg SC<br />
Levomepromazine 6-12.5mg nocte 6mg or 6.25mg PO<br />
6.25mg SC<br />
2.5-10mg<br />
6.25-50mg<br />
Metoclopramide<br />
10-20mg, 6-8hrly<br />
(1/2 hr pre meals)<br />
10mg PO / SC<br />
30-120mg (usual range<br />
30-60mg)<br />
Hyoscine butylbromide 20mg, 6hrly 20mg SC 20-240mg<br />
Hyoscine hydrobromide<br />
150-300 micrograms,<br />
8hrly SL<br />
300micrograms/24hr<br />
TD patch<br />
400micrograms SC<br />
400-1200micrograms<br />
References<br />
1. ABC of palliative care -<strong>Nausea</strong>, <strong>vomiting</strong> <strong>and</strong> intestinal obstruction.BMJ 1997;315;1148-50<br />
2. Twycross R, Back I. <strong>Nausea</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>vomiting</strong> in advanced cancer. Eur J Pall Care 1998;5(2) 39-45<br />
3. Twycross R, Barkby GD, Hallwood PM.The use of low dose levomepromazine in the management of<br />
nausea <strong>and</strong> <strong>vomiting</strong>. Progress in Pall Care 1997;5(2) 49-53<br />
4. Bentley A, Boyd K Management of nausea <strong>and</strong> <strong>vomiting</strong> using clinical pictures. Pall Med 2001;8(4)<br />
137-140<br />
5. Rawlinson F. Malignant bowel obstruction. European Journal of Palliative Care 2001;8(4) 137-140
Lorazepam<br />
Vestibular<br />
CN VIII<br />
Higher Centres: Pain<br />
Fear<br />
Serotonin Receptor<br />
Norepinephrine<br />
Receptors<br />
Chemicals:<br />
Drugs<br />
Uraemia<br />
Hypercalcaemia<br />
CTZ<br />
Floor of 4 th Ventricle<br />
Outside Blood Brain<br />
Barrier<br />
Vomiting Centre<br />
Emetic pattern<br />
generator<br />
Inside Blood Brain Barrier<br />
D 2 Central Receptors<br />
5HT 3 Receptors<br />
NK 1 Receptors<br />
H 1 Receptors<br />
ACH m Receptors<br />
5HT 2 Receptors<br />
NK 1 Receptors<br />
Haloperidol<br />
Metoclopramide<br />
Levomepromazine<br />
5HT 3 Antagonists<br />
- Metoclopramide<br />
- Levomepromazine<br />
- Cyclizine<br />
-Amitriptyline<br />
- Hyoscine<br />
- Levomepromazine<br />
Autonomic Afferents from<br />
Viscera - ENT<br />
- Pleura<br />
(Via vagus) - Peritoneum<br />
CN X - Meninges etc<br />
<strong>St</strong>retch Receptors<br />
5HT ³<br />
Receptors<br />
Brainstem<br />
Centres<br />
Upper GI<br />
Motility<br />
Changes<br />
Peripheral D 2 Receptor<br />
5HT 4<br />
5HT 3<br />
Delayed<br />
gastric<br />
emptying,<br />
gastritis<br />
obstruction<br />
Vomiting Reflex<br />
Including<br />
Closed Glottis<br />
Metoclopramide<br />
Domperidone<br />
5HT 3 Antagonists