An Overview of SSD Write Caching (pdf) - Micron
An Overview of SSD Write Caching (pdf) - Micron
An Overview of SSD Write Caching (pdf) - Micron
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Steps Dialogue<br />
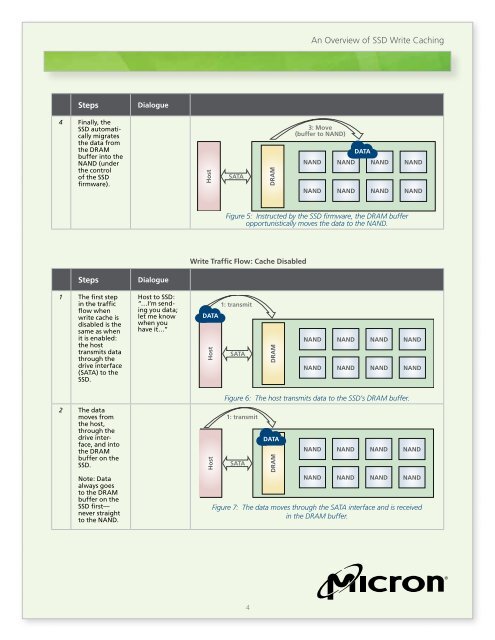
4 Finally, the<br />
<strong>SSD</strong> automatically<br />
migrates<br />
the data from<br />
the DRAM<br />
buffer into the<br />
NAND (under<br />
the control<br />
<strong>of</strong> the <strong>SSD</strong><br />
firmware).<br />
Steps Dialogue<br />
1 The first step<br />
in the traffic<br />
flow when<br />
write cache is<br />
disabled is the<br />
same as when<br />
it is enabled:<br />
the host<br />
transmits data<br />
through the<br />
drive interface<br />
(SATA) to the<br />
<strong>SSD</strong>.<br />
2 The data<br />
moves from<br />
the host,<br />
through the<br />
drive interface,<br />
and into<br />
the DRAM<br />
buffer on the<br />
<strong>SSD</strong>.<br />
Note: Data<br />
always goes<br />
to the DRAM<br />
buffer on the<br />
<strong>SSD</strong> first—<br />
never straight<br />
to the NAND.<br />
Host to <strong>SSD</strong>:<br />
“…I’m sending<br />
you data;<br />
let me know<br />
when you<br />
have it…”<br />
Host<br />
Host<br />
Host<br />
1: transmit<br />
4<br />
DRAM<br />
<strong>An</strong> <strong>Overview</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>SSD</strong> <strong>Write</strong> <strong>Caching</strong><br />
NAND<br />
NAND<br />
NAND<br />
NAND<br />
NAND<br />
NAND<br />
Figure 6: The host transmits data to the <strong>SSD</strong>’s DRAM buffer.<br />
1: transmit<br />
DRAM<br />
<strong>Write</strong> Traffic Flow: Cache Disabled<br />
DATA<br />
DRAM<br />
3: Move<br />
(buffer to NAND)<br />
NAND<br />
NAND<br />
NAND<br />
NAND<br />
NAND<br />
NAND<br />
Figure 5: Instructed by the <strong>SSD</strong> firmware, the DRAM buffer<br />
opportunistically moves the data to the NAND.<br />
NAND<br />
NAND<br />
NAND<br />
NAND<br />
NAND<br />
NAND<br />
NAND<br />
NAND<br />
NAND<br />
NAND<br />
NAND<br />
NAND<br />
Figure 7: The data moves through the SATA interface and is received<br />
in the DRAM buffer.