Algebra 2 Semester 2 Practice Final Summer 13
Algebra 2 Semester 2 Practice Final Summer 13
Algebra 2 Semester 2 Practice Final Summer 13
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Name: ________________________ Period: ___________________ Date: __________<br />
ID: A<br />
<strong>Algebra</strong> II <strong>Semester</strong> 2 <strong>Practice</strong> <strong>Final</strong> Exam (Chapters 6-10)<br />
1. Add or subtract. Simplify if possible.<br />
q 2 − 2q − 35<br />
q 2 + 2q − 15 − 1<br />
q − 3<br />
2. Write a polynomial function in standard form with<br />
zeros at –4, 2, and –5.<br />
3. Simplify.<br />
− 10 + 2 4 − 3 10<br />
4. Multiply.<br />
Ê ˆ Ê ˆ<br />
−2 − 10<br />
Ë<br />
Á<br />
¯<br />
˜ −3 + 10<br />
Ë<br />
Á<br />
¯<br />
˜<br />
5. Rationalize the denominator of the expression.<br />
7 − 3<br />
7 + 3<br />
6. Write an exponential function y = ab x for a graph<br />
that includes (1, 17.5) and (–1, 2.8).<br />
7. Write 2x 3 + 2x 2 – 40x in factored form.<br />
8. For the function f(x) = (5 − 6x) 2 , find f −1 .<br />
9. Solve. Check for extraneous solutions.<br />
6x = 24 − 12x<br />
10. Find the product ( 5x − 3)(x 3 − 5x + 2).<br />
11. Factor the expression.<br />
x 3 − 27<br />
12. Solve the equation. Check the solution.<br />
5<br />
3k + 1 k =−3<br />
<strong>13</strong>. Find the center and radius of the circle with<br />
equation ( x + 8) 2 + Ê<br />
Ë<br />
Á y − 8ˆ¯˜ 2<br />
= 16.<br />
14. Solve the equation.<br />
x − 9 − 10 =−5<br />
15. Solve log(3x + 11) = 2.<br />
16. Divide using synthetic division.<br />
(x 4 − 18x 3 + 44x 2 + 55x − 28) ÷ (x − 4)<br />
17. Solve the equation. Check the solution.<br />
d + 7<br />
d − 4 = d − 5<br />
d + 2<br />
18. Divide 4x 3 + 2x 2 − 2x + 3 by x + 3.<br />
3<br />
19. Simplify 48a <strong>13</strong> b 12<br />
positive.<br />
. Assume that all variables are<br />
20. Use the Change of Base Formula to evaluate<br />
log 4<br />
62. Then convert log 4<br />
62 to a logarithm in base<br />
2. Round to the nearest thousandth.<br />
21. Is the relationship between the variables in the table<br />
a direct variation, an inverse variation, or neither?<br />
If it is a direct or inverse variation, write a function<br />
to model it.<br />
x 0 1 2 3<br />
y 0 9<br />
9<br />
2<br />
3<br />
22. Expand the logarithmic expression.<br />
log 8<br />
3d 2<br />
23. Let f(x) = 4x + 6 and g(x) = 2x + 7. Find<br />
(f û g)(5).<br />
24. Rationalize the denominator of the expression.<br />
3<br />
4<br />
3<br />
7<br />
25. In how many different orders can you line up 6<br />
cards on a shelf?<br />
1
ID: A<br />
26. Write an equation for the translation of y = −7<br />
x<br />
that has the asymptotes x = –2 and y = –7.<br />
27. The values (5.1, 10) and (x, 3) are from an inverse<br />
variation. Find the missing value and round to the<br />
nearest hundredth.<br />
28. Solve 27x 3 + 343 = 0. Find all complex roots.<br />
29. Zach wrote the formula w(w – 1)(2w + 3) for the<br />
volume of a rectangular prism he is designing, with<br />
width w, which is always has a positive value<br />
greater than 1. Find the product and then classify<br />
this polynomial by degree and by number of terms.<br />
30. Use synthetic division to find P(–4) for<br />
P(x) = x 4 + 8x 3 + 2x 2 + 5x − 9.<br />
31. Expand the logarithmic expression.<br />
log 4<br />
8k 4<br />
32. Divide using synthetic division.<br />
(x 4 − 12x 3 + 20x 2 + 36x − 45) ÷ (x − 3)<br />
33. Use natural logarithms to solve the equation. Round<br />
to the nearest thousandth.<br />
2e 4x + 11 = 22<br />
34. Solve the equation.<br />
x + 9 − 8 =−4<br />
35. Use natural logarithms to solve the equation. Round<br />
to the nearest thousandth.<br />
8e 4x + 11 = 30<br />
36. Multiply or divide. State any restrictions on the<br />
variables.<br />
x 2<br />
x − 4 ⋅ x 2 + x − 20<br />
x 2 + 4x<br />
37. Write the equation in logarithmic form.<br />
4 2 = 16<br />
38. Find the foci of the ellipse with the equation x 2<br />
9 + y 2<br />
49<br />
= 1. Graph the ellipse.<br />
39. Write an equation in standard form of an ellipse<br />
that has a vertex at (–3, 0), a co-vertex at (0, –5),<br />
and is centered at the origin.<br />
40. Write an equation for the translation of<br />
x 2 + y 2 = 49, 4 units right and 2 units down.<br />
41. Use the Pascal’s Triangle to expand the bionomial<br />
(d + 2b) 3 .<br />
42. Multiply or divide. State any restrictions on the<br />
variables.<br />
t 2<br />
t + 2 ⋅ t2 + t − 2<br />
t 2 − 3t<br />
43. Factor the expression.<br />
x 4 − 25x 2 + 144<br />
44. Divide and simplify.<br />
3<br />
120x 27<br />
3<br />
3x<br />
45. Solve ln(4x − 4) = 8. Round to the nearest<br />
thousandth.<br />
46. Simplify.<br />
1<br />
3<br />
3<br />
⋅ 9<br />
1<br />
3<br />
47. Suppose that y varies jointly with w and x and<br />
inversely with z and y = 160 when w = 5, x = 24<br />
and z = 6. Write the equation that models the<br />
relationship. Then find y when w = 4, x = 10 and z<br />
= 5.<br />
2
ID: A<br />
48. Multiply.<br />
Ê ˆ<br />
−5 − 3<br />
Ë<br />
Á<br />
¯<br />
˜<br />
49. Graph the equation.<br />
16x 2 + 4y 2 = 49<br />
2<br />
50. Use a graphing calculator. Use the graph of y = e x<br />
to evaluate e 1.7 to four decimal places.<br />
51. Simplify the rational expression. State any<br />
restrictions on the variable.<br />
p 2 − 4p − 32<br />
p + 4<br />
52. Write an equation of an ellipse in standard form<br />
with the center at the origin and with the given<br />
characteristics.<br />
vertices at (–5, 0) and co-vertices (0, 4)<br />
53. Find the inverse of y = 7x 2 + 7.<br />
54. Rationalize the denominator of the expression.<br />
Assume that all variables are positive.<br />
7x 9 y 7<br />
2x 3 y 2<br />
56. Suppose that x and y vary inversely, and x = 7 when<br />
y = 11. Write the function that models the inverse<br />
variation.<br />
57. Is the relationship between the variables in the table<br />
a direct variation, an inverse variation, or neither?<br />
If it is a direct or inverse variation, write a function<br />
to model it.<br />
x 6 10 11 15<br />
y 84 140 154 210<br />
58. Describe the combined variation that is modeled by<br />
the formula or equation.<br />
y =<br />
w<br />
2x 2<br />
59. Describe the combined variation that is modeled by<br />
the formula or equation.<br />
a = F m<br />
55. Write the equation in logarithmic form.<br />
6 4 = 1, 296<br />
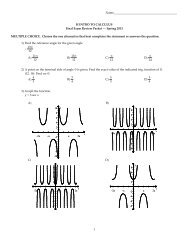
60. Graph the conic section.<br />
4x 2 − 9y 2 = 144<br />
61. Write an equation of an ellipse with center (3, –3),<br />
vertical major axis of length 12, and minor axis of<br />
length 6.<br />
62. Write an equation of a hyperbola with vertices (3,<br />
–2) and (–9, –2), and foci (7, –2) and (–<strong>13</strong>, –2).<br />
63. Sketch the asymptotes and graph the function.<br />
2<br />
y =<br />
x + 2 − 3<br />
3
ID: A<br />
64. Simplify the rational expression. State any<br />
69. Simplify the complex fraction.<br />
restrictions on the variable.<br />
3<br />
q 2 + 11q + 24<br />
4y − 2 y<br />
q 2 − 5q − 24<br />
1<br />
y + 3 2y<br />
65. Solve the equation. Check the solution.<br />
−2<br />
x + 4 = 4<br />
70. Solve the equation. Check the solution.<br />
x + 3<br />
a<br />
a 2 − 36 + 2<br />
a − 6 = 1<br />
a + 6<br />
66. Multiply or divide. State any restrictions on the<br />
variables.<br />
x 2 − 16<br />
x 2 + 5x + 6 ÷ x 2 71. Write an exponential function for the graph.<br />
+ 5x + 4<br />
x 2 − 2x − 8<br />
67. Add or subtract. Simplify if possible.<br />
w 2 + 2w − 24<br />
w 2 + w − 30 + 8<br />
w − 5<br />
68. State the property or properties of logarithms used<br />
to rewrite the expression.<br />
log 20 625x 4 = 1 5 log 5x<br />
72. Graph y = 76 () x + 2 + 1.<br />
73. Evaluate the logarithm.<br />
log 5<br />
1<br />
625<br />
74. Write the equation log 32<br />
8 = 3 5<br />
in exponential form.<br />
Write the expression as a single logarithm.<br />
5log b<br />
q + 2log b<br />
y<br />
78. Write the expression as a single logarithm.<br />
log 3<br />
4 − log 3<br />
2<br />
75. State the property or properties of logarithms used<br />
to rewrite the expression.<br />
log 5<br />
6 − log 5<br />
2 = log 5<br />
3<br />
76. State the property or properties of logarithms used<br />
to rewrite the expression.<br />
2log6 + log 1 3<br />
= log 12<br />
77.<br />
79. Expand the logarithmic expression.<br />
log 7<br />
n<br />
2<br />
80. Expand the logarithmic expression.<br />
57<br />
log b<br />
74<br />
81. Solve 15 2x = 36. Round to the nearest<br />
ten-thousandth.<br />
4
ID: A<br />
82. Use the Change of Base Formula to solve 2 2x = 90.<br />
Round to the nearest ten-thousandth.<br />
83. Write the expression as a single natural logarithm.<br />
3ln3 + 3lnc<br />
84. Find all the real square roots of 0.0004.<br />
85. Find the real-number root.<br />
− 125<br />
3<br />
343<br />
86. Multiply and simplify if possible.<br />
6 ⋅ 2<br />
87. Multiply and simplify if possible.<br />
Ê<br />
ˆ<br />
7x x − 7 7<br />
Ë<br />
Á<br />
¯<br />
˜<br />
88. Divide and simplify.<br />
3<br />
3<br />
162<br />
2<br />
89. Divide and simplify.<br />
90x 18<br />
2x<br />
90. Rationalize the denominator of the expression.<br />
Assume that all variables are positive.<br />
6x 8 y 9<br />
5x 2 y 4<br />
91. Rationalize the denominator of the expression.<br />
Assume that all variables are positive.<br />
3<br />
2 + 3<br />
3<br />
6<br />
92. Add if possible.<br />
4<br />
2 2x<br />
4<br />
+ 6 2x<br />
93. Add if possible.<br />
3<br />
4 3x<br />
3<br />
+ 5 10x<br />
94. Subtract if possible.<br />
4<br />
4<br />
2 5a − 6 5a<br />
95. Simplify.<br />
1<br />
20 2<br />
⋅ 20<br />
1<br />
2<br />
8<br />
96. Write the exponential expression 3x in radical<br />
form.<br />
97. Solve the equation.<br />
2<br />
( x − 7)<br />
3 = 4<br />
98. Solve the equation.<br />
1<br />
1<br />
( −2x + 6)<br />
5 = ( −8 + 10x)<br />
5<br />
99. Let f(x) =−3x − 6 and g(x) = 5x + 2. Find f(x) +<br />
g(x).<br />
100. Let f(x) = x 2 + 2x − 1 and g(x) = 2x − 4. Find<br />
2f(x) – 3g(x).<br />
101. Let f(x) = x 2 + 6 and g(x) = x + 8 . Find<br />
x<br />
Ê<br />
Ë<br />
Á g û f ˆ¯˜ ( −7).<br />
102. Find the inverse of y = 7x 2 − 3.<br />
103. For the function f(x) = x + 9, find (f û f −1 )(5).<br />
104. Let f(x) = 4 + 5x and g(x) = 2x − 1. Find f(g(x))<br />
and g(f(x)).<br />
105. Evaluate the logarithm.<br />
log 3<br />
1<br />
243<br />
3<br />
106. Graph the function.<br />
y = x + 3<br />
5
ID: A<br />
107. Classify –3x 5 – 2x 3 by degree and by number of<br />
terms.<br />
108. Classify –7x 5 – 6x 4 + 4x 3 by degree and by number<br />
of terms.<br />
109. Write the polynomial 6x 2 − 9x 3 + 3<br />
in standard<br />
3<br />
form.<br />
110. Find the zeros of f(x) = (x + 3) 2 (x − 5) 6 and state<br />
the multiplicity.<br />
111. Divide using synthetic division.<br />
(x 3 + 4 − 11x + 3x 2 ) ÷ (6 + x)<br />
112. Solve x 4 − 34x 2 =−225.<br />
1<strong>13</strong>. Evaluate the expression.<br />
5!<br />
114. Evaluate the expression.<br />
7!<br />
4! 3!<br />
115. Use Pascal’s Triangle to expand the binomial.<br />
(s − 5v) 5<br />
116. Simplify.<br />
− 2 − 2 25 − 6 2<br />
117. Divide and simplify.<br />
225x 24<br />
3x<br />
125. Solve the equation. Check the solution.<br />
k + 5<br />
k + 8 = k + 4<br />
k − 5<br />
118. Multiply.<br />
Ê ˆ<br />
6 + 5<br />
Ë<br />
Á<br />
¯<br />
˜<br />
2<br />
119. Write 5x 3 – 5x 2 – 30x in factored form.<br />
3<br />
120. Simplify 162a <strong>13</strong> b 6<br />
positive.<br />
. Assume that all variables are<br />
121. Write an exponential function y = ab x for a graph<br />
that includes (0, 4) and (1, 14).<br />
122. Simplify.<br />
1<br />
10 3<br />
⋅ 100<br />
1<br />
3<br />
123. Write a polynomial function in standard form with<br />
zeros at –5, –2, and –4.<br />
124. Find the inverse of y = 6x 2 − 2.<br />
6
ID: A<br />
<strong>Algebra</strong> II <strong>Semester</strong> 2 <strong>Practice</strong> <strong>Final</strong> Exam (Chapters 6-10)<br />
Answer Section<br />
1. ANS:<br />
q − 8<br />
q − 3<br />
REF: 9-5 Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions<br />
OBJ: 9-5.1 Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions TOP: 9-5 Example 4<br />
KEY: simplifying a rational expression | subtracting rational expressions<br />
2. ANS:<br />
f(x) = x 3 + 7x 2 + 2x − 40<br />
REF: 6-2 Polynomials and Linear Factors<br />
OBJ: 6-2.2 Factors and Zeros of a Polynomial Function TOP: 6-2 Example 5<br />
KEY: polynomial function | standard form of a polynomial | zeros of a polynomial function<br />
3. ANS:<br />
−4 10 + 4<br />
REF: 7-3 Binomial Radical Expressions<br />
TOP: 7-3 Example 3<br />
4. ANS:<br />
−4 + 10<br />
OBJ: 7-3.1 Adding and Subtracting Radical Expressions<br />
KEY: like radicals | simplifying a radical expression<br />
REF: 7-3 Binomial Radical Expressions OBJ: 7-3.2 Multiplying and Dividing Binomial Radical Expressions<br />
TOP: 7-3 Example 4<br />
KEY: binomial radical expressions | simplifying a radical expression | multiplying binomial radical expressions<br />
5. ANS:<br />
10 − 2 21<br />
4<br />
REF: 7-3 Binomial Radical Expressions OBJ: 7-3.2 Multiplying and Dividing Binomial Radical Expressions<br />
TOP: 7-3 Example 6<br />
KEY: binomial radical expressions | conjugates | multiplying binomial radical expressions | simplifying a radical<br />
expression<br />
6. ANS:<br />
y = 7(2.5) x<br />
REF: 8-1 Exploring Exponential Models OBJ: 8-1.1 Exponential Growth<br />
TOP: 8-1 Example 3<br />
KEY: exponential function | growth factor<br />
7. ANS:<br />
2x(x + 5)(x – 4)<br />
REF: 6-2 Polynomials and Linear Factors<br />
OBJ: 6-2.1 The Factored Form of a Polynomial TOP: 6-2 Example 2<br />
KEY: factoring a polynomial | polynomial<br />
1
ID: A<br />
8. ANS:<br />
f −1 (x) = 5 ±<br />
6<br />
x<br />
REF: 7-7 Inverse Relations and Functions<br />
TOP: 7-7 Example 4<br />
9. ANS:<br />
2<br />
3<br />
REF: 7-5 Solving Radical Equations<br />
TOP: 7-5 Example 4<br />
10. ANS:<br />
5x 4 − 3x 3 − 25x 2 + 25x − 6<br />
OBJ: 7-7.1 The Inverse of a Function<br />
KEY: domain | inverse relations and functions | range<br />
OBJ: 7-5.1 Solving Radical Equations<br />
KEY: radical equation | extraneous solutions<br />
REF: Page 414 OBJ: 6-2.2 Multiplying Polynomials NAT: 12.5.3.c<br />
TOP: 6-2 Multiplying Polynomials KEY: multiplying polynomials<br />
11. ANS:<br />
(x − 3)(x 2 + 3x + 9)<br />
REF: 6-4 Solving Polynomial Equations<br />
TOP: 6-4 Example 3<br />
12. ANS:<br />
OBJ: 6-4.2 Solving Equations by Factoring<br />
KEY: polynomial | factoring a polynomial<br />
− 8 9<br />
REF: 9-6 Solving Rational Equations<br />
TOP: 9-6 Example 2<br />
<strong>13</strong>. ANS:<br />
(–8, 8); 4<br />
OBJ: 9-6.1 Solving Rational Equations<br />
KEY: rational equation<br />
REF: 10-3 Circles OBJ: 10-3.2 Using the Center and Radius of a Circle<br />
TOP: 10-3 Example 4<br />
KEY: center of a circle | circle | equation of a circle | radius | translation<br />
14. ANS:<br />
34<br />
REF: 7-5 Solving Radical Equations OBJ: 7-5.1 Solving Radical Equations<br />
TOP: 7-5 Example 1 KEY: radical equation |<br />
15. ANS:<br />
89<br />
3<br />
REF: 8-5 Exponential and Logarithmic Equations<br />
OBJ: 8-5.2 Solving Logarithmic Equations<br />
TOP: 8-5 Example 6<br />
KEY: logarithmic equation | properties of logarithms<br />
2
ID: A<br />
16. ANS:<br />
x 3 − 14x 2 − 12x + 7<br />
REF: 6-3 Dividing Polynomials<br />
TOP: 6-3 Example 3<br />
17. ANS:<br />
1<br />
3<br />
REF: 9-6 Solving Rational Equations<br />
TOP: 9-6 Example 1<br />
18. ANS:<br />
4x 2 − 10x + 28, R –81<br />
REF: 6-3 Dividing Polynomials<br />
TOP: 6-3 Example 1<br />
19. ANS:<br />
2a 4 b 4 3<br />
6a<br />
OBJ: 6-3.2 Using Synthetic Division<br />
KEY: division of polynomials | polynomial | synthetic division<br />
OBJ: 9-6.1 Solving Rational Equations<br />
KEY: rational equation<br />
OBJ: 6-3.1 Using Long Division<br />
KEY: polynomial | division of polynomials<br />
REF: 7-2 Multiplying and Dividing Radical Expressions OBJ: 7-2.1 Multiplying Radical Expressions<br />
TOP: 7-2 Example 2<br />
KEY: multiplying radical expressions | simplifying a radical expression<br />
20. ANS:<br />
2.977; log 2<br />
7.874<br />
REF: 8-5 Exponential and Logarithmic Equations<br />
OBJ: 8-5.2 Solving Logarithmic Equations<br />
TOP: 8-5 Example 5<br />
KEY: Change of Base Formula | evaluating logarithms<br />
21. ANS:<br />
inverse variation; y = 9 x<br />
REF: 9-1 Inverse Variation<br />
TOP: 9-1 Example 2<br />
22. ANS:<br />
log 8<br />
3 + 2log 8<br />
d<br />
OBJ: 9-1.1 Using Inverse Variation<br />
KEY: rational function | inverse variation<br />
REF: 8-4 Properties of Logarithms OBJ: 8-4.1 Using the Properties of Logarithms<br />
TOP: 8-4 Example 3<br />
KEY: properties of logarithms | expanding logarithms | Product Property of Logarithms | Power Property of<br />
Logarithms<br />
23. ANS:<br />
74<br />
REF: 7-6 Function Operations<br />
TOP: 7-6 Example 3<br />
OBJ: 7-6.2 Composition of Functions<br />
KEY: composition of functions | operations with functions<br />
3
ID: A<br />
24. ANS:<br />
3<br />
196<br />
7<br />
REF: 7-2 Multiplying and Dividing Radical Expressions OBJ: 7-2.2 Dividing Radical Expressions<br />
TOP: 7-2 Example 5<br />
KEY: divide radical expressions | simplifying a radical expression<br />
25. ANS:<br />
720<br />
REF: 6-7 Permutations and Combinations<br />
TOP: 6-7 Example 1<br />
26. ANS:<br />
−7<br />
y =<br />
x + 2 − 7<br />
OBJ: 6-7.1 Permutations<br />
KEY: permutation | factorial | problem solving<br />
REF: 9-2 The Reciprocal Function Family<br />
OBJ: 9-2.2 Graphing Translations of Reciprocal Functions TOP: 9-2 Example 5<br />
KEY: asymptote | translation<br />
27. ANS:<br />
17.00<br />
REF: 9-1 Inverse Variation<br />
TOP: 9-1 Example 3<br />
28. ANS:<br />
− 7 21 ± 21i 3<br />
,<br />
3 18<br />
REF: 6-4 Solving Polynomial Equations<br />
TOP: 6-4 Example 4<br />
29. ANS:<br />
2w 3 + w 2 − 3w; cubic trinomial<br />
REF: 6-1 Polynomial Functions<br />
TOP: 6-1 Example 1<br />
30. ANS:<br />
–253<br />
REF: 6-3 Dividing Polynomials<br />
TOP: 6-3 Example 5<br />
31. ANS:<br />
log 4<br />
8 + 4log 4<br />
k<br />
OBJ: 9-1.1 Using Inverse Variation<br />
KEY: inverse variation | pair of values<br />
OBJ: 6-4.2 Solving Equations by Factoring<br />
KEY: factoring a polynomial | polynomial function<br />
OBJ: 6-1.1 Exploring Polynomial Functions<br />
KEY: degree of a polynomial | polynomial<br />
OBJ: 6-3.2 Using Synthetic Division<br />
KEY: division of polynomials | polynomial | synthetic division<br />
REF: 8-4 Properties of Logarithms OBJ: 8-4.1 Using the Properties of Logarithms<br />
TOP: 8-4 Example 3<br />
KEY: properties of logarithms | expanding logarithms | Product Property of Logarithms | Power Property of<br />
Logarithms<br />
4
ID: A<br />
32. ANS:<br />
x 3 − 9x 2 − 7x + 15<br />
REF: 6-3 Dividing Polynomials<br />
TOP: 6-3 Example 3<br />
33. ANS:<br />
0.426<br />
REF: 8-6 Natural Logarithms<br />
TOP: 8-6 Example 4<br />
34. ANS:<br />
7<br />
OBJ: 6-3.2 Using Synthetic Division<br />
KEY: division of polynomials | polynomial | synthetic division<br />
OBJ: 8-6.2 Natural Logarithmic and Exponential Equations<br />
KEY: exponential equation | properties of logarithms<br />
REF: 7-5 Solving Radical Equations OBJ: 7-5.1 Solving Radical Equations<br />
TOP: 7-5 Example 1 KEY: radical equation |<br />
35. ANS:<br />
0.216<br />
REF: 8-6 Natural Logarithms<br />
TOP: 8-6 Example 4<br />
36. ANS:<br />
x 2 + 5x<br />
, x ≠ 4, 0, − 4<br />
x + 4<br />
OBJ: 8-6.2 Natural Logarithmic and Exponential Equations<br />
KEY: exponential equation | properties of logarithms<br />
REF: 9-4 Rational Expressions OBJ: 9-4.2 Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions<br />
TOP: 9-4 Example 3<br />
KEY: simplifying a rational expression | restrictions on a variable | multiplying rational expressions<br />
37. ANS:<br />
log 4<br />
16 = 2<br />
REF: 8-3 Logarithmic Functions as Inverses<br />
OBJ: 8-3.1 Writing and Evaluating Logarithmic Expressions TOP: 8-3 Example 2<br />
KEY: logarithm | logarithmic form<br />
5
ID: A<br />
38. ANS:<br />
foci (0, ± 2 10)<br />
REF: 10-4 Ellipses<br />
OBJ: 10-4.2 Finding and Using the Foci of an Ellipse<br />
TOP: 10-4 Example 3<br />
KEY: co-vertex of an ellipse | ellipse | equation of an ellipse | graphing | foci of an ellipse | major axis of an ellipse<br />
| minor axis of an ellipse<br />
39. ANS:<br />
x 2<br />
9 + y 2<br />
25 = 1<br />
REF: 10-4 Ellipses<br />
OBJ: 10-4.1 Writing the Equation of an Ellipse<br />
TOP: 10-4 Example 1<br />
KEY: ellipse | equation of an ellipse | vertex of an ellipse | co-vertex of an ellipse | minor axis of an ellipse | major<br />
axis of an ellipse<br />
40. ANS:<br />
( x − 4) 2 + Ê<br />
Ë<br />
Á y + 2ˆ¯˜ 2<br />
= 49<br />
REF: 10-3 Circles OBJ: 10-3.1 Writing the Equation of a Circle<br />
TOP: 10-3 Example 2<br />
KEY: center of a circle | circle | equation of a circle | radius<br />
41. ANS:<br />
d 3 + 6d 2 b + 12db 2 + 8b 3<br />
REF: 6-8 The Binomial Theorem<br />
TOP: 6-8 Example 3<br />
42. ANS:<br />
t 2 − t<br />
, t ≠ −2, 0, 3<br />
t − 3<br />
OBJ: 6-8.2 The Binomial Theorem<br />
KEY: Pascal's Triangle | binomial expansion<br />
REF: 9-4 Rational Expressions OBJ: 9-4.2 Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions<br />
TOP: 9-4 Example 3<br />
KEY: simplifying a rational expression | restrictions on a variable | multiplying rational expressions<br />
6
ID: A<br />
43. ANS:<br />
(x − 4)(x + 4)(x − 3)(x + 3)<br />
REF: 6-4 Solving Polynomial Equations<br />
TOP: 6-4 Example 5<br />
44. ANS:<br />
2x 8 3<br />
5x 2<br />
OBJ: 6-4.2 Solving Equations by Factoring<br />
KEY: factoring a polynomial | polynomial<br />
REF: 7-2 Multiplying and Dividing Radical Expressions OBJ: 7-2.2 Dividing Radical Expressions<br />
TOP: 7-2 Example 4<br />
KEY: simplifying a radical expression | divide radical expressions | rationalize the denominator<br />
45. ANS:<br />
746.239<br />
REF: 8-6 Natural Logarithms<br />
TOP: 8-6 Example 3<br />
46. ANS:<br />
3<br />
REF: 7-4 Rational Exponents<br />
TOP: 7-4 Example 1<br />
47. ANS:<br />
y = 8wx<br />
z ; 64<br />
REF: 9-1 Inverse Variation<br />
TOP: 9-1 Example 5<br />
48. ANS:<br />
28 + 10 3<br />
OBJ: 8-6.2 Natural Logarithmic and Exponential Equations<br />
KEY: natural logarithmic equation | properties of logarithms<br />
OBJ: 7-4.1 Simplifying Expressions with Rational Exponents<br />
KEY: rational exponent<br />
OBJ: 9-1.2 Using Combined Variation<br />
KEY: direct variation | combined variation | joint variation<br />
REF: 7-3 Binomial Radical Expressions OBJ: 7-3.2 Multiplying and Dividing Binomial Radical Expressions<br />
TOP: 7-3 Example 4<br />
KEY: binomial radical expressions | multiplying binomial radical expressions | simplifying a radical expression<br />
7
ID: A<br />
49. ANS:<br />
The graph is an ellipse. The center is at the origin. It has two lines of<br />
symmetry, the x-axis and the y-axis.<br />
REF: 10-1 Exploring Conic Sections<br />
TOP: 10-1 Example 2<br />
50. ANS:<br />
5.4739<br />
OBJ: 10-1.1 Graphing Equations of Conic Sections<br />
KEY: conic sections | graphing | ellipse | domain | range<br />
REF: 8-2 Properties of Exponential Functions<br />
OBJ: 8-2.2 The Number e<br />
TOP: 8-2 Example 4<br />
KEY: exponential function | graphing | the number e<br />
51. ANS:<br />
p − 8; p ≠ −4<br />
REF: 9-4 Rational Expressions OBJ: 9-4.1 Simplifying Rational Expressions<br />
TOP: 9-4 Example 1<br />
KEY: rational expression | simplifying a rational expression | restrictions on a variable<br />
52. ANS:<br />
x 2<br />
25 + y 2<br />
16 = 1<br />
REF: 10-4 Ellipses<br />
OBJ: 10-4.1 Writing the Equation of an Ellipse<br />
TOP: 10-4 Example 1<br />
KEY: co-vertex of an ellipse | ellipse | equation of an ellipse | major axis of an ellipse | minor axis of an ellipse |<br />
vertex of an ellipse<br />
53. ANS:<br />
y =±<br />
x − 7<br />
7<br />
REF: 7-7 Inverse Relations and Functions<br />
OBJ: 7-7.1 The Inverse of a Function<br />
TOP: 7-7 Example 2 KEY: inverse relations and functions |<br />
8
ID: A<br />
54. ANS:<br />
x 3 y 2<br />
2<br />
14y<br />
REF: 7-2 Multiplying and Dividing Radical Expressions OBJ: 7-2.2 Dividing Radical Expressions<br />
TOP: 7-2 Example 5<br />
KEY: divide radical expressions | simplifying a radical expression<br />
55. ANS:<br />
log 6<br />
1, 296 = 4<br />
REF: 8-3 Logarithmic Functions as Inverses<br />
OBJ: 8-3.1 Writing and Evaluating Logarithmic Expressions TOP: 8-3 Example 2<br />
KEY: logarithm | logarithmic form<br />
56. ANS:<br />
y = 77<br />
x<br />
REF: 9-1 Inverse Variation<br />
TOP: 9-1 Example 1<br />
57. ANS:<br />
direct variation; y = 14x<br />
OBJ: 9-1.1 Using Inverse Variation<br />
KEY: rational function | inverse variation<br />
REF: 9-1 Inverse Variation<br />
OBJ: 9-1.1 Using Inverse Variation<br />
TOP: 9-1 Example 2<br />
KEY: rational function | direct variation<br />
58. ANS:<br />
y varies directly as w and inversely as the square of x.<br />
REF: 9-1 Inverse Variation<br />
TOP: 9-1 Example 4<br />
59. ANS:<br />
a varies directly as F and inversely as m.<br />
REF: 9-1 Inverse Variation<br />
TOP: 9-1 Example 4<br />
OBJ: 9-1.2 Using Combined Variation<br />
KEY: direct variation | inverse variation | combined variation<br />
OBJ: 9-1.2 Using Combined Variation<br />
KEY: direct variation | inverse variation | combined variation<br />
9
ID: A<br />
60. ANS:<br />
REF: 10-5 Hyperbolas<br />
OBJ: 10-5.1 Graphing Hyperbolas Centered at the Origin<br />
TOP: 10-5 Example 1<br />
KEY: hyperbola | equation of a hyperbola | graphing | transverse axis of a hyperbola | vertices of a hyperbola |<br />
asymptotes of a hyperbola<br />
61. ANS:<br />
( x − 3) 2 Ê<br />
Ë<br />
Á y + 3 ˆ¯˜ 2<br />
+ = 1<br />
9 36<br />
REF: 10-6 Translating Conic Sections OBJ: 10-6.1 Writing Equations of Translated Conic Sections<br />
TOP: 10-6 Example 1<br />
KEY: conic sections | co-vertex of an ellipse | equation of an ellipse | major axis of an ellipse | minor axis of an<br />
ellipse | translation | vertex of an ellipse<br />
62. ANS:<br />
Ê<br />
(x + 3) 2 Ë<br />
Á y + 2 ˆ¯˜ 2<br />
− = 1<br />
36 64<br />
REF: 10-6 Translating Conic Sections OBJ: 10-6.1 Writing Equations of Translated Conic Sections<br />
TOP: 10-6 Example 2<br />
KEY: conic sections | equation of a hyperbola | hyperbola | translation | transverse axis of a hyperbola | vertices of<br />
a hyperbola<br />
10
ID: A<br />
63. ANS:<br />
REF: 9-2 The Reciprocal Function Family<br />
OBJ: 9-2.2 Graphing Translations of Reciprocal Functions TOP: 9-2 Example 4<br />
KEY: graphing | asymptote<br />
64. ANS:<br />
q + 8<br />
q − 8 ; q ≠ −3, q ≠ 8<br />
REF: 9-4 Rational Expressions OBJ: 9-4.1 Simplifying Rational Expressions<br />
TOP: 9-4 Example 1<br />
KEY: rational expression | simplifying a rational expression | restrictions on a variable<br />
65. ANS:<br />
− 11<br />
3<br />
REF: 9-6 Solving Rational Equations<br />
TOP: 9-6 Example 1<br />
66. ANS:<br />
(x − 4) 2<br />
; x ≠ − 4, − 3, − 2, − 1, 4<br />
(x + 3)(x + 1)<br />
REF: 9-4 Rational Expressions<br />
TOP: 9-4 Example 4<br />
67. ANS:<br />
w + 4<br />
w − 5<br />
OBJ: 9-6.1 Solving Rational Equations<br />
KEY: rational equation<br />
OBJ: 9-4.2 Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions<br />
KEY: restrictions on a variable | dividing rational expressions<br />
REF: 9-5 Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions<br />
OBJ: 9-5.1 Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions TOP: 9-5 Example 3<br />
KEY: simplifying a rational expression | adding rational expressions<br />
11
ID: A<br />
68. ANS:<br />
Power Property<br />
REF: 8-4 Properties of Logarithms<br />
TOP: 8-4 Example 1<br />
69. ANS:<br />
OBJ: 8-4.1 Using the Properties of Logarithms<br />
KEY: properties of logarithms | Power Property of Logarithms<br />
− 1 2<br />
REF: 9-5 Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions OBJ: 9-5.2 Simplifying Complex Fractions<br />
TOP: 9-5 Example 5<br />
KEY: complex fraction | simplifying a rational expression | simplifying a complex fraction<br />
70. ANS:<br />
–9<br />
REF: 9-6 Solving Rational Equations<br />
TOP: 9-6 Example 2<br />
71. ANS:<br />
y = 0.5(2) x<br />
OBJ: 9-6.1 Solving Rational Equations<br />
KEY: rational equation | no solutions<br />
REF: 8-1 Exploring Exponential Models OBJ: 8-1.1 Exponential Growth<br />
TOP: 8-1 Example 3<br />
KEY: exponential function | graphing | growth factor<br />
72. ANS:<br />
REF: 8-2 Properties of Exponential Functions<br />
OBJ: 8-2.1 Comparing Graphs<br />
TOP: 8-2 Example 2<br />
KEY: exponential function | graphing<br />
73. ANS:<br />
–4<br />
REF: 8-3 Logarithmic Functions as Inverses<br />
OBJ: 8-3.1 Writing and Evaluating Logarithmic Expressions TOP: 8-3 Example 3<br />
KEY: evaluating logarithms<br />
12
ID: A<br />
74. ANS:<br />
3<br />
5<br />
32 = 8<br />
REF: 8-3 Logarithmic Functions as Inverses<br />
OBJ: 8-3.1 Writing and Evaluating Logarithmic Expressions TOP: 8-3 Example 3<br />
KEY: logarithmic form | logarithm | exponential form<br />
75. ANS:<br />
Quotient Property<br />
REF: 8-4 Properties of Logarithms<br />
TOP: 8-4 Example 1<br />
76. ANS:<br />
Power Property and Product Property<br />
REF: 8-4 Properties of Logarithms<br />
TOP: 8-4 Example 1<br />
77. ANS:<br />
log b<br />
(q 5 y 2 )<br />
OBJ: 8-4.1 Using the Properties of Logarithms<br />
KEY: properties of logarithms | Quotient Property of Logarithms<br />
OBJ: 8-4.1 Using the Properties of Logarithms<br />
KEY: properties of logarithms<br />
REF: 8-4 Properties of Logarithms OBJ: 8-4.1 Using the Properties of Logarithms<br />
TOP: 8-4 Example 2<br />
KEY: properties of logarithms | logarithm | Product Property of Logarithms | Power Property of Logarithms<br />
78. ANS:<br />
log 3<br />
2<br />
REF: 8-4 Properties of Logarithms OBJ: 8-4.1 Using the Properties of Logarithms<br />
TOP: 8-4 Example 2<br />
KEY: properties of logarithms | simplifying a logarithm | Quotient Property of Logarithms<br />
79. ANS:<br />
log 7<br />
n − log 7<br />
2<br />
REF: 8-4 Properties of Logarithms OBJ: 8-4.1 Using the Properties of Logarithms<br />
TOP: 8-4 Example 3<br />
KEY: properties of logarithms | expanding logarithms | Quotient Property of Logarithms<br />
80. ANS:<br />
1<br />
2 log 57 − 1 b<br />
2 log 74 b<br />
REF: 8-4 Properties of Logarithms OBJ: 8-4.1 Using the Properties of Logarithms<br />
KEY: properties of logarithms | expanding logarithms | Power Property of Logarithms | Quotient Property of<br />
Logarithms<br />
81. ANS:<br />
0.6616<br />
REF: 8-5 Exponential and Logarithmic Equations<br />
OBJ: 8-5.1 Solving Exponential Equations<br />
TOP: 8-5 Example 1<br />
KEY: exponential equation<br />
<strong>13</strong>
ID: A<br />
82. ANS:<br />
3.2459<br />
REF: 8-5 Exponential and Logarithmic Equations<br />
OBJ: 8-5.2 Solving Logarithmic Equations<br />
TOP: 8-5 Example 5<br />
KEY: exponential equation | Change of Base Formula<br />
83. ANS:<br />
ln 27c 3<br />
REF: 8-6 Natural Logarithms<br />
TOP: 8-6 Example 1<br />
84. ANS:<br />
0.02 and –0.02<br />
OBJ: 8-6.1 Natural Logarithms<br />
KEY: simplifying a natural logarithm | properties of logarithms<br />
REF: 7-1 Roots and Radical Expressions OBJ: 7-1.1 Roots and Radical Expressions<br />
TOP: 7-1 Example 1<br />
KEY: square root | real roots<br />
85. ANS:<br />
− 5 7<br />
REF: 7-1 Roots and Radical Expressions OBJ: 7-1.1 Roots and Radical Expressions<br />
TOP: 7-1 Example 2<br />
KEY: real roots<br />
86. ANS:<br />
2 3<br />
REF: 7-2 Multiplying and Dividing Radical Expressions OBJ: 7-2.1 Multiplying Radical Expressions<br />
TOP: 7-2 Example 1<br />
KEY: multiplying radical expressions | simplifying a radical expression<br />
87. ANS:<br />
x 7 − 49 x<br />
REF: 7-2 Multiplying and Dividing Radical Expressions OBJ: 7-2.1 Multiplying Radical Expressions<br />
TOP: 7-2 Example 3<br />
KEY: multiplying radical expressions | simplifying a radical expression<br />
88. ANS:<br />
3<br />
3 3<br />
REF: 7-2 Multiplying and Dividing Radical Expressions OBJ: 7-2.2 Dividing Radical Expressions<br />
TOP: 7-2 Example 4<br />
KEY: simplifying a radical expression | divide radical expressions | rationalize the denominator<br />
89. ANS:<br />
3x 8 5x<br />
REF: 7-2 Multiplying and Dividing Radical Expressions OBJ: 7-2.2 Dividing Radical Expressions<br />
TOP: 7-2 Example 4<br />
KEY: simplifying a radical expression | divide radical expressions | rationalize the denominator<br />
14
ID: A<br />
90. ANS:<br />
x 3 y 2<br />
5<br />
30y<br />
REF: 7-2 Multiplying and Dividing Radical Expressions OBJ: 7-2.2 Dividing Radical Expressions<br />
TOP: 7-2 Example 5<br />
KEY: divide radical expressions | simplifying a radical expression<br />
91. ANS:<br />
3<br />
2 36<br />
3<br />
+ 3 4<br />
6<br />
REF: 7-3 Binomial Radical Expressions OBJ: 7-3.2 Multiplying and Dividing Binomial Radical Expressions<br />
TOP: 7-3 Example 6<br />
KEY: binomial radical expressions | multiplying binomial radical expressions | rationalize the denominator<br />
92. ANS:<br />
4<br />
8 2x<br />
REF: 7-3 Binomial Radical Expressions OBJ: 7-3.1 Adding and Subtracting Radical Expressions<br />
TOP: 7-3 Example 1<br />
KEY: binomial radical expressions | adding radical expressions | like radicals<br />
93. ANS:<br />
not possible to simplify<br />
REF: 7-3 Binomial Radical Expressions OBJ: 7-3.1 Adding and Subtracting Radical Expressions<br />
TOP: 7-3 Example 1<br />
KEY: binomial radical expressions | adding radical expressions | like radicals<br />
94. ANS:<br />
4<br />
−4 5a<br />
REF: 7-3 Binomial Radical Expressions OBJ: 7-3.1 Adding and Subtracting Radical Expressions<br />
TOP: 7-3 Example 1<br />
KEY: binomial radical expressions | adding radical expressions | like radicals<br />
95. ANS:<br />
20<br />
REF: 7-4 Rational Exponents<br />
TOP: 7-4 Example 1<br />
96. ANS:<br />
8<br />
3 x 3<br />
REF: 7-4 Rational Exponents<br />
TOP: 7-4 Example 2<br />
97. ANS:<br />
15; –1<br />
REF: 7-5 Solving Radical Equations<br />
TOP: 7-5 Example 2<br />
OBJ: 7-4.1 Simplifying Expressions with Rational Exponents<br />
KEY: rational exponent<br />
OBJ: 7-4.1 Simplifying Expressions with Rational Exponents<br />
KEY: rational exponent | radical form<br />
OBJ: 7-5.1 Solving Radical Equations<br />
KEY: radical equation | rational exponent<br />
15
ID: A<br />
98. ANS:<br />
7<br />
6<br />
REF: 7-5 Solving Radical Equations<br />
TOP: 7-5 Example 5<br />
99. ANS:<br />
2x – 4<br />
OBJ: 7-5.1 Solving Radical Equations<br />
KEY: extraneous solutions | radical equation | rational exponent<br />
REF: 7-6 Function Operations<br />
OBJ: 7-6.1 Operations with Functions<br />
TOP: 7-6 Example 1<br />
KEY: addition and subtraction of functions | operations with functions<br />
100. ANS:<br />
2x 2 − 2x + 10<br />
REF: 7-6 Function Operations<br />
OBJ: 7-6.1 Operations with Functions<br />
TOP: 7-6 Example 2<br />
KEY: addition and subtraction of functions | operations with functions<br />
101. ANS:<br />
63<br />
55<br />
REF: 7-6 Function Operations<br />
TOP: 7-6 Example 3<br />
102. ANS:<br />
y =±<br />
x + 3<br />
7<br />
OBJ: 7-6.2 Composition of Functions<br />
KEY: composition of functions | operations with functions<br />
REF: 7-7 Inverse Relations and Functions<br />
OBJ: 7-7.1 The Inverse of a Function<br />
TOP: 7-7 Example 2 KEY: inverse relations and functions |<br />
103. ANS:<br />
5<br />
REF: 7-7 Inverse Relations and Functions<br />
TOP: 7-7 Example 6<br />
104. ANS:<br />
f(g(x)) = 10x – 1; g(f(x)) = 10x + 7<br />
REF: 7-6 Function Operations<br />
TOP: 7-6 Example 3<br />
105. ANS:<br />
–5<br />
OBJ: 7-7.1 The Inverse of a Function<br />
KEY: composition of functions | inverse relations and functions<br />
OBJ: 7-6.2 Composition of Functions<br />
KEY: composition of functions | operations with functions<br />
REF: 8-3 Logarithmic Functions as Inverses<br />
OBJ: 8-3.1 Writing and Evaluating Logarithmic Expressions TOP: 8-3 Example 3<br />
KEY: evaluating logarithms<br />
16
ID: A<br />
106. ANS:<br />
REF: 7-8 Graphing Radical Functions<br />
TOP: 7-8 Example 2<br />
107. ANS:<br />
quintic binomial<br />
REF: 6-1 Polynomial Functions<br />
TOP: 6-1 Example 1<br />
108. ANS:<br />
quintic trinomial<br />
REF: 6-1 Polynomial Functions<br />
TOP: 6-1 Example 1<br />
109. ANS:<br />
−3x 3 + 2x 2 + 1<br />
REF: 6-1 Polynomial Functions<br />
TOP: 6-1 Example 1<br />
110. ANS:<br />
–3, multiplicity 2; 5, multiplicity 6<br />
OBJ: 7-8.1 Radical Functions<br />
KEY: domain | graphing | range | radical function | translation<br />
OBJ: 6-1.1 Exploring Polynomial Functions<br />
KEY: polynomial | degree of a polynomial<br />
OBJ: 6-1.1 Exploring Polynomial Functions<br />
KEY: degree of a polynomial | polynomial<br />
OBJ: 6-1.1 Exploring Polynomial Functions<br />
KEY: polynomial | standard form of a polynomial<br />
REF: 6-2 Polynomials and Linear Factors<br />
OBJ: 6-2.2 Factors and Zeros of a Polynomial Function TOP: 6-2 Example 6<br />
KEY: polynomial function | zeros of a polynomial function | multiplicity | multiple zero<br />
111. ANS:<br />
x 2 − 3x + 7, R –38<br />
REF: 6-3 Dividing Polynomials<br />
TOP: 6-3 Example 3<br />
112. ANS:<br />
3, –3, 5, –5<br />
REF: 6-4 Solving Polynomial Equations<br />
TOP: 6-4 Example 6<br />
OBJ: 6-3.2 Using Synthetic Division<br />
KEY: division of polynomials | polynomial | synthetic division<br />
OBJ: 6-4.2 Solving Equations by Factoring<br />
KEY: factoring a polynomial | polynomial<br />
17
ID: A<br />
1<strong>13</strong>. ANS:<br />
120<br />
REF: 6-7 Permutations and Combinations<br />
TOP: 6-7 Example 1<br />
114. ANS:<br />
35<br />
KEY: factorial<br />
OBJ: 6-7.1 Permutations<br />
REF: 6-7 Permutations and Combinations<br />
TOP: 6-7 Example 1<br />
KEY: factorial<br />
115. ANS:<br />
s 5 − 25s 4 v + 250s 3 v 2 − 1250s 2 v 3 + 3125sv 4 − 3125v 5<br />
OBJ: 6-7.1 Permutations<br />
REF: 6-8 The Binomial Theorem<br />
TOP: 6-8 Example 2<br />
116. ANS:<br />
−7 2 − 10<br />
REF: 7-3 Binomial Radical Expressions<br />
TOP: 7-3 Example 3<br />
117. ANS:<br />
5x 11 3x<br />
OBJ: 6-8.1 Binomial Expansion and Pascal's Triangle<br />
KEY: Pascal's Triangle | binomial expansion<br />
OBJ: 7-3.1 Adding and Subtracting Radical Expressions<br />
KEY: like radicals | simplifying a radical expression<br />
REF: 7-2 Multiplying and Dividing Radical Expressions OBJ: 7-2.2 Dividing Radical Expressions<br />
TOP: 7-2 Example 4<br />
KEY: simplifying a radical expression | divide radical expressions | rationalize the denominator<br />
118. ANS:<br />
41 + 12 5<br />
REF: 7-3 Binomial Radical Expressions OBJ: 7-3.2 Multiplying and Dividing Binomial Radical Expressions<br />
TOP: 7-3 Example 4<br />
KEY: binomial radical expressions | multiplying binomial radical expressions | simplifying a radical expression<br />
119. ANS:<br />
5x(x + 2)(x – 3)<br />
REF: 6-2 Polynomials and Linear Factors<br />
OBJ: 6-2.1 The Factored Form of a Polynomial TOP: 6-2 Example 2<br />
KEY: factoring a polynomial | polynomial<br />
120. ANS:<br />
3a 4 b 2 3<br />
6a<br />
REF: 7-2 Multiplying and Dividing Radical Expressions OBJ: 7-2.1 Multiplying Radical Expressions<br />
TOP: 7-2 Example 2<br />
KEY: multiplying radical expressions | simplifying a radical expression<br />
18
ID: A<br />
121. ANS:<br />
y = 4(3.5) x<br />
REF: 8-1 Exploring Exponential Models OBJ: 8-1.1 Exponential Growth<br />
TOP: 8-1 Example 3<br />
KEY: exponential function | growth factor<br />
122. ANS:<br />
10<br />
REF: 7-4 Rational Exponents<br />
TOP: 7-4 Example 1<br />
123. ANS:<br />
f(x) = x 3 + 11x 2 + 38x + 40<br />
OBJ: 7-4.1 Simplifying Expressions with Rational Exponents<br />
KEY: rational exponent<br />
REF: 6-2 Polynomials and Linear Factors<br />
OBJ: 6-2.2 Factors and Zeros of a Polynomial Function TOP: 6-2 Example 5<br />
KEY: polynomial function | standard form of a polynomial | zeros of a polynomial function<br />
124. ANS:<br />
y =±<br />
x + 2<br />
6<br />
REF: 7-7 Inverse Relations and Functions<br />
OBJ: 7-7.1 The Inverse of a Function<br />
TOP: 7-7 Example 2 KEY: inverse relations and functions |<br />
125. ANS:<br />
− 19<br />
4<br />
REF: 9-6 Solving Rational Equations<br />
TOP: 9-6 Example 1<br />
OBJ: 9-6.1 Solving Rational Equations<br />
KEY: rational equation<br />
19







![1. Given: BD is tangent to circle O at C, , and m ACE [A] 41° [C] 40 ...](https://img.yumpu.com/42456754/1/190x245/1-given-bd-is-tangent-to-circle-o-at-c-and-m-ace-a-41a-c-40-.jpg?quality=85)