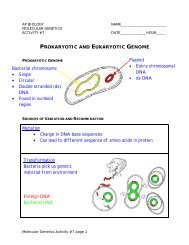
PROKARYOTIC AND EUKARYOTIC GENOME
PROKARYOTIC AND EUKARYOTIC GENOME
PROKARYOTIC AND EUKARYOTIC GENOME
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
AP BIOLOGYMOLECULAR GENETICSACTIVITY #7NAME_____________________DATE____________HOUR____<strong>PROKARYOTIC</strong> <strong>AND</strong> <strong>EUKARYOTIC</strong> <strong>GENOME</strong><strong>PROKARYOTIC</strong> <strong>GENOME</strong>SOURCES OF VARIATION <strong>AND</strong> RECOMBINATIONMolecular Genetics Activity #7 page 1
Molecular Genetics Activity #7 page 2
OPERONS – TRP OPERONMolecular Genetics Activity #7 page 3
OPERONS – LAC OPERONMolecular Genetics Activity #7 page 4
<strong>EUKARYOTIC</strong> <strong>GENOME</strong>Molecular Genetics Activity #7 page 5
QUESTIONS:1. Listed below are descriptions and examples of the different types ofrecombination in bacteria. Classify each type as:A) transformationB) transductionC) conjugationD) transposons______ Bacteria assimilate genetic material from surroundings______ Bacteria take up DNA from environment______ Gene transfer from one bacterium to another via bacteriophage______ Direct transfer of genes between two bacterial temporarily joined bysex pili______ Jumping genes first described by Barbara McClintock______ Pieces of DNA move from one location to another location in cell’sgenome______ A DNA segment is moved from one location to another______ DNA is transferred from one bacterium to another by a virus______ A plasmid is exchanged between two bacteria through a pilus______ Bacterial strains A and B are growing together in a colony that hasbeen infected with viruses. After a short period of time, a newstrain of bacteria is detected that is very similar to strain A butshas a few characteristics of B.______ The conversion of live R strain Streptococcus pneumoniae into Sstrain when heat-killed S strain is added to R strain______ E. coli bacteria are induced to take up the pBLU plasmid2. List and describe the two main strategies used by cells to controlmetabolism.METHOD OF CONTROLDESCRIPTION OF METHODMolecular Genetics Activity #7 page 6
3. Match the description/function with the correct term.______ Regulated cluster of adjacent structuralgenes with related functions______ Gene that codes for polypeptide______ Transcript of several genes; translatedinto several polypeptides______ RNA segment between promoter &structural genes; controls access ofRNA polymerase to structural gene______ Specific protein that binds to operatorand blocks transcription______ Genes that code for repressor orregulators of other genes______ RNA polymerase binding site______ Molecule that binds to repressorprotein; complex then binds to operatorA. CorepressorB. OperatorC. OperonD. PolycistronicmRNAE. PromoterF. RegulatorygeneG. RepressorH. Structural gene4. Explain how the trp operon works:a. If tryptophan is absent from the cell.________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________b. If tryptophan is present in the cell________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________Molecular Genetics Activity #7 page 7
5. Explain how tryptophan acts as a corepressor.__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________6. Match these components of the lac operon with their functions.______ β-galactosidase A. is inactivated whenattached to lactose______ cAMP-CAP complex B. codes for synthesis ofrepressor______ lactose C. hydrolyzes lactose______ operator D. stimulates geneexpression______ promoter E. repressor attaches here______ regulator gene F. RNA polymerase attacheshere______ repressor G. acts as inducer thatinactivates repressor______ structural gene H. codes for an enzyme7. Listed below are characteristics of repressible and inducible enzymes.Identify each of the following as true of repressible or inducible enzymes.______ genes are switched off until a specific metabolite inactivates therepressor______ genes are switched on until a specific metabolite activates therepressor______ Generally function in anabolic pathways______ Usually function in catabolic pathways______ Pathway end product switches off its own production______ Enzyme synthesis is switched on by the nutrient in used in thepathwayMolecular Genetics Activity #7 page 8
8. Match the term with the correct definition or description.A. 30-nm chromatin fiber B. EuchromatinC. Heterochromatin D. Histone proteinsE. Looped domains F. Metaphase chromosomeG. Nucleosomes______ Small proteins associate with DNA packing______ Beads on a string; DNA wound around histone proteins______ Tightly would coil with 6 nucleosomes per turn; molecules of onetype of histone protein pull the nucleosomes into a cylinder witha diameter of 30 nm______ Loops of 30-nm chromatin fibers; each loop contains 20,000 to100,000 base pairs______ Folding of the looped domains______ Chromatin that remains highly condensed during interphase; notactively transcribed______ Chromatin that is less condensed during interphase; activelytranscribed9. Listed below are the levels of chromatin (DNA) packing in the eukaryoticgenome. Put them in the correct order starting with the least condensed.______ Looped domains______ Nucleosomes______ Metaphase chromosome______ 30-nm chromatin fiberMolecular Genetics Activity #7 page 9







![1. Given: BD is tangent to circle O at C, , and m ACE [A] 41° [C] 40 ...](https://img.yumpu.com/42456754/1/190x245/1-given-bd-is-tangent-to-circle-o-at-c-and-m-ace-a-41a-c-40-.jpg?quality=85)