this pdf excerpt
this pdf excerpt
this pdf excerpt
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
nbina-<br />
These<br />
_rs repployee<br />
s con-<br />
,1 COn-<br />
binary<br />
entity<br />
) type,<br />
-tment<br />
'ee can<br />
ios for<br />
rlates a<br />
:esents<br />
lanage<br />
lationminin<br />
have<br />
'3u<br />
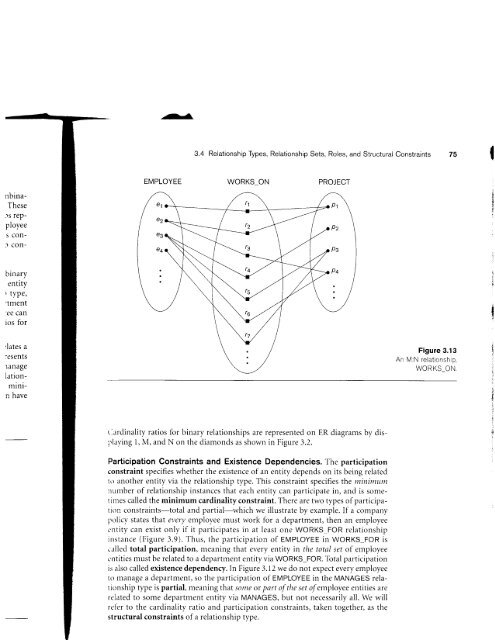
EMPLOYEE<br />
€1<br />
e2<br />
€a<br />
3.4 Relationship Types, Relationship Sets, Roles, and Structural Constraints<br />
WORKS ON PROJECT<br />
t-ardinality ratios for binary relationships are represented on ER diagrams by displaving<br />
l, M, and N on the diamonds as shown in Figure 3.2.<br />
Participation Constraints and Existence Dependencies. The participation<br />
constraint specifies whether the exister.rce of an entity depends on its being reiated<br />
ttr irnother entity via the relationship type. This constraint specifies the minimurn<br />
number of relationship instances that each entity can participate in, and is somet<br />
imes called the minimum cardinality constraint. There are two types of participation<br />
constraints-total and partial-which we illustrate by example. If a company<br />
policy states thal every employee must work for a department, then an employee<br />
r.rltity can exist only if it participates in at least one WORKS FOR relationship<br />
instance (Figure 3.9). Thus, the participation of EMPLOYEE in WORKS_FOR is<br />
c.rlled total participation, meaning that every entity in the total sel of employee<br />
cntities must be related to a department entity via WORKS_FOR. Total participation<br />
is trlso called existence dependenry. In Figure 3.12 we do not expect every employee<br />
to nanage a department, so the participation of EMPLOYEE in the MANAGES reiationship<br />
type is partial, meaning thar some or part of the set o/employee entities are<br />
rc'lated to some department entity via MANAGES, but not necessarily all. We will<br />
ret-er to the cardinality ratio and participation constraints, taken together, as the<br />
structural constraints of a relationship type.<br />
Pt<br />
Pz<br />
Ps<br />
P4<br />
Figure 3.13<br />
An M:N relationship,<br />
WORKS_ON